Floor rearing allows birds to exhibit natural behaviors such as scratching and dust bathing, promoting better welfare and reducing stress in poultry farming pets. Cage rearing offers easier management and disease control but restricts movement, which can negatively impact bird health and behavior. Choosing between floor and cage rearing depends on balancing animal welfare with practical farming needs for optimal bird management.
Table of Comparison
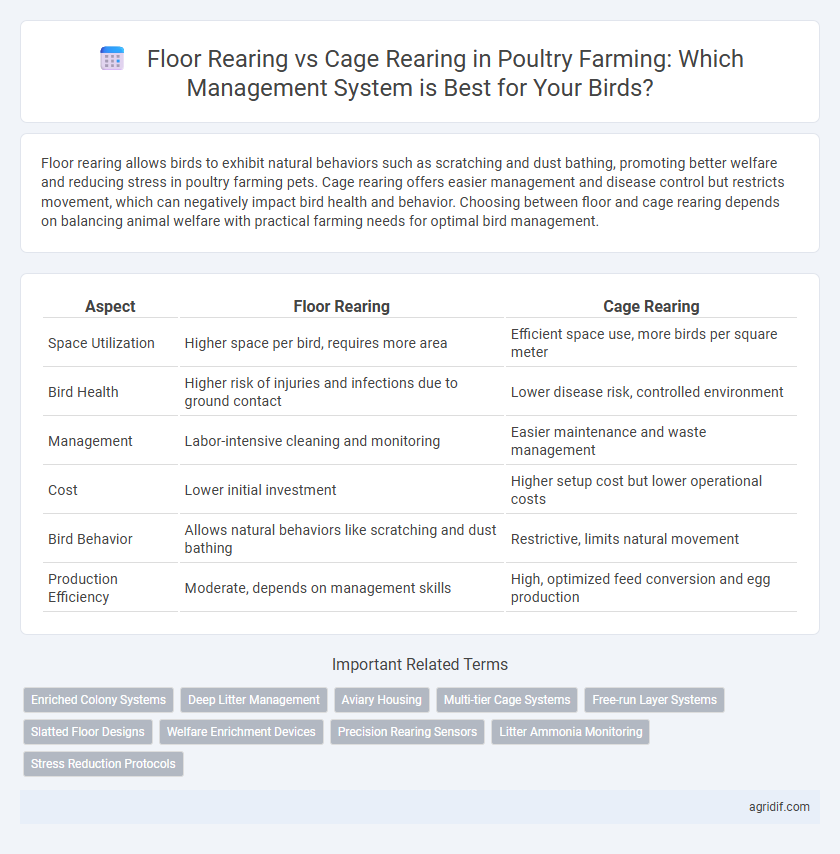
| Aspect | Floor Rearing | Cage Rearing |
|---|---|---|
| Space Utilization | Higher space per bird, requires more area | Efficient space use, more birds per square meter |
| Bird Health | Higher risk of injuries and infections due to ground contact | Lower disease risk, controlled environment |
| Management | Labor-intensive cleaning and monitoring | Easier maintenance and waste management |
| Cost | Lower initial investment | Higher setup cost but lower operational costs |
| Bird Behavior | Allows natural behaviors like scratching and dust bathing | Restrictive, limits natural movement |
| Production Efficiency | Moderate, depends on management skills | High, optimized feed conversion and egg production |
Introduction to Poultry Rearing Systems
Floor rearing and cage rearing represent two primary poultry management systems with distinct impacts on bird welfare and productivity. Floor rearing allows birds to move freely and express natural behaviors, enhancing welfare but requiring more space and sanitation management. Cage rearing optimizes space and eases egg collection, increasing efficiency in commercial production but potentially restricting movement and natural behaviors.
Overview of Floor Rearing Methods
Floor rearing in poultry farming involves raising birds directly on the poultry house floor covered with litter such as wood shavings or straw, promoting natural behaviors like scratching and dust bathing. This method supports better leg health and freedom of movement compared to cage rearing, which confines birds in restricted spaces, limiting their physical activity. Effective floor management includes regular litter maintenance, proper ventilation, and controlled stocking density to reduce disease risk and enhance bird welfare.
Understanding Cage Rearing Systems
Cage rearing systems for poultry farming offer enhanced biosecurity by minimizing bird contact with feces, reducing disease outbreaks and improving overall flock health. This method enables better space utilization and streamlined management practices such as automated feeding, watering, and egg collection, increasing production efficiency. However, cage systems may restrict natural behaviors, necessitating optimized cage design to balance welfare standards and productivity.
Welfare and Health Implications
Floor rearing allows birds to exhibit natural behaviors such as dust bathing and foraging, improving overall welfare by reducing stress and feather pecking. Cage rearing restricts movement, potentially leading to skeletal disorders and increased susceptibility to diseases due to limited exercise and problematic hygiene. Effective bird management must balance health benefits with welfare considerations, prioritizing environments that promote natural behaviors and minimize injury risks.
Productivity and Egg Production Comparison
Floor rearing allows birds more freedom of movement, often resulting in better overall health and higher egg quality, but may lead to lower egg production rates compared to cage rearing. Cage rearing systems typically achieve higher productivity per square meter through controlled feeding and reduced disease exposure, enhancing egg production efficiency. However, cage systems may compromise bird welfare, which can impact long-term productivity and egg shell quality.
Feed Efficiency in Floor vs Cage Systems
Feed efficiency in poultry farming varies significantly between floor rearing and cage rearing systems due to differences in bird activity levels and feed wastage. Cage rearing typically results in higher feed efficiency as birds have restricted movement, reducing energy expenditure and minimizing feed spillage. In contrast, floor-reared birds exhibit increased physical activity, which can lead to greater feed consumption but potentially lower feed conversion ratios.
Disease Management and Biosecurity
Floor rearing allows birds to exhibit natural behaviors but increases exposure to pathogens through direct contact with droppings, requiring stringent litter management and regular cleaning to maintain biosecurity. Cage rearing minimizes contact with manure, reducing the risk of disease transmission and facilitating easier monitoring of individual birds for early detection of illness. Effective disease management in poultry farming depends on balancing these rearing systems with targeted biosecurity measures like controlled access, disinfection protocols, and vaccination programs.
Labor and Operational Costs
Floor rearing in poultry farming generally incurs higher labor costs due to manual tasks such as feeding, cleaning, and bird monitoring, whereas cage rearing reduces labor requirements by enabling automated feeding and waste removal systems. Operational costs in floor rearing increase with the need for frequent bedding replacement and larger space utilization, while cage systems optimize space efficiency and lower maintenance expenses. Choosing cage rearing can significantly decrease labor intensity and operational costs, enhancing overall farm profitability.
Environmental Impact of Rearing Systems
Floor rearing systems for poultry typically result in higher ammonia emissions and greater nutrient runoff due to litter accumulation, contributing to environmental pollution. In contrast, cage rearing minimizes direct contact with waste, reducing immediate contamination but often generates concentrated manure that requires careful management to prevent soil and water degradation. Sustainable practices in both systems emphasize effective waste treatment and ventilation improvements to mitigate the environmental footprint of poultry production.
Choosing the Right System for Your Poultry Farm
Floor rearing promotes natural bird behaviors and reduces stress by providing ample space and litter for scratching and dust bathing, which can improve overall health and productivity. Cage rearing enables better control over individual bird hygiene, feed efficiency, and egg collection, leading to enhanced biosecurity and consistent production metrics. Selecting the right system depends on farm size, management goals, welfare regulations, and economic considerations to optimize both bird welfare and operational efficiency.
Related Important Terms
Enriched Colony Systems
Enriched colony systems combine the benefits of floor rearing and cage rearing by providing birds with enhanced space, perches, nesting areas, and litter for natural behaviors, improving welfare and productivity. These systems reduce stress and aggression compared to conventional cages while maintaining better hygiene and ease of management than traditional floor-based systems.
Deep Litter Management
Deep litter management in floor rearing promotes natural behaviors and improved welfare by allowing birds to move freely and engage in dust bathing, while maintaining dry, clean bedding to inhibit pathogens. Cage rearing restricts movement, increasing stress and disease risk, but simplifies manure control, making deep litter management less relevant in this system.
Aviary Housing
Aviary housing integrates floor rearing and cage rearing by providing multi-level platforms that enhance bird movement, natural behaviors, and welfare compared to traditional cage systems. This method optimizes space utilization and improves ventilation while reducing stress and injury risks associated with confined cage environments.
Multi-tier Cage Systems
Multi-tier cage systems in poultry farming maximize space efficiency and improve bird management by housing layers across several vertical levels, enhancing productivity per square meter compared to traditional floor rearing. These systems offer better disease control, easier manure collection, and automated feeding and egg collection, reducing labor costs and improving overall farm hygiene.
Free-run Layer Systems
Free-run layer systems promote natural behaviors by allowing birds to move freely on the floor, enhancing welfare and reducing stress compared to cage rearing. This method supports better bone strength and feather condition, contributing to improved overall health and productivity in poultry farming.
Slatted Floor Designs
Slatted floor designs in floor rearing offer enhanced waste management and improved bird hygiene by allowing droppings to fall through the gaps, reducing direct contact and disease risk compared to cage rearing. These systems promote natural behaviors like scratching and dust bathing while minimizing ammonia buildup and moisture retention, leading to healthier poultry and better growth performance.
Welfare Enrichment Devices
Floor rearing in poultry farming offers greater space for natural behaviors and easier integration of welfare enrichment devices such as perches, dust baths, and pecking objects that enhance bird well-being. Cage rearing restricts movement but can incorporate enrichment through manipulable materials and visual barriers to reduce stress, though welfare benefits are generally more limited compared to floor systems.
Precision Rearing Sensors
Precision rearing sensors in floor rearing systems enable real-time monitoring of bird health, behavior, and environmental conditions, enhancing welfare management and disease detection. In cage rearing, sensors optimize space usage and feed efficiency but may limit natural behaviors, making precision technology crucial for balancing productivity and animal well-being.
Litter Ammonia Monitoring
Litter ammonia monitoring is crucial in both floor rearing and cage rearing systems, with higher ammonia levels typically observed in floor rearing due to accumulated manure and moisture in the litter. Effective ventilation and regular litter management significantly reduce ammonia concentration, improving bird health and productivity in poultry farms.
Stress Reduction Protocols
Floor rearing allows birds to exhibit natural behaviors such as foraging and dust bathing, which significantly lowers cortisol levels and reduces stress compared to cage rearing. Implementing environmental enrichments like perches and litter bedding in floor systems enhances bird welfare and minimizes physiological stress markers linked to confinement in cages.
Floor rearing vs Cage rearing for bird management Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com