GNSS provides general geolocation accuracy suitable for many agricultural applications, but RTK enhances precision by correcting satellite signals in real time, achieving centimeter-level accuracy. This improved accuracy is critical for precision agriculture tasks such as planting, fertilizing, and harvesting, ensuring optimal input use and crop yield. Farmers relying on RTK technology benefit from reduced overlap and gaps, leading to more efficient field management and resource conservation.
Table of Comparison
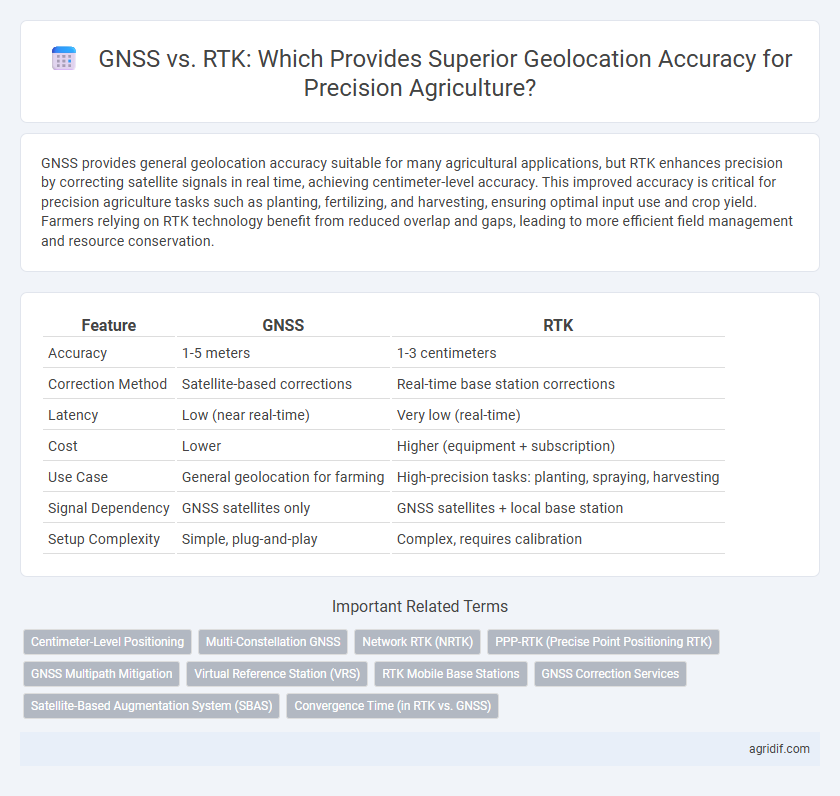
| Feature | GNSS | RTK |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 1-5 meters | 1-3 centimeters |
| Correction Method | Satellite-based corrections | Real-time base station corrections |
| Latency | Low (near real-time) | Very low (real-time) |
| Cost | Lower | Higher (equipment + subscription) |
| Use Case | General geolocation for farming | High-precision tasks: planting, spraying, harvesting |
| Signal Dependency | GNSS satellites only | GNSS satellites + local base station |
| Setup Complexity | Simple, plug-and-play | Complex, requires calibration |
Understanding GNSS and RTK: Core Concepts
Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) utilize satellite signals to provide geolocation data essential for precision agriculture, with standard GNSS offering meter-level accuracy. Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) technology enhances GNSS by applying carrier-phase measurements and correction data from nearby base stations, achieving centimeter-level precision critical for tasks like variable rate application and autonomous machinery guidance. Understanding the core concepts of these systems enables farmers to select the appropriate technology for maximizing efficiency and crop yield through precise field mapping and positioning.
Key Differences Between GNSS and RTK Geolocation
GNSS provides global satellite positioning with typical accuracies ranging from 5 to 10 meters, suitable for general farm mapping and navigation. RTK enhances GNSS by using a fixed base station to transmit correction signals, achieving centimeter-level accuracy essential for tasks like planting, spraying, and field mapping. The key difference lies in RTK's real-time corrections, drastically improving precision and reliability over standard GNSS solutions in precision agriculture.
Precision Levels: GNSS vs RTK in Agriculture
GNSS systems typically provide horizontal accuracy of 2 to 5 meters, which suits basic agricultural tasks but falls short for high-precision needs. RTK technology enhances geolocation accuracy to within 1 to 2 centimeters by using real-time correction data from base stations, making it ideal for precision farming operations such as planting and spraying. The sub-decimeter precision offered by RTK significantly reduces input costs and optimizes yield by ensuring exact machinery positioning in field management.
Hardware Requirements for GNSS and RTK Systems
GNSS systems rely on satellite signals and require basic hardware including a GNSS receiver and an antenna, making them cost-effective and easy to deploy for general agricultural mapping. RTK systems demand more advanced hardware such as dual-frequency GNSS receivers, base stations, or access to reference networks to provide centimeter-level positioning accuracy essential for precision planting and variable-rate applications. The hardware complexity and costs for RTK are higher, but the improved geolocation accuracy significantly benefits crop management and yield optimization in precision agriculture.
Signal Reliability: GNSS Versus RTK Performance
GNSS offers broad satellite coverage with moderate geolocation accuracy, but its signal reliability can be affected by atmospheric conditions and multi-path interference. RTK enhances precision by using a fixed base station to provide real-time corrections, significantly increasing signal reliability and achieving centimeter-level accuracy. This improvement makes RTK the preferred choice in precision agriculture applications requiring high-accuracy positioning for tasks like variable rate application and autonomous machinery guidance.
Cost Implications: Investment in GNSS versus RTK
GNSS systems offer cost-effective geolocation for broad agricultural applications, typically requiring less initial investment compared to RTK systems. RTK technology delivers centimeter-level accuracy by leveraging real-time correction data but entails higher upfront costs for base stations and subscription services. While GNSS suits farmers with moderate precision needs, RTK's premium expense is justified by its ability to enhance yield efficiency through precise field mapping and machinery guidance.
Real-World Applications: When to Use GNSS or RTK
GNSS provides reliable geolocation accuracy for general field mapping and large-scale farming operations, offering meter-level precision suitable for crop monitoring and resource management. RTK enhances this by delivering centimeter-level accuracy, ideal for precision tasks such as seed planting, fertilizer application, and autonomous vehicle guidance. Choosing between GNSS and RTK depends on the required spatial precision and operational needs of precision agriculture workflows.
Impact on Crop Yields: Accuracy and Productivity
RTK (Real-Time Kinematic) GNSS technology offers centimeter-level geolocation accuracy compared to standard GNSS systems, significantly enhancing precision in planting, fertilizing, and harvesting. This heightened accuracy reduces overlaps and gaps in field operations, directly improving crop yields by optimizing input use and minimizing resource waste. Precision agriculture leveraging RTK GNSS increases productivity through more efficient field management and precise application of agrochemicals, leading to better overall crop performance.
Integration with Precision Farming Technologies
GNSS provides essential geolocation capabilities with meter-level accuracy suitable for general field mapping, while RTK enhances this precision to centimeter-level accuracy critical for tasks like automated steering and variable rate application. RTK's real-time correction signals integrate seamlessly with precision farming technologies, enabling precise seed placement, fertilizer application, and crop monitoring. The integration of RTK with IoT sensors and farm management systems optimizes resource use and boosts overall crop yields by delivering highly accurate spatial data.
Future Trends: GNSS and RTK Advancements in Agriculture
Future trends in precision agriculture emphasize enhanced GNSS and RTK technologies to achieve centimeter-level geolocation accuracy, critical for optimizing crop management and resource use. The integration of multi-constellation GNSS with real-time kinematic corrections improves signal reliability and positioning precision, even in challenging environments. Advances in AI-driven data analysis and edge computing further accelerate decision-making processes based on high-accuracy location data, driving smarter and more efficient farming practices.
Related Important Terms
Centimeter-Level Positioning
RTK (Real-Time Kinematic) technology enhances GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) by providing centimeter-level positioning accuracy essential for precision agriculture. This high-precision geolocation enables precise field mapping, variable rate application, and automated machinery guidance, optimizing crop yields and resource efficiency.
Multi-Constellation GNSS
Multi-Constellation GNSS enhances geolocation accuracy in precision agriculture by utilizing multiple satellite systems such as GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and BeiDou, improving signal reliability and coverage. RTK further refines this accuracy to centimeter-level precision by applying real-time corrections from a base station, crucial for tasks like automated machinery guidance and variable rate applications.
Network RTK (NRTK)
Network RTK (NRTK) significantly enhances geolocation accuracy in precision agriculture by utilizing a network of base stations to provide real-time corrections, achieving centimeter-level precision compared to standalone GNSS systems. This technology reduces positional errors caused by atmospheric interference, enabling precise machinery guidance, optimized input application, and improved crop monitoring efficiency.
PPP-RTK (Precise Point Positioning RTK)
PPP-RTK combines Precise Point Positioning with Real-Time Kinematic corrections, enhancing geolocation accuracy beyond traditional GNSS methods by reducing reliance on local base stations and providing centimeter-level precision globally. This technology optimizes field-level decision making in precision agriculture through improved satellite signal correction, enabling highly accurate mapping and machinery guidance regardless of local infrastructure constraints.
GNSS Multipath Mitigation
GNSS multipath mitigation techniques significantly enhance geolocation accuracy by reducing signal reflections that interfere with satellite positioning, crucial for precision agriculture applications. While RTK offers centimeter-level accuracy through real-time corrections, advanced GNSS receivers with robust multipath suppression provide reliable positioning in challenging environments without the need for base stations.
Virtual Reference Station (VRS)
GNSS-based geolocation in precision agriculture offers meter-level accuracy, whereas RTK systems using Virtual Reference Stations (VRS) improve positioning precision to within centimeters by correcting GNSS signals in real-time. VRS technology leverages a network of base stations to provide localized corrections tailored to the user's exact location, optimizing field operations and enhancing yield management.
RTK Mobile Base Stations
RTK Mobile Base Stations enhance geolocation accuracy in precision agriculture by providing real-time corrections to GNSS signals, reducing positional errors to centimeter-level precision crucial for field operations. These mobile RTK stations offer flexibility and reliability over traditional GNSS alone, enabling precise machinery guidance and efficient resource management.
GNSS Correction Services
GNSS correction services enhance geolocation accuracy by providing real-time data adjustments to raw satellite signals, significantly reducing positioning errors in precision agriculture. While RTK offers centimeter-level precision using local base stations, GNSS correction services such as SBAS and PPP provide scalable and reliable positioning across vast agricultural areas without the need for extensive ground infrastructure.
Satellite-Based Augmentation System (SBAS)
Satellite-Based Augmentation System (SBAS) enhances GNSS accuracy by providing correction signals, achieving meter-level precision beneficial for broad-field applications. RTK offers centimeter-level geolocation accuracy through real-time correction from a base station, ideal for tasks demanding high precision but limited by a shorter effective range compared to SBAS.
Convergence Time (in RTK vs. GNSS)
RTK technology significantly reduces convergence time compared to standard GNSS, achieving centimeter-level geolocation accuracy within seconds to a few minutes. This rapid convergence enables real-time precision in agricultural applications, enhancing field mapping and automated guidance systems efficiency.
GNSS vs RTK for geolocation accuracy Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com