Antibiotics are commonly used in dairy farming to treat bacterial infections and prevent disease outbreaks within the herd, but their overuse can lead to antibiotic resistance and residue issues in milk production. Probiotics offer a natural alternative by enhancing gut health, boosting the immune system, and improving digestion, which helps maintain overall herd health and reduce reliance on antibiotics. Integrating probiotics into dairy farming practices supports sustainable animal health management and promotes higher milk quality.
Table of Comparison
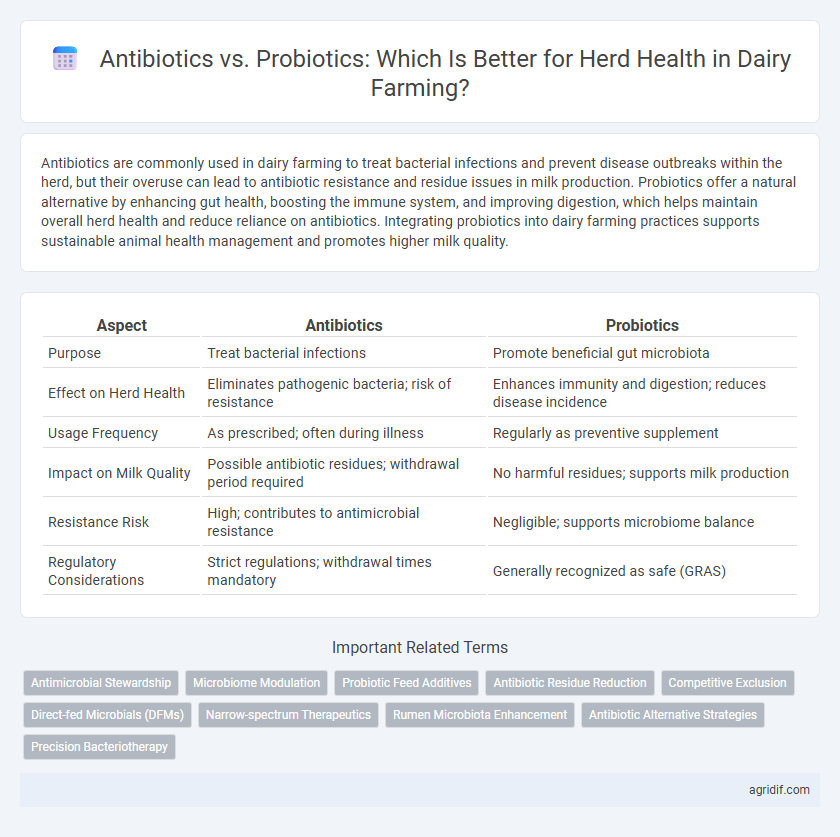
| Aspect | Antibiotics | Probiotics |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Treat bacterial infections | Promote beneficial gut microbiota |
| Effect on Herd Health | Eliminates pathogenic bacteria; risk of resistance | Enhances immunity and digestion; reduces disease incidence |
| Usage Frequency | As prescribed; often during illness | Regularly as preventive supplement |
| Impact on Milk Quality | Possible antibiotic residues; withdrawal period required | No harmful residues; supports milk production |
| Resistance Risk | High; contributes to antimicrobial resistance | Negligible; supports microbiome balance |
| Regulatory Considerations | Strict regulations; withdrawal times mandatory | Generally recognized as safe (GRAS) |
Understanding Antibiotics and Probiotics in Dairy Farming
Antibiotics are commonly used in dairy farming to treat bacterial infections and prevent disease outbreaks, but their overuse can lead to antibiotic resistance and residues in milk. Probiotics offer a natural alternative by promoting beneficial gut bacteria, enhancing immune function, and improving digestion in dairy cows. Understanding the balance between antibiotics for acute treatments and probiotics for maintaining overall herd health is critical for sustainable dairy farming practices.
Historical Use of Antibiotics in Dairy Herds
Antibiotics have been widely used in dairy herds since the mid-20th century to treat bacterial infections and promote growth, significantly reducing morbidity and mortality rates. However, concerns over antibiotic resistance and residues in milk have driven interest in probiotics as a natural alternative to support gut health and immunity in dairy cattle. Probiotics enhance microbial balance and feed efficiency, offering a sustainable strategy to maintain herd health without relying solely on antibiotics.
The Rising Popularity of Probiotics in Dairy Operations
Probiotics are gaining traction in dairy farming as a natural alternative to antibiotics for maintaining herd health and improving milk production. Unlike antibiotics that may lead to resistance and residue concerns, probiotics enhance gut microbiota stability, boost the immune system, and promote overall digestive health in dairy cows. This shift reflects growing consumer demand for antibiotic-free dairy products and sustainable livestock management practices.
Mechanisms: How Antibiotics and Probiotics Work
Antibiotics function by directly killing or inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria in the herd, disrupting bacterial cell walls or protein synthesis to eliminate infections. Probiotics enhance gut health by introducing beneficial microorganisms that compete with pathogens, modulate immune responses, and improve nutrient absorption. This microbial balance promoted by probiotics supports long-term herd immunity and digestion, unlike antibiotics, which may lead to resistance and microbiome disruption.
Impact on Herd Health and Milk Production
Antibiotics in dairy farming effectively control bacterial infections but can lead to antibiotic resistance and residue in milk, impacting herd health and milk safety. Probiotics enhance gut health and immune function, promoting better nutrient absorption and reducing disease incidence, which supports consistent milk production and quality. Integrating probiotics can reduce dependency on antibiotics, fostering sustainable herd health management and improving overall lactation performance.
Antibiotic Resistance Concerns in Dairy Farming
Antibiotic use in dairy farming raises significant concerns due to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, which pose risks to both animal and human health. Probiotics offer a sustainable alternative by promoting gut health and enhancing immunity without contributing to resistance issues. Implementing probiotics supports herd health management while mitigating the threat of antibiotic resistance in dairy production systems.
Probiotics: Enhancing Immunity and Gut Health
Probiotics play a crucial role in enhancing dairy herd immunity by promoting a balanced gut microbiome, which reduces the incidence of infections and supports nutrient absorption. Unlike antibiotics that target pathogens broadly, probiotics strengthen natural defenses without disrupting beneficial bacteria, minimizing the risk of antibiotic resistance. Incorporating probiotics into dairy cattle diets improves overall herd health and productivity by maintaining digestive efficiency and boosting immune responses.
Regulatory Guidelines for Antibiotic and Probiotic Use
Regulatory guidelines for antibiotic use in dairy farming strictly limit dosages and withdrawal periods to prevent antibiotic residues in milk and ensure food safety. Probiotics, generally recognized as safe, face fewer regulatory restrictions but must comply with standards for strain identification and efficacy claims. Both antibiotic and probiotic applications require adherence to veterinary oversight and record-keeping to maintain herd health and meet national food safety regulations.
Practical Considerations: Implementing Probiotics vs Antibiotics
Implementing probiotics in dairy herds promotes natural gut flora balance, enhancing immunity without the risk of antibiotic resistance, making them ideal for long-term health management. Antibiotics provide rapid infection control but require strict veterinary oversight to prevent residue issues and resistance development. Practical herd health strategies increasingly favor probiotics for routine maintenance while reserving antibiotics for acute cases, balancing animal welfare and regulatory compliance.
Future Trends: Sustainable Herd Health Management
Emerging trends in dairy farming emphasize the shift from antibiotics to probiotics for sustainable herd health management, reducing antibiotic resistance risks and promoting natural immunity. Probiotics enhance gut microbiota balance, improving digestion and disease resistance, which supports overall productivity and animal welfare. Integrating precision farming technologies enables targeted probiotic applications, optimizing herd health while minimizing environmental impact and antibiotic reliance.
Related Important Terms
Antimicrobial Stewardship
Antibiotics play a critical role in treating bacterial infections in dairy herds but their overuse can contribute to antimicrobial resistance, posing risks to animal and public health. Probiotics offer a sustainable alternative by enhancing gut microbiota balance and immunity, supporting antimicrobial stewardship initiatives aimed at reducing reliance on antibiotics in dairy farming.
Microbiome Modulation
Antibiotics in dairy farming effectively control bacterial infections but can disrupt the gut microbiome, leading to antibiotic resistance and reduced long-term herd health. Probiotics enhance microbiome modulation by promoting beneficial gut bacteria, improving digestion, immune function, and overall herd resilience without contributing to antimicrobial resistance.
Probiotic Feed Additives
Probiotic feed additives enhance dairy herd health by promoting beneficial gut microbiota, improving digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune response, while reducing reliance on antibiotics and minimizing antimicrobial resistance risks. These natural supplements support milk production efficiency and animal welfare by maintaining balanced intestinal flora and preventing pathogenic bacterial overgrowth.
Antibiotic Residue Reduction
Probiotics enhance gut health and immunity in dairy cows, significantly reducing the need for antibiotics and minimizing antibiotic residues in milk. Implementing probiotics in herd management promotes safer dairy products and supports compliance with residue regulations.
Competitive Exclusion
Probiotics enhance herd health by promoting beneficial gut bacteria, which competitively exclude pathogenic microbes, reducing reliance on antibiotics and minimizing antimicrobial resistance risks. Using probiotics in dairy farming supports a balanced microbiome, improving digestion, immune response, and overall productivity without the negative impacts of antibiotic residues.
Direct-fed Microbials (DFMs)
Direct-fed microbials (DFMs), a category of probiotics, improve dairy herd health by enhancing gut microbiota balance and boosting immune function, reducing the reliance on antibiotics and minimizing antimicrobial resistance risks. Unlike antibiotics, which target pathogens directly and may disrupt beneficial microbes, DFMs support long-term digestive efficiency and overall animal productivity by promoting beneficial bacterial populations.
Narrow-spectrum Therapeutics
Narrow-spectrum antibiotics target specific pathogens in dairy herds, reducing the risk of antibiotic resistance and preserving beneficial microbiota essential for overall health. Probiotics enhance gut flora balance and immune function, offering a natural complement or alternative to narrow-spectrum therapeutics in maintaining dairy herd health and productivity.
Rumen Microbiota Enhancement
Administering probiotics in dairy farming enhances rumen microbiota by promoting beneficial bacterial growth, improving digestion and nutrient absorption in the herd. Antibiotics, while effective against infections, can disrupt the delicate balance of rumen microbes, potentially impairing fermentation processes and overall herd productivity.
Antibiotic Alternative Strategies
Antibiotic alternative strategies in dairy farming emphasize probiotics to enhance herd health by promoting beneficial gut microbiota, reducing reliance on antibiotics and lowering the risk of antimicrobial resistance. Probiotics improve immune function and digestion, supporting overall animal welfare and productivity without compromising food safety.
Precision Bacteriotherapy
Precision bacteriotherapy in dairy farming leverages targeted probiotics to enhance herd health by promoting beneficial gut microbiota while reducing reliance on antibiotics that risk resistance development. Implementing probiotics tailored to specific bacterial profiles improves immune response and productivity, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional antibiotic use in dairy herds.
Antibiotics vs Probiotics for herd health Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com