Automatic milking systems enhance herd management by providing precise data on milk yield, cow health, and milking frequency, enabling timely interventions and improved overall productivity. Traditional milking relies heavily on manual labor and scheduled routines, which can limit flexibility and delay the detection of health issues. Integrating automatic milking technology streamlines operations and supports better welfare monitoring for dairy farming pets.
Table of Comparison
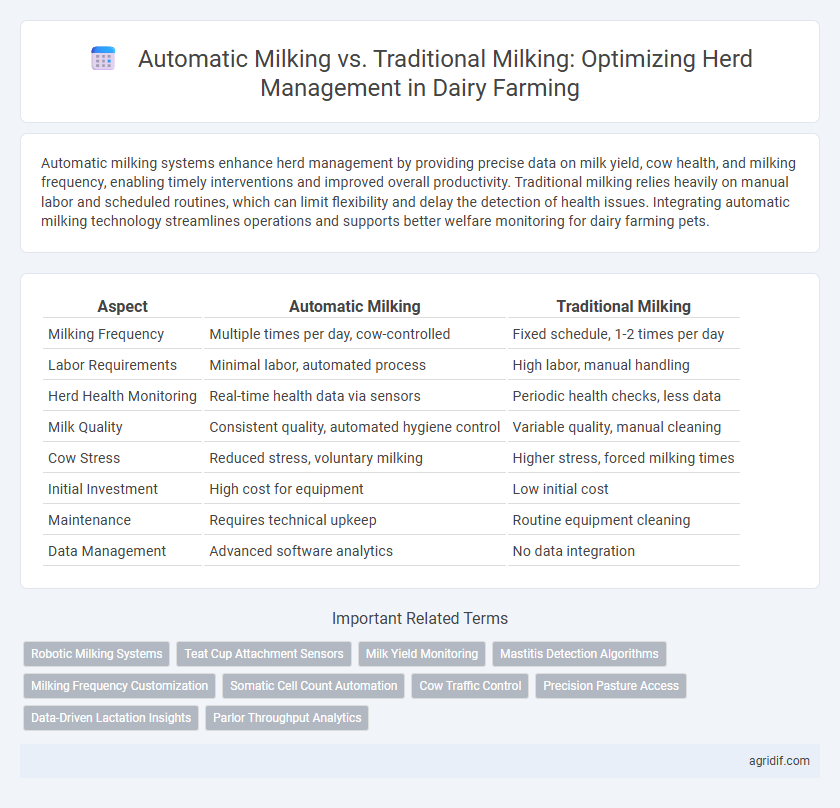
| Aspect | Automatic Milking | Traditional Milking |
|---|---|---|
| Milking Frequency | Multiple times per day, cow-controlled | Fixed schedule, 1-2 times per day |
| Labor Requirements | Minimal labor, automated process | High labor, manual handling |
| Herd Health Monitoring | Real-time health data via sensors | Periodic health checks, less data |
| Milk Quality | Consistent quality, automated hygiene control | Variable quality, manual cleaning |
| Cow Stress | Reduced stress, voluntary milking | Higher stress, forced milking times |
| Initial Investment | High cost for equipment | Low initial cost |
| Maintenance | Requires technical upkeep | Routine equipment cleaning |
| Data Management | Advanced software analytics | No data integration |
Introduction to Milking Methods in Dairy Farming
Automatic milking systems (AMS) leverage robotic technology to streamline herd management by enabling cows to be milked voluntarily, increasing milking frequency and improving udder health. Traditional milking methods rely on manual or semi-automatic equipment operated by farm workers, requiring scheduled milking times and more labor input. The choice between automatic and traditional milking affects labor efficiency, animal welfare, and data collection for herd productivity analysis in dairy farming.
Evolution of Automatic Milking Systems
Automatic milking systems (AMS) have revolutionized herd management by increasing efficiency through robotic technology that enables cows to be milked on their own schedule, improving animal welfare and milk yield consistency. These systems use advanced sensors and data analytics to monitor individual cow health, milk quality, and milking frequency, facilitating precise and timely interventions compared to traditional manual milking methods. The evolution of AMS integrates artificial intelligence and IoT, reducing labor costs while enhancing herd productivity and sustainability in modern dairy farming.
Traditional Milking Techniques Explained
Traditional milking techniques involve manual or machine-assisted milking performed by farm workers at scheduled times, requiring consistent labor and close animal handling. These methods allow direct observation of individual cows, enabling early detection of health issues and individualized care. Although labor-intensive, traditional milking provides hands-on herd management, preserving familiar routines critical for smaller or less technologically-equipped dairy farms.
Labor Efficiency in Automatic vs Traditional Milking
Automatic milking systems (AMS) significantly enhance labor efficiency by reducing the need for manual labor and allowing farmers to monitor multiple cows simultaneously through advanced sensors and data analytics. In contrast, traditional milking requires more time-intensive human labor, leading to higher labor costs and potential for human error. The integration of AMS streamlines herd management by automating routine tasks, improving consistency, and freeing labor resources for other farm operations.
Animal Health and Welfare Considerations
Automatic milking systems enhance herd management by providing consistent milking schedules, reducing stress and improving udder health through precise monitoring of individual cow data. Traditional milking relies heavily on manual observation, which can lead to delayed identification of health issues and increased risk of mastitis. Incorporating automatic milking technology supports proactive animal health management, promoting welfare through individualized care and reduced human error.
Impact on Milk Yield and Quality
Automatic milking systems significantly enhance milk yield by enabling more frequent and consistent milking schedules compared to traditional methods, reducing stress on cows and improving udder health. These systems also improve milk quality through real-time monitoring and precise herd management, detecting issues such as mastitis early and minimizing contamination. While traditional milking relies heavily on manual labor and timing, automatic systems optimize both production efficiency and product safety, benefiting overall herd management strategies.
Cost Analysis: Investment and Operational Expenses
Automatic milking systems require substantial initial investment, typically ranging from $150,000 to $200,000 per unit, but reduce long-term labor costs by up to 50% compared to traditional milking. Operational expenses for automatic systems include maintenance, software updates, and energy consumption, while traditional milking incurs higher ongoing labor wages and lower equipment costs. Cost analysis reveals that automatic milking becomes more economical over time with herd sizes above 100 cows due to enhanced efficiency and reduced human error.
Data Tracking and Herd Monitoring Capabilities
Automatic milking systems provide continuous data tracking and real-time herd monitoring, enabling precise health assessments and individualized dairy management. Traditional milking relies on manual recording, limiting the frequency and accuracy of data collection for herd performance and health indicators. Advanced sensors in automatic milking optimize milk yield and detect early signs of illness faster than conventional methods.
Environmental Sustainability and Resource Use
Automatic milking systems significantly reduce water usage and lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional milking methods by optimizing milking schedules and minimizing energy consumption. Precision technology in automatic systems enhances herd health monitoring, leading to more efficient feed use and less waste, which contributes to improved environmental sustainability. Traditional milking relies heavily on manual labor and fixed schedules, often resulting in higher resource input and increased environmental impact.
Choosing the Best Milking System for Your Herd
Automatic milking systems utilize robotic technology to enhance herd management by providing consistent milking schedules, real-time health monitoring, and labor efficiency, leading to improved milk yield and animal welfare. Traditional milking relies on manual labor, offering direct interaction with cows but requiring more time, personnel, and limiting scalability for larger herds. Choosing the best milking system depends on herd size, budget, labor availability, and goals for productivity and animal health monitoring.
Related Important Terms
Robotic Milking Systems
Robotic milking systems enhance herd management by providing precise data on milk yield, cow health, and milking frequency, increasing efficiency compared to traditional milking methods. These automatic systems reduce labor costs and improve animal welfare through individualized care and stress reduction during milking processes.
Teat Cup Attachment Sensors
Teat cup attachment sensors in automatic milking systems enhance herd management by ensuring precise and consistent teat stimulation, reducing the risk of udder infections and improving milk quality. Traditional milking methods lack this sensor integration, often resulting in less consistent attachment, increased labor, and higher chances of teat injury or contamination.
Milk Yield Monitoring
Automatic milking systems enable precise, real-time milk yield monitoring for each cow, improving herd management by identifying health issues early and optimizing production. Traditional milking relies on manual recording, which limits data accuracy and delays detection of abnormalities affecting milk yield.
Mastitis Detection Algorithms
Automatic milking systems equipped with advanced mastitis detection algorithms use real-time sensor data such as milk conductivity, temperature, and somatic cell count to identify early signs of infection, improving herd health management and reducing treatment costs. Traditional milking relies on manual observation and periodic testing, which often delays mastitis detection and increases the risk of severe outbreaks and decreased milk quality.
Milking Frequency Customization
Automatic milking systems enable precise milking frequency customization based on individual cow health and production metrics, enhancing udder health and milk yield. Traditional milking follows fixed schedules, limiting responsiveness to each cow's unique needs and potentially impacting overall herd productivity.
Somatic Cell Count Automation
Automatic milking systems significantly reduce somatic cell count (SCC) by continuously monitoring individual cows and detecting early signs of mastitis through advanced sensors, enabling timely intervention and improved udder health. Traditional milking methods lack real-time SCC monitoring, often leading to delayed detection and higher incidences of mastitis, adversely affecting milk quality and herd health management.
Cow Traffic Control
Automatic milking systems enhance cow traffic control by using sensor-based technology to guide cows voluntarily to milking stations, improving milking frequency and herd health monitoring. Traditional milking relies on scheduled manual herd movement, which can increase stress and reduce efficiency in managing large-scale dairy operations.
Precision Pasture Access
Automatic milking systems enhance precision pasture access by integrating real-time monitoring data to optimize grazing schedules and improve herd health, increasing milk yield and reducing labor costs. Traditional milking methods lack this seamless synchronization, often resulting in less efficient pasture use and inconsistent animal management.
Data-Driven Lactation Insights
Automatic milking systems provide continuous, real-time data on individual cow lactation patterns, enabling precise monitoring of milk yield, quality, and health indicators compared to traditional milking methods. This data-driven approach enhances herd management by identifying early signs of mastitis and optimizing feeding strategies, ultimately increasing overall dairy productivity and animal welfare.
Parlor Throughput Analytics
Automatic milking systems enhance parlor throughput analytics by providing real-time data on milking speed, cow flow, and individual animal performance, allowing farmers to optimize herd management efficiently. Traditional milking methods rely on manual observation and timing, which limits detailed throughput analysis and can reduce overall productivity in herd management strategies.
Automatic milking vs traditional milking for herd management Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com