Deep litter systems in poultry housing promote natural behaviors by providing a comfortable bedding material that absorbs waste and reduces stress, resulting in improved bird welfare and reduced disease risk. Battery cages offer higher space efficiency and easier management but often restrict movement, leading to increased stress and health problems in birds. Choosing between deep litter and battery cage systems involves balancing animal welfare with production efficiency and management practices.
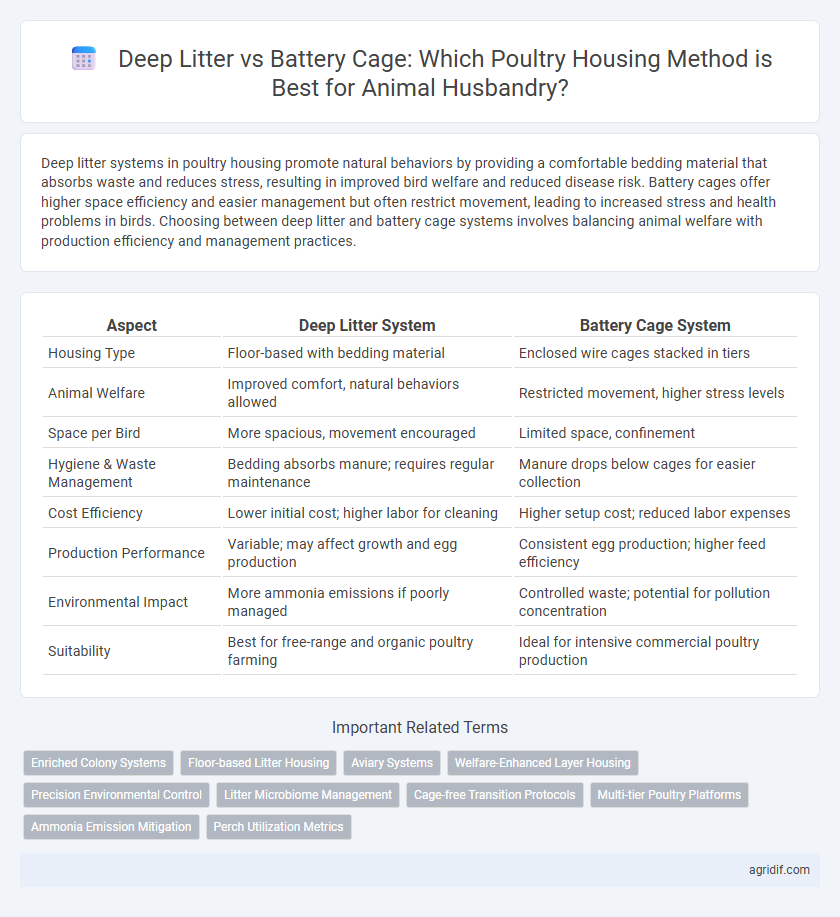
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Deep Litter System | Battery Cage System |
|---|---|---|
| Housing Type | Floor-based with bedding material | Enclosed wire cages stacked in tiers |
| Animal Welfare | Improved comfort, natural behaviors allowed | Restricted movement, higher stress levels |
| Space per Bird | More spacious, movement encouraged | Limited space, confinement |
| Hygiene & Waste Management | Bedding absorbs manure; requires regular maintenance | Manure drops below cages for easier collection |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower initial cost; higher labor for cleaning | Higher setup cost; reduced labor expenses |
| Production Performance | Variable; may affect growth and egg production | Consistent egg production; higher feed efficiency |
| Environmental Impact | More ammonia emissions if poorly managed | Controlled waste; potential for pollution concentration |
| Suitability | Best for free-range and organic poultry farming | Ideal for intensive commercial poultry production |
Introduction to Poultry Housing Systems
Deep litter and battery cage systems represent two primary poultry housing methods that significantly impact animal welfare and productivity. Deep litter systems use a bedding material layer, promoting natural behaviors and providing thermal insulation, while battery cages confine birds in individual wire cages, optimizing space and egg collection efficiency. Choosing the appropriate poultry housing system depends on factors such as flock size, welfare standards, and production goals.
Overview of the Deep Litter System
The Deep Litter System for poultry housing involves maintaining a thick bedding layer of materials such as wood shavings, straw, or rice hulls, which absorb moisture and provide insulation, promoting natural behaviors like scratching and dust bathing. This method enhances bird welfare by reducing stress and allowing for better movement compared to the restrictive environment of battery cages. Nutrient-rich litter can be composted, improving sustainability in poultry production by recycling waste into valuable organic fertilizer.
Overview of the Battery Cage System
The battery cage system for poultry housing involves confining hens in small, individual wire cages arranged in rows and tiers, optimizing space utilization and facilitating automated feeding and egg collection. This intensive system enhances production efficiency and disease control but raises concerns regarding animal welfare due to limited movement and natural behaviors. Despite criticisms, battery cages remain widely used in commercial egg production for their economic benefits and standardized management.
Space Utilization: Deep Litter vs Battery Cage
Deep litter systems offer better space utilization by allowing poultry to move freely and engage in natural behaviors within a larger area, promoting animal welfare and reducing stress. Battery cages, although space-efficient in terms of stocking density, restrict movement and limit behavioral expression, leading to potential health issues such as osteoporosis and feather pecking. Optimizing space utilization requires balancing bird welfare with production efficiency, where deep litter provides a more humane environment and battery cages enable higher flock density per square meter.
Animal Welfare and Bird Health Considerations
Deep litter systems promote natural behaviors such as dust bathing and foraging, significantly enhancing bird welfare and reducing stress-related illnesses. In contrast, battery cages restrict movement, leading to higher incidences of osteoporosis, feather pecking, and respiratory issues due to poor ventilation. Optimizing poultry housing with deep litter improves overall health, welfare, and productivity by providing a more enriched environment.
Feed and Resource Management Efficiency
Deep litter systems enhance feed and resource management efficiency by promoting natural foraging behavior and reducing feed wastage through manure recycling, which improves nutrient utilization. In contrast, battery cages limit movement, often leading to higher feed conversion ratios due to stress and restricted feeding behaviors, while increasing resource consumption for cleaning and waste management. Optimizing deep litter housing can reduce input costs and environmental impact, supporting sustainable poultry production.
Egg Production and Quality Comparison
Deep litter systems promote higher egg quality by reducing stress and encouraging natural behaviors, resulting in thicker shells and improved albumen consistency. Battery cages enable higher egg production rates through controlled environments but often compromise shell strength and yolk quality due to restricted movement and increased stress. Studies reveal that while battery cages maximize quantity, deep litter housing enhances overall egg nutritional value and consumer preference.
Labor and Management Requirements
Deep litter systems for poultry housing demand less intensive daily labor with simplified cleaning and maintenance, enhancing overall management efficiency. Battery cage systems require constant monitoring, frequent manure removal, and regular equipment checks, resulting in higher labor input and specialized management skills. Efficient labor allocation in deep litter systems supports sustainable poultry production through reduced operational complexity.
Environmental Impact and Waste Management
Deep litter systems in poultry housing promote natural decomposition of manure within bedding materials, reducing environmental pollution and facilitating nutrient recycling through composting. Battery cages generate concentrated waste that requires efficient collection and treatment to prevent soil and water contamination, often resulting in higher management costs and environmental risks. Efficient waste management in deep litter systems lowers greenhouse gas emissions compared to battery cages by minimizing manure runoff and enhancing organic matter breakdown.
Economic Analysis: Cost and Profitability
Deep litter systems offer lower initial investment and reduced labor costs compared to battery cages, making them economically beneficial for small to medium-scale poultry farms. Battery cages, while having higher upfront costs due to construction and equipment, enable higher stocking density and improved feed conversion ratios, which can lead to increased profitability in large-scale operations. Economic analysis reveals that profitability depends on factors like market demand, input costs, and scale; deep litter favors cost-efficiency and animal welfare, whereas battery cages optimize production output and revenue per unit area.
Related Important Terms
Enriched Colony Systems
Enriched colony systems combine the welfare benefits of deep litter with the space efficiency of battery cages by providing hens with perches, nesting areas, and dust baths within a confined group environment. This method reduces stress and promotes natural behaviors while maintaining productivity and biosecurity compared to traditional battery cage systems.
Floor-based Litter Housing
Floor-based litter housing in poultry farming promotes natural behaviors like scratching and dust bathing by providing a deep layer of litter material, enhancing bird welfare and reducing stress-related issues compared to battery cages. This system improves air quality and manure management through microbial decomposition in the litter, contributing to healthier living conditions and sustainable farm practices.
Aviary Systems
Aviary systems in poultry housing combine the benefits of deep litter bedding and battery cage designs by providing hens with multi-level perches, nesting areas, and littered floors that promote natural behaviors like dust bathing and foraging. These systems enhance bird welfare and productivity by allowing free movement and social interaction while maintaining efficient space utilization and manure management.
Welfare-Enhanced Layer Housing
Deep litter systems promote natural behaviors and improved welfare by allowing poultry to move freely and forage, leading to reduced stress and better feather condition. In contrast, battery cages restrict movement and natural activities, often causing higher stress levels and physical issues, making deep litter a preferred choice for welfare-enhanced layer housing.
Precision Environmental Control
Deep litter systems in poultry housing enable better precision environmental control by maintaining stable temperature and humidity levels through natural composting processes, reducing ammonia emissions and enhancing bird welfare. In contrast, battery cages offer limited environmental regulation, often resulting in higher stress levels and less effective management of air quality and microclimate conditions.
Litter Microbiome Management
Deep litter systems promote a diverse and dynamic litter microbiome that aids in pathogen suppression and nutrient recycling, enhancing poultry health and reducing reliance on chemical disinfectants. In contrast, battery cage systems limit microbial diversity due to frequent cleaning and minimal litter, increasing vulnerability to opportunistic pathogens and necessitating stringent biosecurity measures.
Cage-free Transition Protocols
Deep litter systems promote natural behaviors and improve poultry welfare by providing birds with bedding material to scratch and dust-bathe, while battery cages restrict movement and increase stress. Cage-free transition protocols emphasize gradual adaptation, environmental enrichment, and management training to ensure a smooth shift from confined battery cages to spacious deep litter housing.
Multi-tier Poultry Platforms
Multi-tier poultry platforms in deep litter systems enhance vertical space utilization, improving natural behaviors and reducing stress compared to battery cages, which restrict movement and cause welfare concerns. These platforms support better litter management and biosecurity, leading to increased productivity and healthier flocks in sustainable poultry housing.
Ammonia Emission Mitigation
Deep litter systems in poultry housing reduce ammonia emissions by promoting microbial breakdown of manure, which minimizes volatilization compared to battery cages where waste accumulates beneath birds. Controlled ventilation and periodic litter turning in deep litter setups optimize ammonia mitigation, enhancing air quality and poultry health relative to the high ammonia levels often found in confined battery cage environments.
Perch Utilization Metrics
Deep litter systems demonstrate higher perch utilization metrics, promoting natural roosting behavior and improved welfare in poultry compared to battery cages. Battery cages restrict perch access, leading to reduced leg strength and increased stress indicators in housed birds.
Deep litter vs battery cage for poultry housing Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com