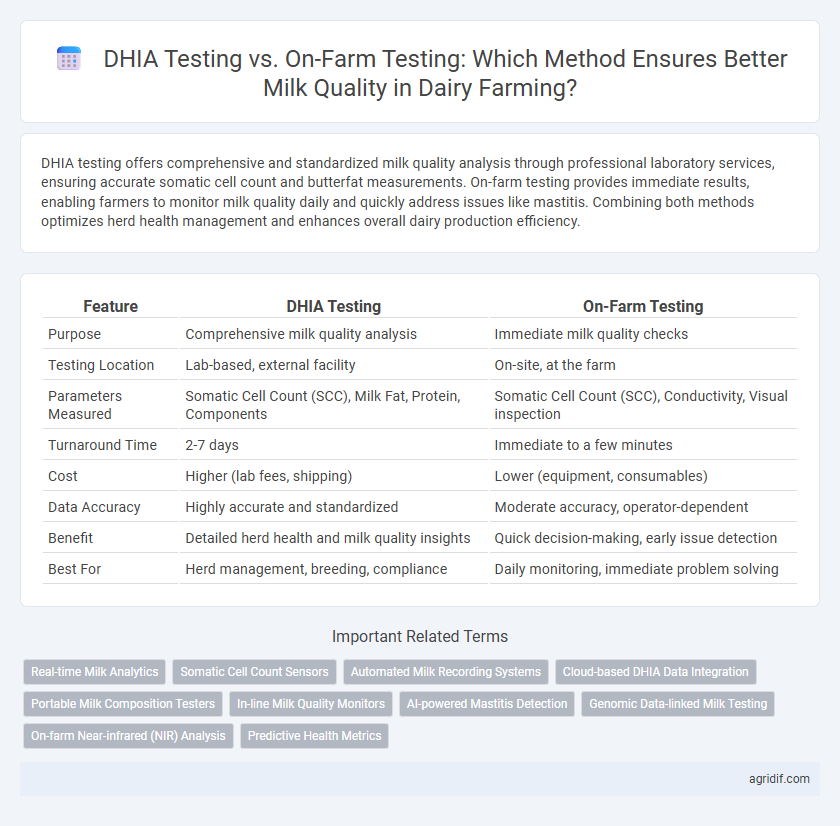
DHIA testing offers comprehensive and standardized milk quality analysis through professional laboratory services, ensuring accurate somatic cell count and butterfat measurements. On-farm testing provides immediate results, enabling farmers to monitor milk quality daily and quickly address issues like mastitis. Combining both methods optimizes herd health management and enhances overall dairy production efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | DHIA Testing | On-Farm Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Comprehensive milk quality analysis | Immediate milk quality checks |
| Testing Location | Lab-based, external facility | On-site, at the farm |
| Parameters Measured | Somatic Cell Count (SCC), Milk Fat, Protein, Components | Somatic Cell Count (SCC), Conductivity, Visual inspection |
| Turnaround Time | 2-7 days | Immediate to a few minutes |
| Cost | Higher (lab fees, shipping) | Lower (equipment, consumables) |
| Data Accuracy | Highly accurate and standardized | Moderate accuracy, operator-dependent |
| Benefit | Detailed herd health and milk quality insights | Quick decision-making, early issue detection |
| Best For | Herd management, breeding, compliance | Daily monitoring, immediate problem solving |
Overview of DHIA Testing and On-farm Milk Testing
DHIA testing provides comprehensive, standardized milk quality analysis through laboratory evaluation, offering detailed insights on somatic cell count, bacterial count, and milk components essential for herd management. On-farm milk testing allows real-time, immediate results using portable devices to monitor key indicators like fat, protein, and somatic cells, facilitating quick decision-making for daily herd health and milk production. Integrating DHIA data with frequent on-farm testing optimizes milk quality control and enhances overall dairy farm productivity.
Key Differences Between DHIA and On-farm Milk Quality Testing
DHIA testing offers standardized, laboratory-based analysis of milk quality, providing comprehensive data on components like fat, protein, and somatic cell count with high accuracy. On-farm testing allows for immediate, real-time assessment using portable devices, enabling farmers to make quick management decisions but with less precision compared to DHIA lab results. The key difference lies in DHIA's detailed, batch-processed reports versus on-farm testing's rapid but less detailed measurements, impacting herd health and milk quality monitoring strategies.
Accuracy and Reliability: DHIA vs On-farm Testing
DHIA testing provides highly accurate and reliable milk quality data due to standardized laboratory procedures and rigorous quality control measures, ensuring consistency across samples. On-farm testing offers rapid results but may lack the precision and reproducibility of DHIA tests, as it depends on operator skill and the quality of portable equipment. For critical herd management decisions, DHIA testing remains the industry gold standard, while on-farm testing serves as a convenient preliminary screening tool.
Cost Comparison: DHIA Testing vs On-farm Testing
DHIA testing typically incurs higher costs due to laboratory fees, sample collection, and data management services, whereas on-farm testing requires upfront investment in equipment but reduces long-term expenses by enabling immediate milk quality assessment. On-farm testing offers cost savings by minimizing sample shipping and turnaround time, allowing producers to make timely management decisions that can prevent costly milk quality issues. However, DHIA testing provides comprehensive, standardized data essential for long-term herd performance analysis that may justify the higher expense for larger operations.
Data Management and Record Keeping in Milk Quality Testing
DHIA testing provides centralized data management with standardized protocols, enabling comprehensive analysis and long-term record keeping crucial for herd performance benchmarking. On-farm testing offers immediate results but often lacks integrated digital record systems, limiting thorough data tracking and historical comparisons. Efficient milk quality testing relies on robust data management systems that aggregate, store, and analyze results to improve herd health and milk production consistently.
Frequency and Convenience of Milk Quality Tests
DHIA testing offers standardized milk quality analysis with monthly frequency, providing detailed herd health insights essential for long-term management. On-farm testing allows for immediate results and can be conducted daily or as needed, enabling quick decision-making to address milk quality issues promptly. The convenience of on-farm testing supports continuous monitoring, while DHIA testing ensures comprehensive data accuracy for strategic planning.
Impact on Herd Health and Production Decisions
DHIA testing provides comprehensive, standardized data on milk quality and herd performance, enabling informed long-term decisions impacting herd health and production efficiency. On-farm testing offers immediate, real-time results that help quickly identify issues like mastitis, allowing prompt management interventions to maintain milk quality and animal well-being. Integrating both testing methods optimizes monitoring accuracy, enhances disease detection, and supports precise production adjustments for improved herd productivity.
Integration with Dairy Farm Management Technology
DHIA testing offers comprehensive milk quality analysis through standardized lab procedures, seamlessly integrating with advanced dairy farm management software to provide detailed herd performance reports. On-farm testing delivers immediate, real-time milk quality data, enabling quick decision-making and direct synchronization with automated farm systems for enhanced operational efficiency. Both methods enhance milk quality monitoring, but combining DHIA's detailed analytics with the rapid feedback of on-farm testing maximizes integration benefits in dairy farm management technology.
Regulatory Compliance and Certification Implications
DHIA testing offers standardized milk quality analysis that meets stringent regulatory compliance requirements, facilitating certification processes essential for market access and consumer trust. On-farm testing provides immediate, practical data but may lack the formal recognition required for official certifications and regulatory audits. Ensuring adherence to national milk quality standards often necessitates DHIA testing for documentation and verification in dairy farming operations.
Choosing the Right Milk Quality Testing Method for Your Dairy Farm
DHIA testing offers comprehensive, laboratory-analyzed milk quality data, including somatic cell counts and milk component percentages, ideal for large-scale dairy operations seeking detailed herd health insights. On-farm testing provides immediate results for critical indicators such as somatic cell count and bacterial levels, allowing rapid response to udder health issues and enhancing daily herd management. Selecting the right method depends on farm size, management goals, and the need for timely versus detailed milk quality information.
Related Important Terms
Real-time Milk Analytics
DHIA testing provides comprehensive, laboratory-validated milk quality data essential for long-term herd management, while on-farm testing with real-time milk analytics delivers immediate insights into milk composition and somatic cell count, enabling rapid decision-making to improve udder health and milk yield. Integrating real-time on-farm sensors with DHIA data enhances precision in detecting mastitis and optimizing feeding strategies, ultimately boosting dairy farm productivity and milk quality.
Somatic Cell Count Sensors
Somatic cell count (SCC) sensors used in on-farm testing provide real-time monitoring of milk quality, enabling immediate detection of mastitis and improving herd health management. In contrast, DHIA (Dairy Herd Improvement Association) testing offers laboratory-validated SCC data with higher accuracy but involves longer turnaround times, making it less responsive for prompt decision-making.
Automated Milk Recording Systems
Automated Milk Recording Systems enhance on-farm testing by providing real-time, accurate data on milk quality parameters such as somatic cell count and milk components, facilitating immediate herd management decisions. Compared to DHIA testing, these systems reduce labor costs and sampling errors while enabling continuous monitoring to improve overall dairy herd health and milk consistency.
Cloud-based DHIA Data Integration
Cloud-based DHIA data integration enables precise tracking of milk quality by aggregating herd health metrics from multiple farms into a centralized platform, enhancing decision-making through comprehensive, real-time analytics. On-farm testing provides immediate results but lacks the broader data context and historical comparisons offered by DHIA's cloud-based systems, which optimize dairy farm management and improve milk production standards.
Portable Milk Composition Testers
Portable milk composition testers offer real-time analysis of fat, protein, and lactose levels directly on the farm, enabling immediate management decisions to improve milk quality. In contrast, DHIA testing provides comprehensive lab-based data with standardized accuracy but involves longer turnaround times and logistical constraints.
In-line Milk Quality Monitors
In-line milk quality monitors provide real-time data on milk components such as somatic cell count, fat, and protein, allowing immediate detection of abnormalities directly on the farm, unlike DHIA testing which involves periodic laboratory analysis with delayed results. This continuous monitoring system enhances dairy herd health management by enabling timely interventions to improve milk quality and productivity.
AI-powered Mastitis Detection
DHIA testing provides standardized, laboratory-verified milk quality analysis while on-farm AI-powered mastitis detection offers real-time, automated screening, enabling faster identification and treatment to minimize milk yield loss. Integrating AI technology with on-farm testing enhances precision in detecting subclinical mastitis, improving overall herd health and dairy productivity.
Genomic Data-linked Milk Testing
Genomic data-linked milk testing through DHIA offers precise insights into herd genetics and milk quality, enabling targeted breeding decisions and improved dairy performance. On-farm testing provides rapid, real-time milk quality analysis but lacks the comprehensive genetic profiling essential for long-term herd improvement strategies.
On-farm Near-infrared (NIR) Analysis
On-farm Near-infrared (NIR) analysis offers real-time, precise measurement of milk components such as fat, protein, and lactose, enabling immediate decision-making to optimize milk quality and herd health. This technology provides a cost-effective and rapid alternative to DHIA testing, reducing turnaround time and enhancing farm-level milk quality management.
Predictive Health Metrics
DHIA testing provides comprehensive, lab-validated data on somatic cell counts and milk composition, enabling precise predictive health metrics for early disease detection. On-farm testing offers immediate results for rapid decision-making, though it may lack the detailed analytical accuracy necessary for long-term health trend predictions.
DHIA testing vs On-farm testing for milk quality Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com