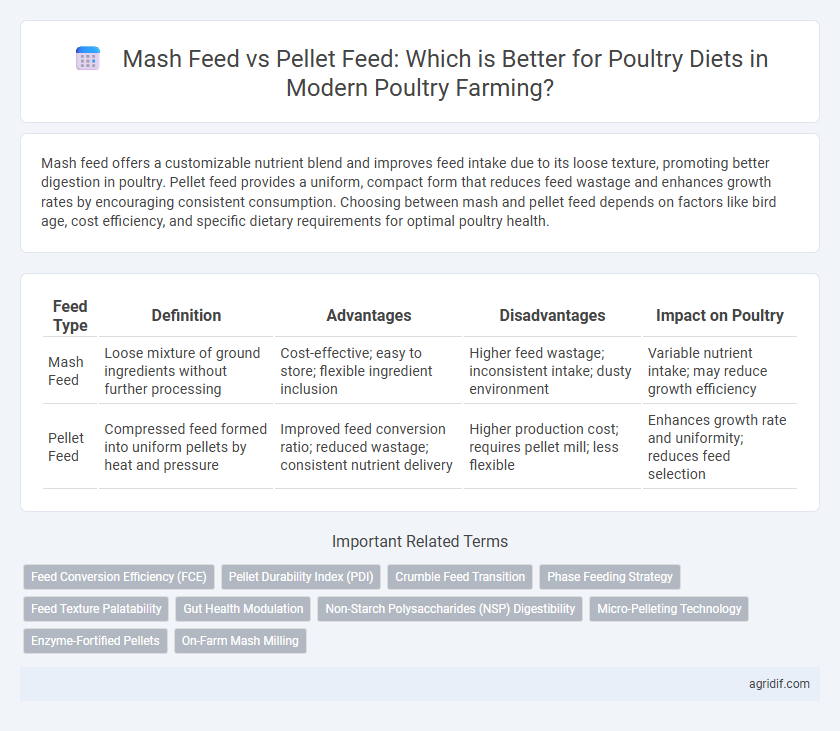
Mash feed offers a customizable nutrient blend and improves feed intake due to its loose texture, promoting better digestion in poultry. Pellet feed provides a uniform, compact form that reduces feed wastage and enhances growth rates by encouraging consistent consumption. Choosing between mash and pellet feed depends on factors like bird age, cost efficiency, and specific dietary requirements for optimal poultry health.
Table of Comparison
| Feed Type | Definition | Advantages | Disadvantages | Impact on Poultry |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mash Feed | Loose mixture of ground ingredients without further processing | Cost-effective; easy to store; flexible ingredient inclusion | Higher feed wastage; inconsistent intake; dusty environment | Variable nutrient intake; may reduce growth efficiency |
| Pellet Feed | Compressed feed formed into uniform pellets by heat and pressure | Improved feed conversion ratio; reduced wastage; consistent nutrient delivery | Higher production cost; requires pellet mill; less flexible | Enhances growth rate and uniformity; reduces feed selection |
Introduction to Poultry Feed Forms
Pellet feed for poultry is composed of compressed particles that enhance uniform nutrient distribution and reduce feed wastage, supporting efficient digestion and growth performance. Mash feed consists of loose, ground ingredients mixed together, offering flexibility in formulation and enabling birds to select preferred particles, which can benefit digestive health. Choosing between pellet and mash feed depends on factors such as poultry species, age, feed conversion ratio, and farm management objectives.
What is Mash Feed?
Mash feed is a type of poultry diet composed of ground or crushed raw ingredients mixed together, offering a balanced nutritional profile. It is easy to prepare and customize, allowing farmers to include specific vitamins, minerals, and proteins required for optimal poultry growth. Mash feed promotes efficient digestion but may result in higher feed wastage compared to pellet feed.
What is Pellet Feed?
Pellet feed consists of finely ground ingredients compressed into uniform, compact pellets that improve feed intake and minimize wastage in poultry. Rich in essential nutrients like proteins, vitamins, and minerals, pellet feed enhances digestion and supports optimal growth and production rates in poultry. Its consistent texture promotes faster consumption and reduces selective feeding compared to mash feed, leading to better feed efficiency and overall flock health.
Nutritional Value Comparison
Mash feed offers a balanced mixture of grains, vitamins, and minerals, allowing precise nutrient adjustment tailored to poultry dietary needs. Pellet feed provides enhanced nutrient density and uniformity by compressing ingredients, reducing feed wastage and improving digestion efficiency. Studies indicate pellet feed often results in better feed conversion ratios and growth performance due to its concentrated nutritional profile.
Feed Conversion Efficiency
Pellet feed significantly improves feed conversion efficiency (FCE) in poultry compared to mash feed by promoting uniform nutrient intake and reducing feed wastage. Studies indicate that birds consuming pellet feed exhibit higher weight gain and lower feed conversion ratios (FCR), making pellets more cost-effective for large-scale production. Optimizing diet formulation with pellets enhances nutrient absorption, leading to better growth performance and overall poultry productivity.
Digestibility and Palatability
Pellet feed offers higher digestibility for poultry due to its compact form, which reduces feed wastage and improves nutrient absorption. Mash feed, while less dense, enhances palatability by allowing birds to selectively consume preferred ingredients, promoting natural foraging behavior. Balancing digestibility and palatability is crucial for optimizing feed efficiency and poultry growth performance.
Impact on Poultry Growth and Productivity
Mash feed offers a cost-effective option that allows poultry to consume feed at a natural pace, promoting better digestion and nutrient absorption, which can support steady growth. Pellet feed enhances feed conversion efficiency by reducing feed wastage and improving uniformity in nutrient intake, often resulting in faster weight gain and higher overall productivity. Studies indicate pellet feeds generally improve feed efficiency by 5-10%, directly impacting growth rates and optimizing poultry production outputs.
Cost Considerations of Mash vs Pellet
Mash feed generally incurs lower initial production costs due to simpler processing requirements compared to pellet feed, which demands specialized equipment and higher energy consumption. However, pellet feed often delivers better feed conversion ratios and reduced wastage, potentially lowering overall expenses in the long term. Evaluating the balance between upfront investment and ongoing efficiency is crucial for cost-effective poultry diet management.
Suitability for Different Poultry Stages
Mash feed offers finer particle size, making it ideal for chicks during early stages to ensure easier digestion and nutrient absorption. Pellet feed, with its compact form, suits broilers and adult layers by enhancing feed intake efficiency and minimizing wastage. Choosing the appropriate feed type at specific growth phases improves overall poultry health, growth rate, and production performance.
Which Feed is Best for Your Flock?
Pellet feed offers better feed conversion efficiency and reduces wastage compared to mash feed, making it ideal for maximizing growth and production in poultry. Mash feed allows for more customized nutrient formulation and is often preferred for young chicks or birds requiring specific dietary adjustments. Choosing between mash and pellet feed depends on flock age, production goals, and cost efficiency, with pellets favored for uniformity and rapid intake, while mash supports flexible nutrition strategies.
Related Important Terms
Feed Conversion Efficiency (FCE)
Pellet feed offers higher Feed Conversion Efficiency (FCE) in poultry farming due to its uniform nutrient distribution and reduced feed wastage, resulting in faster growth rates and better weight gain compared to mash feed. Mash feed, while cheaper, often leads to inconsistent nutrient intake and higher feed spillage, lowering overall FCE and production efficiency.
Pellet Durability Index (PDI)
Pellet Feed offers a higher Pellet Durability Index (PDI), ensuring minimal fines and dust, which improves feed intake and reduces wastage in poultry diets. In contrast, Mash Feed lacks this durability, leading to inconsistent particle sizes that can negatively impact nutrient efficiency and bird performance.
Crumble Feed Transition
Crumble feed, a form of pellet feed broken into smaller pieces, offers enhanced digestibility and reduced feed wastage compared to traditional mash feed, making it ideal for transitioning young poultry. This transition supports better nutrient absorption and encourages consistent feed intake, promoting optimal growth and health in broiler and layer chicks.
Phase Feeding Strategy
Phase feeding strategy in poultry farming optimizes nutrient intake by matching feed type to specific growth stages, where mash feed offers better digestibility and gradual nutrient release during early phases, while pellet feed enhances feed efficiency and growth rate in later stages. Implementing phase-specific transitions from mash to pellet feed maximizes feed conversion ratio and overall flock performance.
Feed Texture Palatability
Mash feed offers a coarse, heterogeneous texture that enhances natural pecking behavior but may reduce uniform nutrient intake, while pellet feed provides a dense, uniform texture that improves feed palatability and digestion efficiency for poultry. Studies indicate pellet feed increases feed intake and weight gain due to its consistent texture and higher palatability, optimizing overall poultry growth performance.
Gut Health Modulation
Mash feed promotes natural chewing activity and enhances gut motility, supporting beneficial microbial populations in the poultry digestive tract; pellet feed offers uniform nutrient distribution and reduces feed wastage but may alter gut pH balance and microbial diversity. Optimizing feed form by combining mash and pellets can improve gut health modulation, leading to better nutrient absorption and strengthened immune response in poultry.
Non-Starch Polysaccharides (NSP) Digestibility
Pellet feed enhances Non-Starch Polysaccharides (NSP) digestibility in poultry diets by improving nutrient availability and feed intake efficiency compared to mash feed. Mash feed tends to have lower NSP digestibility due to its coarse texture, which can reduce enzymatic access and nutrient absorption in the gastrointestinal tract.
Micro-Pelleting Technology
Micro-pelleting technology enhances pellet feed by improving nutrient uniformity, reducing feed wastage, and promoting better feed intake compared to traditional mash feed in poultry diets. This innovative process yields denser, more durable pellets that optimize digestion and growth performance in poultry farming.
Enzyme-Fortified Pellets
Enzyme-fortified pellet feed enhances nutrient digestibility and feed conversion efficiency in poultry by breaking down complex carbohydrates and proteins, promoting better gut health and growth performance. Compared to mash feed, these pellets offer uniform nutrient distribution and reduced feed wastage, supporting cost-effective and sustainable poultry farming.
On-Farm Mash Milling
On-farm mash milling allows poultry farmers to customize feed formulations using locally sourced ingredients, enhancing nutrient availability and reducing costs compared to commercial pellet feed. Mash feed, with its loose texture, improves digestibility and feed intake in poultry, promoting better growth performance and overall flock health.
Mash Feed vs Pellet Feed for Poultry Diet Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com