UAV imagery offers higher spatial resolution and greater flexibility in capturing real-time crop data compared to satellite imagery, enabling precise monitoring of plant health and stress patterns. Satellite imagery covers larger areas with frequent revisit times but often suffers from lower resolution and cloud cover interference, limiting detailed crop analysis. Integrating both UAV and satellite imagery enhances precision agriculture by providing comprehensive insights into crop conditions for optimized management decisions.
Table of Comparison
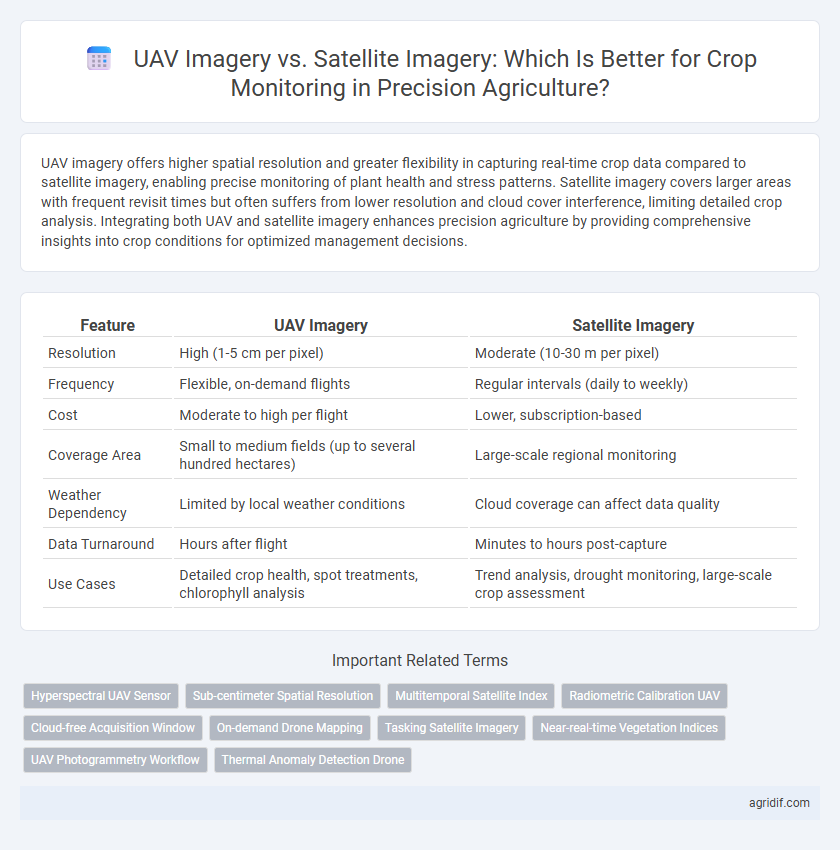
| Feature | UAV Imagery | Satellite Imagery |
|---|---|---|
| Resolution | High (1-5 cm per pixel) | Moderate (10-30 m per pixel) |
| Frequency | Flexible, on-demand flights | Regular intervals (daily to weekly) |
| Cost | Moderate to high per flight | Lower, subscription-based |
| Coverage Area | Small to medium fields (up to several hundred hectares) | Large-scale regional monitoring |
| Weather Dependency | Limited by local weather conditions | Cloud coverage can affect data quality |
| Data Turnaround | Hours after flight | Minutes to hours post-capture |
| Use Cases | Detailed crop health, spot treatments, chlorophyll analysis | Trend analysis, drought monitoring, large-scale crop assessment |
Introduction to Precision Agriculture and Remote Sensing
UAV imagery offers higher spatial resolution and real-time data for crop monitoring, enabling detailed analysis of plant health and stress at the field level. Satellite imagery provides broader coverage and frequent revisit times, making it ideal for monitoring large agricultural areas and temporal changes over growing seasons. Combining UAV and satellite data enhances precision agriculture by integrating fine-scale insights with comprehensive landscape-level monitoring through advanced remote sensing techniques.
Overview of UAV and Satellite Imagery Technologies
UAV imagery leverages high-resolution sensors mounted on drones to capture detailed, real-time aerial data critical for precision agriculture applications such as crop health assessment and stress detection. Satellite imagery employs multispectral and hyperspectral sensors on orbiting satellites, providing extensive coverage and consistent temporal datasets essential for large-scale crop monitoring and analysis. Both technologies integrate advanced imaging sensors, but UAVs offer greater spatial resolution and flexibility, while satellite platforms deliver broad-area insights with regular revisit intervals.
Resolution Differences: UAV vs. Satellite Imagery
UAV imagery offers significantly higher spatial resolution, often capturing details at centimeter-level accuracy, compared to satellite imagery which typically ranges from several meters to tens of meters per pixel. This enhanced resolution of UAVs enables precise detection of crop stress, pest infestations, and nutrient deficiencies at early stages. Satellite imagery provides broader coverage and frequent revisit times but lacks the fine-scale detail essential for targeted interventions in precision agriculture.
Data Acquisition Frequency and Timeliness
UAV imagery offers high-frequency data acquisition with the ability to capture real-time, high-resolution images tailored to specific fields, enabling prompt decision-making in crop monitoring. Satellite imagery, while providing broader coverage, often has lower revisit rates and may face delays due to weather conditions, reducing the timeliness of data availability. Frequent UAV flights enhance precision agriculture by delivering timely insights critical for early stress detection and targeted interventions.
Cost Comparison: UAV Imagery vs. Satellite Imagery
UAV imagery offers high-resolution data at a relatively low operational cost, making it ideal for localized crop monitoring with frequent data captures. Satellite imagery, while providing extensive coverage over large agricultural areas, generally incurs higher costs linked to data purchase and lower revisit frequencies. Cost efficiency depends on farm size, with UAVs preferred for small to medium plots and satellites better suited for large-scale agricultural monitoring.
Coverage Area and Scalability Considerations
UAV imagery provides high-resolution, detailed crop data ideal for small to medium-sized farms but is limited by battery life and flight time, restricting coverage area and scalability. Satellite imagery covers extensive agricultural regions efficiently, enabling large-scale crop monitoring with frequent revisit times, though at lower spatial resolution compared to UAVs. Choosing between UAV and satellite imagery depends on specific farm size, required data detail, and scalability needs.
Image Processing and Data Analysis Capabilities
UAV imagery offers higher spatial resolution and more frequent data acquisition, enabling detailed crop health assessment and precise detection of stress factors. Advanced image processing techniques, such as multispectral and hyperspectral analysis, leverage UAV data to generate actionable insights with lower latency compared to satellite imagery. While satellite imagery provides broader coverage and historical data trends, UAVs excel in fine-scale data analysis and real-time decision support for precision agriculture.
Weather and Environmental Impact on Image Quality
UAV imagery offers higher resolution and flexibility in crop monitoring but is more susceptible to weather conditions such as wind, rain, and cloud cover, which can hinder flight stability and image clarity. Satellite imagery, while less affected by local weather due to consistent orbital paths, can suffer from atmospheric disturbances like haze or cloud cover that obscure ground details and reduce image quality. Environmental factors including sunlight angle, seasonal changes, and soil moisture also influence both UAV and satellite image accuracy, impacting precise analysis in precision agriculture.
Regulatory and Logistical Challenges
UAV imagery offers high-resolution data crucial for precise crop monitoring but faces stringent regulatory restrictions including flight permissions and altitude limits imposed by aviation authorities. Satellite imagery, while offering broader coverage and fewer flight restrictions, often suffers from lower resolution and cloud cover interference that can delay timely agricultural analysis. The logistical challenges of UAV deployment involve operator training and maintenance, whereas satellite imaging requires access to specialized platforms and can incur higher data acquisition delays.
Choosing the Right Solution for Crop Monitoring
UAV imagery offers high-resolution, real-time data ideal for detailed crop stress detection and variable rate application, while satellite imagery provides broader coverage with frequent revisits suitable for monitoring large-scale fields and long-term trends. Selecting the right solution depends on field size, required spatial resolution, budget constraints, and data processing capabilities. Integrating UAV and satellite imagery can enhance precision agriculture by combining detailed local insights with extensive regional monitoring.
Related Important Terms
Hyperspectral UAV Sensor
Hyperspectral UAV sensors provide higher spatial and spectral resolution compared to satellite imagery, enabling precise detection of crop stress, nutrient deficiencies, and disease at an early stage. UAV-based hyperspectral imaging offers flexible deployment and real-time data acquisition, enhancing targeted crop management and optimizing yield prediction accuracy.
Sub-centimeter Spatial Resolution
UAV imagery offers sub-centimeter spatial resolution, enabling highly detailed crop monitoring and precise identification of plant health issues, pest infestations, and nutrient deficiencies. In contrast, satellite imagery typically provides lower spatial resolution, limiting its effectiveness for detecting fine-scale variations critical for precision agriculture decision-making.
Multitemporal Satellite Index
Multitemporal satellite index analysis enables consistent monitoring of crop health and phenology changes over time through high-frequency image capture, offering scalable coverage for large agricultural fields that UAV imagery struggles to match. Satellite imagery provides reliable data for tracking vegetation indices such as NDVI across multiple growth stages, facilitating precise decision-making in precision agriculture by detecting stress patterns and optimizing input applications.
Radiometric Calibration UAV
Radiometric calibration of UAV imagery enhances data accuracy by correcting sensor and atmospheric distortions, enabling precise vegetation health assessments compared to satellite imagery which often lacks such fine calibration due to lower revisit rates and variable atmospheric conditions. This calibration ensures consistent reflectance values critical for monitoring crop stress, nutrient levels, and growth patterns, providing farmers with actionable insights for optimizing yield and resource management.
Cloud-free Acquisition Window
UAV imagery provides high-resolution, cloud-free acquisition windows critical for timely crop monitoring, enabling precise analysis of plant health and stress within localized fields. Satellite imagery often faces limitations due to cloud cover, causing delays and reducing the reliability of continuous data essential for dynamic agricultural decision-making.
On-demand Drone Mapping
On-demand drone mapping using UAV imagery offers higher-resolution, real-time data for precise crop monitoring compared to satellite imagery, enabling farmers to detect stress, pests, and nutrient deficiencies at a field scale. While satellite imagery provides broader coverage, UAVs deliver customizable flight paths and immediate data acquisition that significantly enhances decision-making in precision agriculture.
Tasking Satellite Imagery
Tasking satellite imagery for crop monitoring in precision agriculture enables targeted, high-frequency data collection over large fields with customizable revisit schedules to capture critical growth stages. Unlike UAV imagery, satellite tasking provides consistent spectral bands and automated data delivery, optimizing crop health assessments and timely decision-making.
Near-real-time Vegetation Indices
UAV imagery offers higher spatial resolution and more frequent data acquisition than satellite imagery, enabling near-real-time vegetation indices for precise crop health monitoring. Satellite imagery provides broader coverage and consistent temporal data but often lacks the granularity and immediacy needed for timely decision-making in precision agriculture.
UAV Photogrammetry Workflow
UAV photogrammetry workflow for crop monitoring provides high-resolution, timely, and precise data collection through drone-captured multispectral and RGB images, enabling detailed analysis of plant health, growth patterns, and stress detection. Compared to satellite imagery, UAV-based monitoring offers greater spatial accuracy and flexibility in data acquisition schedules, enhancing precision agriculture decision-making processes.
Thermal Anomaly Detection Drone
UAV imagery offers higher spatial and temporal resolution compared to satellite imagery, enabling precise thermal anomaly detection for early identification of crop stress and irrigation issues. Thermal anomaly detection drones provide real-time, detailed temperature data crucial for optimizing water management and improving crop yield predictions.
UAV Imagery vs Satellite Imagery for crop monitoring Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com