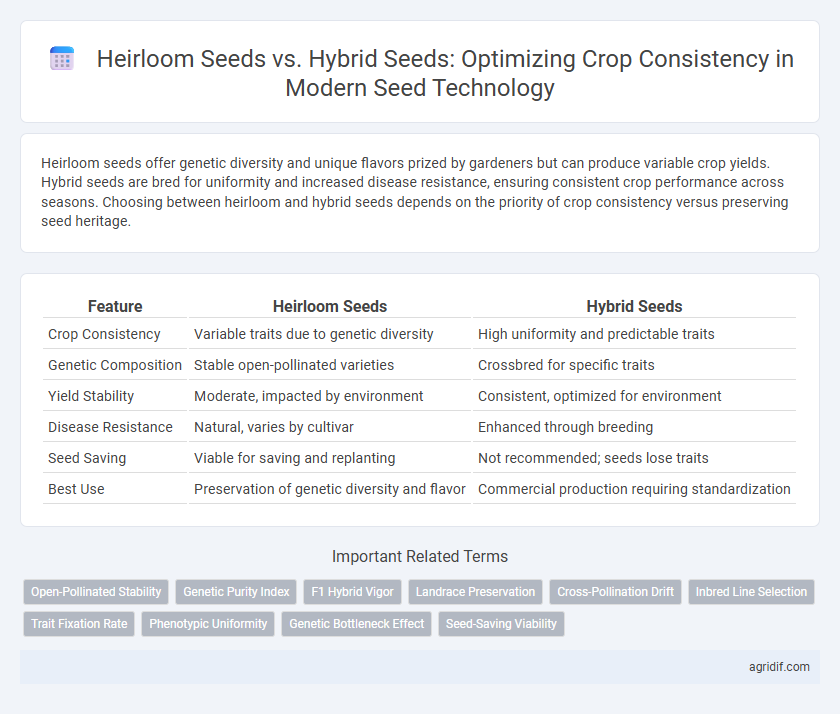
Heirloom seeds offer genetic diversity and unique flavors prized by gardeners but can produce variable crop yields. Hybrid seeds are bred for uniformity and increased disease resistance, ensuring consistent crop performance across seasons. Choosing between heirloom and hybrid seeds depends on the priority of crop consistency versus preserving seed heritage.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Heirloom Seeds | Hybrid Seeds |
|---|---|---|
| Crop Consistency | Variable traits due to genetic diversity | High uniformity and predictable traits |
| Genetic Composition | Stable open-pollinated varieties | Crossbred for specific traits |
| Yield Stability | Moderate, impacted by environment | Consistent, optimized for environment |
| Disease Resistance | Natural, varies by cultivar | Enhanced through breeding |
| Seed Saving | Viable for saving and replanting | Not recommended; seeds lose traits |
| Best Use | Preservation of genetic diversity and flavor | Commercial production requiring standardization |
Understanding Heirloom and Hybrid Seeds
Heirloom seeds are open-pollinated varieties preserved over generations, offering genetic diversity and unique flavors but sometimes less uniform crop consistency. Hybrid seeds result from controlled crossbreeding of two distinct parent plants, designed to enhance traits like yield, disease resistance, and uniformity in crop production. Understanding the differences helps farmers choose between heirloom seeds for biodiversity and flavor or hybrid seeds for reliable, consistent harvests.
Genetic Stability in Heirloom Seeds
Heirloom seeds offer superior genetic stability compared to hybrid seeds, ensuring consistent crop traits across generations without genetic drift. This stability allows farmers to save seeds year after year with predictable outcomes, preserving unique crop varieties and their flavors. Unlike hybrids, heirloom seeds maintain true-to-type characteristics, making them ideal for sustainable agriculture and biodiversity conservation.
Crop Uniformity: The Hybrid Seed Advantage
Hybrid seeds provide superior crop uniformity compared to heirloom seeds due to their controlled genetic makeup, resulting in plants with consistent height, maturity, and yield. This uniformity facilitates efficient harvesting, pest management, and irrigation practices, enhancing overall farm productivity. Farmers seeking reliable and predictable crop performance often prefer hybrid seeds for achieving consistent quality across large-scale cultivation.
Seed Saving: Heirloom vs Hybrid Practices
Heirloom seeds allow farmers to save and reuse seeds year after year, maintaining genetic consistency and preserving crop heritage without loss of vigor. Hybrid seeds, created by crossing two distinct parent lines, often produce superior traits in the first generation but typically do not breed true in subsequent generations, making seed saving unreliable. Seed saving practices favor heirloom varieties for consistent crop performance, while hybrid seeds require annual purchase to ensure uniformity and desired hybrid vigor.
Yield Predictability Across Seed Types
Heirloom seeds offer genetic diversity but present variable yield predictability due to their open-pollinated nature, resulting in inconsistent crop performance. Hybrid seeds are engineered for uniformity and high yield consistency, providing farmers with predictable outcomes across growing seasons. Yield predictability in hybrid seeds supports efficient resource management and market planning, whereas heirloom seeds favor adaptability but with less dependable production levels.
Disease Resistance in Heirloom and Hybrid Crops
Heirloom seeds often exhibit greater genetic diversity, which can contribute to natural disease resistance but may result in inconsistent crop performance across seasons. Hybrid seeds are bred for uniformity and enhanced disease resistance by combining specific traits from parent plants, leading to more predictable and stable crop yields. While hybrids provide targeted resistance to prevalent pathogens, heirlooms may offer broader resilience due to their diverse genetic base.
Flavor and Nutritional Differences
Heirloom seeds offer superior flavor profiles and richer nutritional content due to their open-pollinated nature, preserving genetic diversity for more complex taste and health benefits. Hybrid seeds prioritize crop consistency and higher yields but often sacrifice flavor intensity and nutrient density by focusing on uniformity and disease resistance. Farmers seeking optimal flavor and nutrition tend to prefer heirloom varieties, while large-scale producers prioritize hybrids for reliable performance and market standards.
Adaptability to Local Climates
Heirloom seeds exhibit superior adaptability to local climates due to their open-pollinated nature, preserving genetic traits suited to specific regional conditions, which enhances crop consistency over time. Hybrid seeds, while engineered for uniformity and high yield, often require tailored inputs and may underperform outside controlled environments, limiting their resilience to diverse climatic stresses. Farmers seeking stable production aligned with local environmental factors benefit from choosing heirloom varieties, which maintain genetic diversity and climate resilience essential for sustainable agriculture.
Economic Considerations for Farmers
Heirloom seeds often require more maintenance and offer variable yields, impacting economic stability for farmers who rely on consistent crop output. Hybrid seeds provide uniformity and higher resistance to pests and diseases, leading to increased productivity and potentially greater profitability. However, the dependence on purchasing new hybrid seeds each season can increase operational costs compared to the one-time investment in heirloom seeds.
Choosing the Right Seed for Consistent Harvests
Heirloom seeds offer genetic diversity and adaptability, preserving unique crop traits but may result in variable yields. Hybrid seeds provide uniformity and higher consistency in crop performance due to controlled breeding, ideal for predictable harvests. Selecting the right seed depends on balancing the need for genetic diversity with the demand for uniform, reliable crop output.
Related Important Terms
Open-Pollinated Stability
Open-pollinated heirloom seeds offer greater genetic stability and consistent traits across generations, ensuring reliable crop reproduction without genetic drift. Hybrid seeds, while providing initial uniformity and vigor, often produce variable offspring in subsequent generations due to their heterozygous genetic makeup, reducing long-term crop consistency.
Genetic Purity Index
Heirloom seeds maintain a higher Genetic Purity Index, preserving true-to-type traits across generations for consistent crop quality. Hybrid seeds often show variable Genetic Purity Index due to their crossbred nature, resulting in less predictable genetic stability and crop uniformity.
F1 Hybrid Vigor
F1 hybrid seeds utilize heterosis, or hybrid vigor, to consistently produce crops with superior yield, disease resistance, and uniformity compared to heirloom seeds, which may vary widely in traits due to open-pollination. While heirloom seeds preserve genetic diversity and unique flavors, F1 hybrids are engineered for crop consistency and optimized agricultural performance.
Landrace Preservation
Heirloom seeds preserve landrace genetics, maintaining crop diversity and resilience unique to specific regions, while hybrid seeds prioritize uniformity and higher yields but often lead to genetic erosion. Choosing heirloom seeds supports sustainable agriculture by safeguarding traditional varieties and their adaptive traits essential for long-term crop consistency.
Cross-Pollination Drift
Heirloom seeds preserve genetic purity by maintaining stable traits across generations, whereas hybrid seeds, created by crossing distinct parent lines, often exhibit variability due to cross-pollination drift. Cross-pollination drift in hybrid seeds can lead to inconsistent crop performance, making heirloom seeds preferable for farmers prioritizing uniformity and heritage preservation.
Inbred Line Selection
Inbred line selection in hybrid seeds promotes uniform crop consistency by combining genetically stable parent lines, ensuring predictable traits such as yield and disease resistance. Heirloom seeds, while valued for genetic diversity and unique flavors, often exhibit greater variability in crop performance due to open pollination and lack of controlled breeding.
Trait Fixation Rate
Heirloom seeds exhibit a high trait fixation rate, ensuring consistent crop characteristics across generations due to their stable genetic makeup. Hybrid seeds, while offering initial uniformity and vigor, often display variable trait fixation in subsequent generations, leading to inconsistent crop consistency over time.
Phenotypic Uniformity
Heirloom seeds exhibit significant phenotypic variability due to their open-pollinated nature, resulting in less consistency across crop generations compared to hybrid seeds. Hybrid seeds are genetically uniform, offering superior phenotypic uniformity that ensures consistent crop traits such as size, color, and growth rate, essential for predictable agricultural production.
Genetic Bottleneck Effect
Heirloom seeds preserve genetic diversity by maintaining open-pollinated traits, reducing the risk of the genetic bottleneck effect often seen in hybrid seeds, which are bred for uniformity but limit gene variability. This genetic bottleneck in hybrid seeds can lead to crop vulnerability and reduced adaptability, whereas heirloom varieties promote resilience and long-term sustainability in agricultural systems.
Seed-Saving Viability
Heirloom seeds preserve genetic diversity and allow farmers to save seeds year after year with consistent crop traits, ensuring long-term sustainability in seed-saving viability. Hybrid seeds often produce higher yields initially but typically lose their genetic consistency in subsequent generations, making them less reliable for seed saving and crop uniformity.
Heirloom Seeds vs Hybrid Seeds for Crop Consistency Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com