Pellet feed offers uniform nutrient distribution and reduces feed wastage, promoting better growth and feed conversion in poultry compared to mash feed. Mash feed is easier to produce and allows poultry to select preferred ingredients, but it may result in inconsistent nutrient intake and increased fines. Choosing between pellet and mash feed depends on specific poultry nutrition goals, production scale, and cost considerations.
Table of Comparison
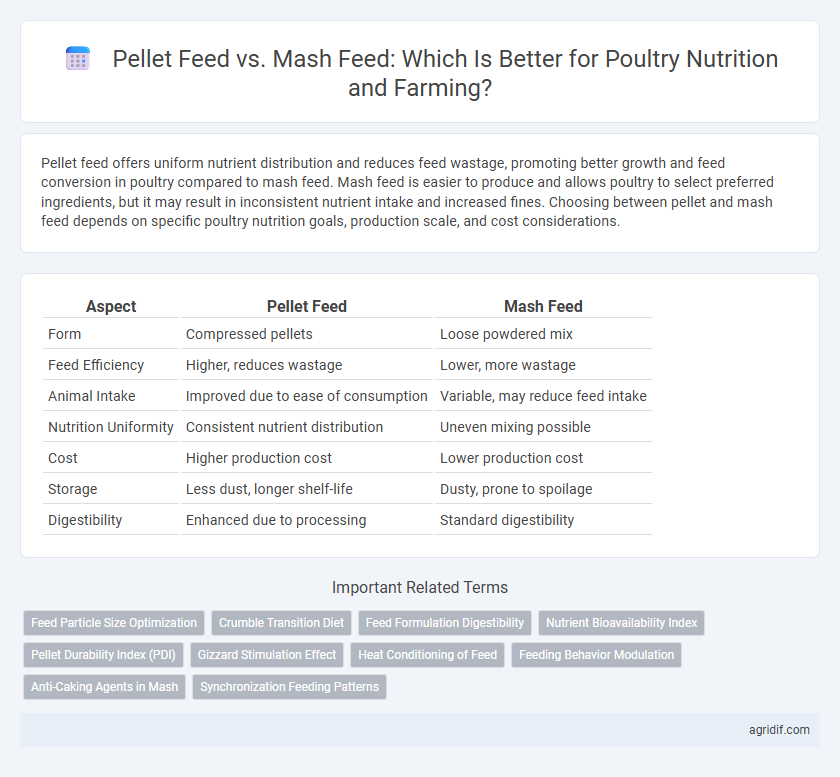
| Aspect | Pellet Feed | Mash Feed |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Compressed pellets | Loose powdered mix |
| Feed Efficiency | Higher, reduces wastage | Lower, more wastage |
| Animal Intake | Improved due to ease of consumption | Variable, may reduce feed intake |
| Nutrition Uniformity | Consistent nutrient distribution | Uneven mixing possible |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Lower production cost |
| Storage | Less dust, longer shelf-life | Dusty, prone to spoilage |
| Digestibility | Enhanced due to processing | Standard digestibility |
Introduction to Poultry Feed Types
Pellet feed and mash feed are two primary forms of poultry nutrition, each offering distinct benefits in terms of digestibility and nutrient absorption. Pellet feed, composed of compressed and uniformly sized particles, enhances feed intake efficiency and reduces waste, while mash feed consists of loose ground ingredients, promoting better digestion for certain poultry species. Selecting the optimal feed type depends on factors such as bird age, breed, and production goals to ensure balanced nutrition and improved poultry performance.
Understanding Pellet Feed: Composition and Features
Pellet feed for poultry consists of ground grains, protein sources, vitamins, and minerals compacted into small, dense pellets that enhance nutrient uniformity and reduce feed wastage. The pelleting process improves feed digestibility by breaking down anti-nutritional factors and increasing starch gelatinization, resulting in better feed conversion ratios. Pellet feed also minimizes selective feeding behavior in poultry, ensuring balanced nutrient intake crucial for optimal growth and egg production.
What Is Mash Feed? Characteristics and Preparation
Mash feed for poultry consists of a mixture of ground raw materials such as grains, protein sources, vitamins, and minerals in a loose, powdery form. It is characterized by its easy digestibility, cost-effectiveness, and suitability for young or small birds due to its fine texture. Preparation involves grinding ingredients to a uniform size, mixing thoroughly to ensure nutrient consistency, and maintaining proper moisture levels to prevent dust and feed wastage.
Nutritional Differences Between Pellet and Mash Feed
Pellet feed provides uniform nutrient distribution and reduces feed wastage due to its compact structure, enhancing nutrient intake efficiency in poultry. Mash feed consists of loose ingredients that may lead to selective feeding, causing nutrient imbalance and inconsistent consumption. The pelleting process also improves feed digestibility by breaking down complex nutrients, which is less efficient in mash feed formulations.
Impact on Growth Rate and Feed Conversion Ratio
Pellet feed enhances poultry growth rate by improving nutrient density and feed intake consistency, leading to better weight gain compared to mash feed. Pellet feed also optimizes feed conversion ratio (FCR) by minimizing feed wastage and promoting efficient digestion, resulting in lower feed costs per unit of weight gain. In contrast, mash feed can cause selective feeding and uneven nutrient intake, negatively affecting overall growth performance and FCR.
Feed Hygiene and Safety Considerations
Pellet feed offers improved feed hygiene by reducing dust and minimizing contamination risks compared to mash feed, which can harbor pathogens in its loose form. The pelleting process involves heat treatment that helps eliminate bacteria and molds, enhancing feed safety for poultry consumption. Proper storage and handling remain critical for both pellet and mash feed to prevent moisture buildup and maintain nutritional integrity.
Cost Analysis: Pellet Feed vs Mash Feed
Pellet feed generally incurs higher production costs due to the additional processing steps like grinding, conditioning, and pelleting, whereas mash feed involves simpler mixing and grinding, making it less expensive initially. Despite higher upfront costs, pellet feed can improve feed efficiency and reduce waste by up to 10-15%, potentially lowering overall feed consumption and costs in the long term. Mash feed, while cheaper to produce, often results in higher feed wastage and lower nutrient density, which can increase the total cost per unit of weight gain in poultry production.
Influence on Poultry Health and Immunity
Pellet feed enhances poultry health by improving nutrient digestibility and reducing feed wastage, leading to stronger immunity and better disease resistance. Mash feed, while promoting natural chewing behavior, may result in inconsistent nutrient intake and lower feed efficiency, potentially weakening immune response. Optimizing feed form is crucial for maximizing poultry growth and maintaining robust immune systems.
Farmer Preferences and Practical Challenges
Pellet feed offers higher feed conversion efficiency and reduced wastage compared to mash feed, making it a preferred choice for many poultry farmers seeking cost-effective nutrition. However, the production of pellet feed requires specialized machinery and higher energy input, which can pose practical challenges for small-scale farmers. Mash feed remains popular for easier customization and adaptability despite being less efficient, highlighting the balance between operational capacity and nutritional goals in poultry farming.
Choosing the Optimal Feed for Your Poultry Farm
Pellet feed offers higher nutrient density and uniformity, promoting better feed conversion ratios and growth rates in poultry compared to mash feed. Mash feed provides flexibility in ingredient composition and is often more cost-effective, but may lead to uneven nutrient intake and feed wastage. Selecting the optimal feed depends on factors like poultry species, farm scale, and economic priorities, with pellet feed preferred for intensive production and mash feed suited for smaller or mixed feeding systems.
Related Important Terms
Feed Particle Size Optimization
Pellet feed offers uniform feed particle size that enhances nutrient digestibility and reduces feed wastage in poultry nutrition compared to mash feed, which has variable particle sizes leading to selective feeding and inconsistent nutrient intake. Optimizing feed particle size through pelleting improves feed conversion ratios and supports better growth performance in poultry.
Crumble Transition Diet
Crumble feed serves as a vital transition diet between mash and pellet feed in poultry nutrition, enhancing pellet feed intake and digestion efficiency in young birds. The optimized texture of crumble feed improves feed conversion ratio (FCR) and supports uniform growth by facilitating easier consumption and nutrient absorption during early developmental stages.
Feed Formulation Digestibility
Pellet feed enhances nutrient digestibility in poultry by improving feed intake consistency and reducing feed wastage compared to mash feed, which often results in selective feeding and inconsistent nutrient consumption. Optimized feed formulation in pellet form ensures uniform nutrient distribution and better pellet durability, leading to improved growth performance and feed conversion ratios in poultry farming.
Nutrient Bioavailability Index
Pellet feed enhances nutrient bioavailability index by improving digestibility and reducing feed wastage compared to mash feed, ensuring better absorption of essential proteins, vitamins, and minerals in poultry. Higher pellet feed nutrient bioavailability supports optimal growth rates, feed conversion ratios, and overall bird health in commercial poultry production.
Pellet Durability Index (PDI)
Pellet Feed demonstrates a higher Pellet Durability Index (PDI), indicating superior resistance to breakage during handling and transportation compared to Mash Feed, thus ensuring consistent nutrient delivery. Maintaining an optimal PDI enhances poultry feed efficiency, reduces wastage, and supports better growth performance in poultry farming.
Gizzard Stimulation Effect
Pellet feed enhances gizzard stimulation in poultry by promoting stronger grinding activity, which improves nutrient absorption and digestive efficiency compared to mash feed. This increased mechanical digestion supports better feed conversion ratios and overall bird health.
Heat Conditioning of Feed
Heat conditioning during pellet feed production improves nutrient digestibility and feed conversion by gelatinizing starch and reducing microbial contamination, whereas mash feed lacks this thermal treatment, resulting in lower bioavailability of nutrients and increased risk of pathogenic bacteria. Pellet feed's enhanced heat conditioning optimizes poultry growth performance and feed efficiency compared to mash feed in poultry nutrition.
Feeding Behavior Modulation
Pellet feed enhances poultry feeding behavior by promoting uniform intake and reducing selective feeding, leading to improved nutrient absorption and growth performance. Mash feed allows more natural pecking activity but may cause feed wastage and inconsistent nutrient consumption, affecting overall feed efficiency.
Anti-Caking Agents in Mash
Anti-caking agents in mash feed prevent clumping and ensure consistent nutrient intake, improving feed efficiency and bird health. Unlike pellet feed, which is compressed into solid form, mash feed's loose texture requires effective anti-caking agents to maintain flowability and reduce feed wastage in poultry farming.
Synchronization Feeding Patterns
Pellet feed enhances synchronization feeding patterns by promoting uniform nutrient intake, leading to improved growth rates and feed efficiency compared to mash feed. Consistent particle size in pellet feed reduces selective feeding behaviors often observed with mash feed, optimizing digestion and nutrient absorption in poultry.
Pellet Feed vs Mash Feed for Poultry Nutrition Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com