Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the plant roots, reducing evaporation and runoff, making it highly efficient for water conservation in horticulture. Overhead irrigation sprays water broadly over plants, which can lead to higher water loss through evaporation and uneven water distribution. Choosing drip irrigation supports precise water management, enhances plant health, and promotes sustainable water use in horticultural practices.
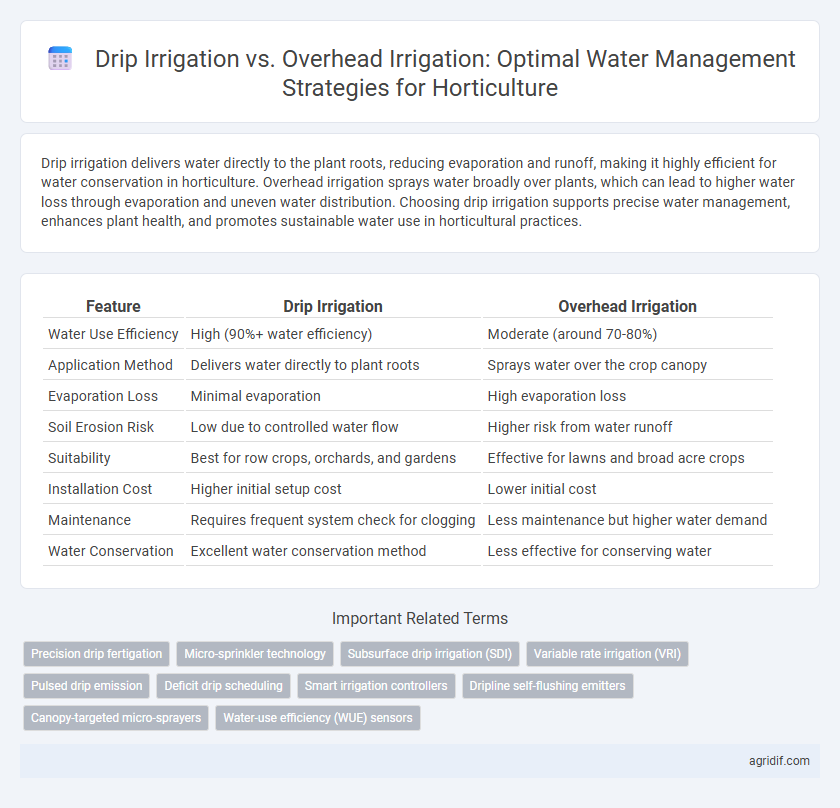
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Drip Irrigation | Overhead Irrigation |
|---|---|---|
| Water Use Efficiency | High (90%+ water efficiency) | Moderate (around 70-80%) |
| Application Method | Delivers water directly to plant roots | Sprays water over the crop canopy |
| Evaporation Loss | Minimal evaporation | High evaporation loss |
| Soil Erosion Risk | Low due to controlled water flow | Higher risk from water runoff |
| Suitability | Best for row crops, orchards, and gardens | Effective for lawns and broad acre crops |
| Installation Cost | Higher initial setup cost | Lower initial cost |
| Maintenance | Requires frequent system check for clogging | Less maintenance but higher water demand |
| Water Conservation | Excellent water conservation method | Less effective for conserving water |
Introduction to Irrigation Methods in Horticulture
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the root zone with high efficiency, minimizing evaporation and runoff, making it ideal for water-sensitive horticultural crops. Overhead irrigation distributes water through sprinklers, covering a larger area but increasing water loss due to evaporation and wind drift. Selecting the optimal irrigation method depends on crop type, soil characteristics, and water conservation goals in horticultural water management.
Fundamentals of Drip Irrigation Systems
Drip irrigation systems deliver water directly to the plant root zone through a network of valves, pipes, tubing, and emitters, maximizing water use efficiency by reducing evaporation and runoff. This method allows precise control over the timing and amount of water applied, promoting healthier plant growth and higher yields in horticulture. Compared to overhead irrigation, drip irrigation minimizes water waste, soil erosion, and foliar diseases, making it a sustainable choice for efficient water management in horticultural practices.
Overview of Overhead Irrigation Techniques
Overhead irrigation techniques include sprinkler systems, center pivots, and lateral move systems, which distribute water by spraying it over the crop canopy. These methods are suitable for uniform water application on various crop types but often face challenges with evaporation and wind drift loss. Proper management and scheduling are essential to optimize water efficiency and reduce runoff in overhead irrigation.
Water Efficiency: Drip vs Overhead Irrigation
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to plant roots with precision, achieving up to 90% water use efficiency by minimizing evaporation and runoff. Overhead irrigation typically results in 40-60% water use efficiency due to significant water loss from evaporation, wind drift, and surface runoff. Implementing drip systems in horticulture reduces water wastage and enhances crop yield by maintaining optimal soil moisture levels.
Crop Health and Disease Management: Comparing the Methods
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the root zone, minimizing leaf wetness and significantly reducing the risk of foliar diseases like powdery mildew and blight compared to overhead irrigation. Overhead irrigation increases humidity and leaf wetness duration, creating favorable conditions for fungal pathogens and other diseases in crops. Effective water management through drip systems enhances plant health by ensuring optimal soil moisture while limiting disease incidence and promoting higher yields in horticulture.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Drip irrigation systems require precise installation of emitters, tubing, and filters to ensure targeted water delivery and minimize waste, demanding moderate initial setup expertise. Maintenance involves regular inspection for clogs and leaks, flushing lines, and replacing components to maintain efficiency. Overhead irrigation installations need robust piping and sprinkler heads positioned for uniform coverage while requiring frequent adjustments and cleaning to prevent nozzle blockages and ensure consistent spray patterns.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-Term Expenses
Drip irrigation systems generally require a higher upfront investment due to the cost of emitters, tubing, and installation, but they offer significant long-term savings through reduced water usage and lower energy costs. Overhead irrigation has lower initial installation expenses but tends to incur higher operational costs over time because of water wastage, increased evaporation, and frequent maintenance. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals drip irrigation as more cost-effective for sustainable water management in horticultural practices.
Suitability for Different Horticultural Crops
Drip irrigation offers precise water delivery directly to the root zone, making it highly suitable for row crops, orchard trees, and greenhouse plants where water efficiency and disease prevention are critical. Overhead irrigation suits turf grasses, seed beds, and crops requiring uniform canopy wetting, but it can increase fungal risks in sensitive horticultural plants. Crop-specific water requirements and microclimate conditions determine the optimal irrigation method for maximizing growth and conserving water resources in horticulture.
Impact on Soil Structure and Nutrient Delivery
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the root zone, minimizing soil erosion and maintaining optimal soil structure by preventing surface runoff and compaction. This targeted watering enhances nutrient uptake efficiency, reducing leaching and ensuring consistent delivery of essential nutrients to plants. In contrast, overhead irrigation can cause soil surface crusting and nutrient runoff, potentially disrupting soil microbial activity and leading to uneven nutrient distribution.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
Drip irrigation significantly reduces water runoff and evaporation compared to overhead irrigation, promoting efficient water use and minimizing soil erosion. Its targeted water delivery supports sustainable horticultural practices by conserving water resources and reducing energy consumption. Overhead irrigation often results in higher water wastage and can contribute to increased humidity, promoting plant diseases and negatively impacting environmental sustainability.
Related Important Terms
Precision drip fertigation
Precision drip fertigation delivers targeted water and nutrients directly to the root zone, enhancing water efficiency up to 90% and reducing nutrient runoff compared to overhead irrigation. This method supports optimal plant growth by maintaining consistent soil moisture levels and minimizing evaporation losses in horticultural crops.
Micro-sprinkler technology
Micro-sprinkler technology in drip irrigation delivers precise water application directly to the root zone, reducing evaporation and runoff compared to overhead irrigation systems that spray water over the entire canopy. This targeted approach enhances water use efficiency and promotes healthier plant growth in horticulture by minimizing water waste and soil erosion.
Subsurface drip irrigation (SDI)
Subsurface drip irrigation (SDI) delivers water directly to the root zone, significantly reducing evaporation and runoff compared to overhead irrigation methods. This targeted water application enhances water-use efficiency, promotes healthier plant growth, and reduces weed proliferation in horticultural crops.
Variable rate irrigation (VRI)
Variable Rate Irrigation (VRI) enhances water efficiency by applying precise volumes through drip irrigation systems, targeting root zones to minimize evaporation and runoff. Overhead irrigation with VRI allows for adjustable spray patterns but often results in higher water loss compared to the more localized and controlled delivery of drip irrigation.
Pulsed drip emission
Pulsed drip emission in drip irrigation enhances precise water delivery by releasing small, frequent water pulses directly to the root zone, significantly reducing water runoff and evaporation compared to overhead irrigation. This targeted approach improves water use efficiency, promotes better root oxygenation, and minimizes disease risk associated with leaf wetness in horticultural crops.
Deficit drip scheduling
Deficit drip scheduling in drip irrigation delivers precise water directly to plant roots, reducing water wastage and improving water-use efficiency compared to overhead irrigation, which often leads to evaporation and runoff. This targeted approach enhances crop yield and stress resistance under limited water availability by maintaining optimal soil moisture levels.
Smart irrigation controllers
Smart irrigation controllers optimize water usage by precisely scheduling drip irrigation, reducing evaporation and runoff compared to traditional overhead irrigation methods. These controllers integrate soil moisture sensors and weather data to enhance water efficiency, promote plant health, and minimize resource waste in horticultural applications.
Dripline self-flushing emitters
Dripline self-flushing emitters in drip irrigation systems enhance water efficiency by delivering precise moisture directly to plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff compared to overhead irrigation. These emitters reduce clogging risks through automatic flushing, ensuring consistent water flow and promoting healthier plant growth while conserving water resources.
Canopy-targeted micro-sprayers
Canopy-targeted micro-sprayers in overhead irrigation enhance water distribution efficiency by delivering precise droplets directly to plant foliage, reducing evaporation losses compared to traditional overhead systems. Drip irrigation, while effective for soil moisture management, lacks the ability to uniformly wet the canopy, limiting foliar nutrient uptake and pest control benefits provided by micro-sprayer technology.
Water-use efficiency (WUE) sensors
Drip irrigation systems enhance water-use efficiency (WUE) by delivering precise amounts of water directly to plant roots, reducing evaporation and runoff, while overhead irrigation often results in significant water loss due to spray drift and surface evaporation. Integrating WUE sensors with drip irrigation optimizes irrigation scheduling and water distribution, ensuring maximum plant uptake and minimal waste in horticultural water management.
Drip irrigation vs Overhead irrigation for water management Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com