Grain augers offer efficient vertical and horizontal movement of grain, making them ideal for loading and unloading in confined spaces, while conveyor belts provide continuous, gentle handling suited for long-distance grain transport with minimal damage. Augers are typically more cost-effective and portable, facilitating quick setup and adjustment in various agricultural settings. Conveyor belts excel in reducing grain breakage and dust generation, improving overall grain quality during bulk transfer operations.
Table of Comparison
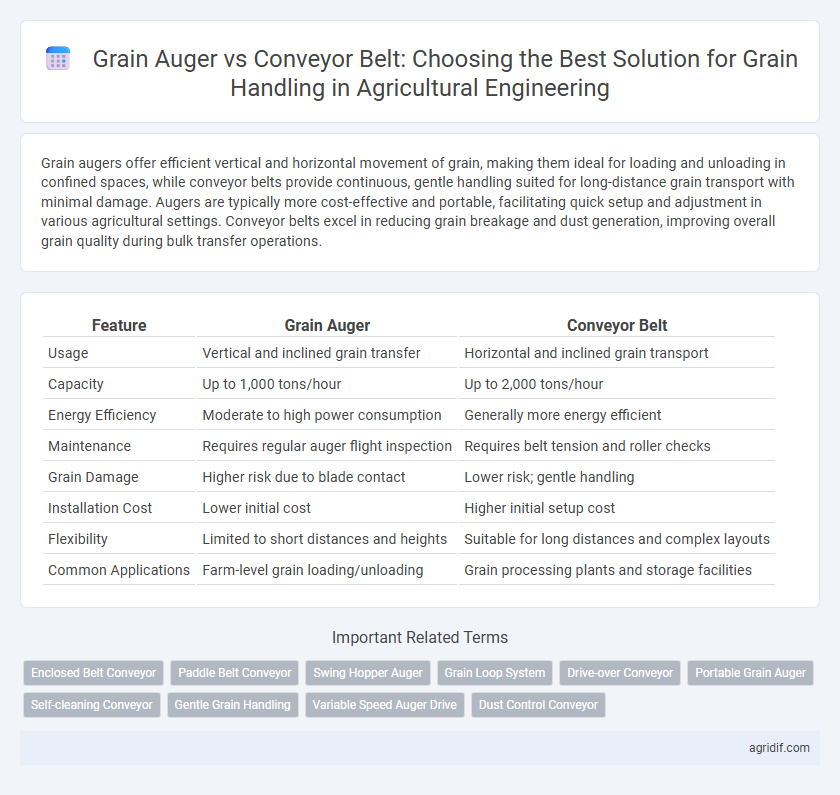
| Feature | Grain Auger | Conveyor Belt |
|---|---|---|
| Usage | Vertical and inclined grain transfer | Horizontal and inclined grain transport |
| Capacity | Up to 1,000 tons/hour | Up to 2,000 tons/hour |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate to high power consumption | Generally more energy efficient |
| Maintenance | Requires regular auger flight inspection | Requires belt tension and roller checks |
| Grain Damage | Higher risk due to blade contact | Lower risk; gentle handling |
| Installation Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial setup cost |
| Flexibility | Limited to short distances and heights | Suitable for long distances and complex layouts |
| Common Applications | Farm-level grain loading/unloading | Grain processing plants and storage facilities |
Introduction to Grain Handling Technologies
Grain augers and conveyor belts represent fundamental technologies in modern grain handling systems, each offering unique advantages in efficiency and capacity. Grain augers, characterized by their helical screw design, excel in vertical grain transfer and are widely used for loading and unloading grain bins. Conveyor belts provide continuous horizontal or inclined grain movement, supporting large-scale operations with high volume throughput and reduced mechanical complexity.
Overview of Grain Augers
Grain augers are mechanical devices used for transferring grain from one location to another by means of a rotating helical screw blade inside a tube, providing efficient vertical or inclined movement of bulk materials. Their design enables quick installation and easy mobility, making them ideal for loading grain into storage bins, trucks, or silos. Compared to conveyor belts, grain augers are typically more gentle on grain quality due to reduced exposure and less surface contact during handling.
Overview of Conveyor Belts
Conveyor belts in grain handling offer efficient, continuous transport of bulk materials with low maintenance requirements and customizable length and speed, making them ideal for high-volume agricultural operations. Their enclosed design reduces grain contamination and spillage compared to open grain augers, enhancing product quality and workplace safety. Advanced conveyor belt systems can be integrated with automation technology to optimize grain flow and minimize labor costs in large-scale farming environments.
Key Differences Between Grain Augers and Conveyor Belts
Grain augers utilize a helical screw blade within a tube to move grains vertically or horizontally, offering efficient grain handling for loading and unloading silos with minimal spillage. Conveyor belts provide continuous, flat surface transport ideal for horizontal grain movement over longer distances, supporting higher throughput with easier maintenance and adaptability to varied materials. Key differences include augers' reduced footprint and versatility in elevation changes versus conveyor belts' superior capacity and lower mechanical complexity for consistent, large-scale grain transfer.
Efficiency Comparison: Auger vs Conveyor Belt
Grain augers offer high efficiency for vertical and short-distance grain handling, with a typical capacity ranging from 500 to 2,500 bushels per hour depending on diameter and horsepower. Conveyor belts excel in horizontal and long-distance conveyance, providing consistent throughput and reduced grain damage, often achieving capacities upwards of 3,000 bushels per hour in large-scale operations. Augers tend to consume more energy per ton of grain moved due to friction and grain breakdown, whereas conveyor belts provide energy-efficient continuous movement with minimal grain degradation, optimizing overall handling efficiency.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Operation
Grain augers generally involve lower initial investment costs compared to conveyor belts, making them suitable for small to medium-scale grain handling operations. Conveyor belts, while requiring higher upfront expenses for installation and equipment, offer greater operational efficiency and reduced labor costs over time. Operational expenses for grain augers include regular maintenance and fuel or electricity, whereas conveyor belts primarily incur energy costs and less frequent maintenance, impacting long-term cost-effectiveness.
Maintenance and Durability Considerations
Grain augers require regular lubrication and inspection of flighting for wear to maintain efficient performance, while conveyor belts demand frequent checks for belt tension and roller alignment to prevent breakdowns. Augers generally exhibit higher durability in abrasive grain handling but may suffer from mechanical stress-related fatigue, whereas conveyor belts offer smoother grain flow yet face challenges from belt wear and potential tearing. Selecting between these systems depends on balancing the specific agricultural operation's maintenance capacity and desired lifespan under varying grain moisture and handling conditions.
Safety Aspects in Grain Handling
Grain augers present hazards such as entanglement and grain engulfment, requiring strict use of safety shields and lockout/tagout procedures to prevent accidents during maintenance. Conveyor belts offer safer grain handling by minimizing direct operator contact, though they require proper guarding and emergency stop systems to reduce risks of pinch points and mechanical injuries. Effective grain handling safety protocols must address specific equipment dangers, emphasizing operator training and routine inspections for both grain augers and conveyor belts.
Suitability for Different Grain Types and Operations
Grain augers are highly effective for handling small to medium-sized grains such as wheat, barley, and corn, offering efficient vertical and inclined transfer suitable for varying grain conditions. Conveyor belts excel in transporting large volumes of bulk grains like soybeans and rice over longer horizontal distances, providing continuous flow with minimal grain damage. Selection depends on grain type, operation scale, and required transfer type, with augers preferred for elevation changes and conveyors for horizontal bulk movement.
Choosing the Right System for Your Agricultural Needs
Grain augers provide efficient vertical and horizontal grain movement, ideal for smaller operations requiring flexibility and portability. Conveyor belts offer higher capacity and continuous grain flow, suited for larger farms with fixed installations and bulk handling needs. Selecting the right system depends on factors such as farm size, grain volume, desired speed, and installation complexity to optimize grain handling efficiency and reduce labor costs.
Related Important Terms
Enclosed Belt Conveyor
Enclosed belt conveyors provide superior protection against grain contamination and moisture compared to traditional grain augers, enhancing grain quality during transport. Their energy-efficient design and low maintenance requirements make them ideal for large-scale grain handling operations seeking to minimize spillage and dust emissions.
Paddle Belt Conveyor
Paddle belt conveyors offer efficient grain handling by minimizing grain damage and separation during transport, making them ideal for conveying irregular or fragile grains compared to traditional grain augers. Their design reduces clogging and maintenance requirements while maintaining a consistent flow rate, enhancing overall operational efficiency in agricultural engineering.
Swing Hopper Auger
Swing hopper augers offer precise grain handling with enhanced mobility, reducing spillage and minimizing labor compared to conveyor belts, which are typically fixed and less flexible. Their efficiency in transferring grain directly from hoppers to storage or transport vehicles makes them ideal for dynamic agricultural environments requiring quick setup and repositioning.
Grain Loop System
Grain Loop Systems integrate grain augers and conveyor belts to optimize efficiency in grain handling by leveraging the auger's vertical lift capability with the conveyor belt's horizontal transport strength. This combination reduces grain damage, increases throughput rates, and provides flexible routing options tailored to storage and processing facility layouts.
Drive-over Conveyor
Drive-over conveyors offer superior flexibility and efficiency in grain handling compared to traditional grain augers, enabling trucks to unload directly onto the conveyor system, reducing spillage and labor costs. Their robust design supports higher throughput rates and easier integration into automated grain handling operations, making them ideal for large-scale agricultural facilities.
Portable Grain Auger
Portable grain augers offer superior mobility and flexibility for transferring grain compared to conveyor belts, enabling efficient loading and unloading in varied locations on a farm. Their design reduces grain damage and energy consumption, making them a cost-effective solution in agricultural grain handling operations.
Self-cleaning Conveyor
Grain augers provide efficient vertical grain transfer but can face clogging issues, whereas self-cleaning conveyor belts offer continuous, low-maintenance grain handling with reduced spillage and higher throughput. Self-cleaning conveyors utilize specialized scrapers and belts designed to prevent grain buildup, enhancing operational efficiency and minimizing downtime in agricultural grain processing.
Gentle Grain Handling
Grain augers provide efficient grain handling but can cause kernel damage due to their high-friction, mechanical conveyance, whereas conveyor belts offer gentler grain transport by minimizing impact and abrasion, preserving grain integrity and reducing breakage. Selecting conveyor belts over augers enhances grain quality, especially for fragile crops, by maintaining kernel shape and reducing grain dust and fines during transfer.
Variable Speed Auger Drive
Variable speed auger drives provide precise control over grain flow rates, reducing spillage and minimizing grain damage during handling compared to fixed-speed systems. Conveyor belts offer continuous transport but lack the fine-tuned speed adjustment that augers achieve, making variable speed augers more adaptable for efficient grain management in diverse agricultural settings.
Dust Control Conveyor
Grain augers often generate significant dust due to their high-speed rotation and grain impact, increasing airborne particulates during transfer, whereas dust control conveyors utilize enclosed systems and dust extraction technology to minimize emissions and improve air quality in grain handling facilities. Dust control conveyors enhance operational safety and reduce grain loss by containing dust within sealed units and integrating vacuum or filtration mechanisms, making them superior in maintaining environmental compliance and worker health.
Grain auger vs Conveyor belt for grain handling Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com