Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) GPS delivers centimeter-level accuracy for field mapping, enabling precise data collection and enhanced decision-making in precision agriculture. Standard GPS provides meter-level accuracy, which may suffice for general mapping but lacks the precision needed for detailed variable-rate applications. Employing RTK GPS improves spatial data quality, optimizing resource use and crop management efficiency.
Table of Comparison
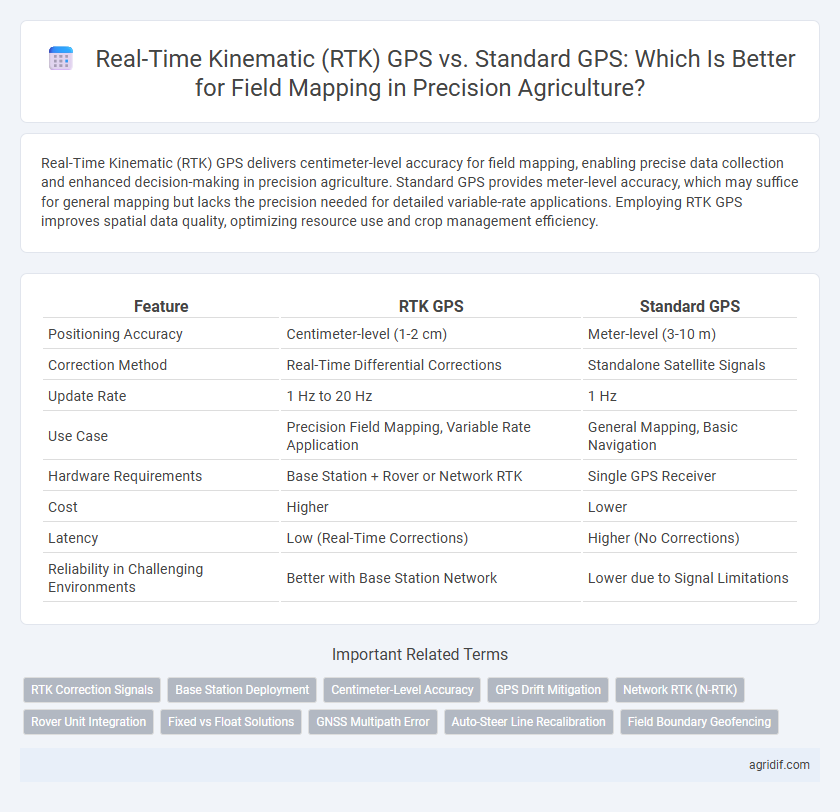
| Feature | RTK GPS | Standard GPS |
|---|---|---|
| Positioning Accuracy | Centimeter-level (1-2 cm) | Meter-level (3-10 m) |
| Correction Method | Real-Time Differential Corrections | Standalone Satellite Signals |
| Update Rate | 1 Hz to 20 Hz | 1 Hz |
| Use Case | Precision Field Mapping, Variable Rate Application | General Mapping, Basic Navigation |
| Hardware Requirements | Base Station + Rover or Network RTK | Single GPS Receiver |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Latency | Low (Real-Time Corrections) | Higher (No Corrections) |
| Reliability in Challenging Environments | Better with Base Station Network | Lower due to Signal Limitations |
Introduction: The Role of GPS in Precision Agriculture
Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) GPS offers centimeter-level accuracy for field mapping, significantly enhancing precision agriculture practices compared to standard GPS, which typically provides meter-level accuracy. This high-precision positioning enables optimized planting, fertilizing, and irrigation by accurately guiding machinery and reducing overlap or gaps in field coverage. Enhanced GPS accuracy directly contributes to increased crop yields, resource efficiency, and sustainable farming operations.
Understanding Standard GPS Technology for Field Mapping
Standard GPS technology for field mapping provides geospatial data with accuracy typically within 3 to 10 meters, which is sufficient for general navigation but less effective for precise agricultural applications. It relies on signals from multiple satellites to determine location but lacks the differential corrections available in Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) GPS, resulting in greater positional errors. This level of accuracy may limit the effectiveness in tasks requiring fine-scale precision like planting or soil sampling in precision agriculture.
What is Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) GPS?
Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) GPS is an advanced satellite navigation technology that enhances the precision of position data by using carrier-based ranging and a fixed base station to provide centimeter-level accuracy. Unlike standard GPS that offers meter-level accuracy, RTK GPS corrects signal errors in real time, making it critical for precise field mapping in precision agriculture. This high accuracy enables farmers to optimize planting, fertilizing, and harvesting, ultimately improving crop yield and resource management.
Accuracy Comparison: RTK GPS vs Standard GPS
Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) GPS offers centimeter-level accuracy by utilizing correction signals from a fixed base station, significantly outperforming standard GPS, which typically provides accuracy within several meters. This precision enables more detailed and reliable field mapping, crucial for site-specific farming practices and resource management. The high accuracy of RTK GPS reduces overlap and gaps in data collection, optimizing inputs like fertilizer and irrigation for enhanced crop yield.
Field Mapping Applications: Benefits and Limitations
Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) GPS provides centimeter-level accuracy in field mapping applications, significantly enhancing precision in crop monitoring and variable rate application compared to standard GPS, which typically offers meter-level accuracy. RTK facilitates accurate boundary delineation, efficient resource management, and improved yield predictions, while standard GPS may result in less precise data, potentially affecting decision-making and operational efficiency. Limitations of RTK include higher equipment costs, reliance on base stations or correction networks, and potential signal disruptions, whereas standard GPS offers broader accessibility and simpler setup but with reduced spatial accuracy.
Initial Setup and Operational Costs
Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) GPS offers centimeter-level accuracy for field mapping, requiring a more complex initial setup including base stations and communication systems, which increases upfront costs compared to Standard GPS. Standard GPS provides meter-level accuracy with simpler installation and lower initial expenses but may result in less precise data for precision agriculture applications. Operational costs for RTK include maintenance of base stations and subscription services, whereas Standard GPS generally incurs minimal ongoing costs.
Signal Stability and Reliability in Agricultural Environments
Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) GPS offers centimeter-level accuracy with superior signal stability compared to standard GPS, crucial for precision agriculture field mapping. RTK's use of correction signals from base stations enhances reliability, minimizing positional errors caused by environmental factors like tree cover and uneven terrain. Standard GPS, while more broadly available, often suffers from fluctuations and signal interference, leading to less consistent data critical to optimizing crop management and resource use.
Impact on Yield Monitoring and Data Collection
Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) GPS offers centimeter-level accuracy compared to the meter-level precision of standard GPS, significantly enhancing yield monitoring and data collection in precision agriculture. RTK GPS enables precise field mapping, allowing for accurate placement of sensors and sampling points, which leads to more reliable yield data and better-informed decision-making. This improved spatial resolution reduces errors in yield variability analysis and optimizes resource allocation for increased crop productivity.
User Experience: Ease of Integration and Scalability
Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) GPS offers superior accuracy down to centimeter-level precision, significantly enhancing field mapping for precision agriculture compared to standard GPS, which typically provides meter-level accuracy. RTK systems integrate seamlessly with existing agricultural equipment through modular hardware and software compatible with various farming platforms, facilitating ease of use and minimal learning curves. Scalability is achieved as RTK networks can expand coverage across larger fields by leveraging mobile base stations or satellite corrections, ensuring consistent, high-precision data collection as farm operations grow.
Choosing the Right GPS Solution for Your Farm
RTK GPS offers centimeter-level accuracy by utilizing a fixed base station and real-time corrections, making it ideal for precision field mapping and automated machinery guidance. Standard GPS provides meter-level accuracy sufficient for general field mapping but lacks the precision needed for tasks requiring exact positioning. Investing in RTK GPS ensures optimized crop management, reduced input costs, and enhanced yield by enabling precise planting, fertilizing, and harvesting decisions.
Related Important Terms
RTK Correction Signals
Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) GPS provides centimeter-level accuracy for field mapping by using correction signals from base stations, significantly enhancing precision compared to Standard GPS, which typically offers meter-level accuracy. RTK correction signals reduce positioning errors caused by satellite timing and atmospheric delays, enabling more reliable and precise data collection essential for optimizing agricultural inputs and improving crop yields.
Base Station Deployment
Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) GPS offers centimeter-level accuracy in field mapping through the use of a fixed base station that transmits correction signals to rovers, significantly enhancing positional precision compared to standard GPS, which typically provides meter-level accuracy without correction support. Strategic deployment of the base station within proximity to the agricultural site ensures minimal signal latency and maximizes correction effectiveness, critical for precise variable rate applications and soil sampling in precision agriculture.
Centimeter-Level Accuracy
Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) GPS provides centimeter-level accuracy by using satellite corrections and base stations, significantly enhancing field mapping precision compared to standard GPS, which typically offers meter-level accuracy. This high precision allows for more efficient resource management and improved crop yield optimization in precision agriculture.
GPS Drift Mitigation
Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) GPS enhances field mapping precision by reducing GPS drift to centimeter-level accuracy through real-time corrections from base stations, outperforming Standard GPS which typically exhibits meter-level positional errors due to satellite signal delays and atmospheric interference. This drift mitigation enables precise crop monitoring, variable rate applications, and efficient resource management in precision agriculture.
Network RTK (N-RTK)
Network RTK (N-RTK) enhances field mapping accuracy in precision agriculture by providing centimeter-level positioning through a network of base stations, outperforming standard GPS, which typically offers meter-level precision. This increased accuracy enables precise seed planting, fertilization, and pesticide application, optimizing crop yields and reducing resource waste.
Rover Unit Integration
Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) GPS offers centimeter-level accuracy for field mapping through seamless integration with rover units, enabling precise positioning and improved data reliability compared to standard GPS systems, which typically provide meter-level accuracy. Rover units equipped with RTK capabilities enhance precision agriculture by facilitating accurate planting, fertilizing, and harvesting operations, ultimately optimizing crop yield and resource management.
Fixed vs Float Solutions
Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) GPS offers fixed solutions with centimeter-level accuracy by correcting signal errors through a base station, outperforming standard GPS that typically provides float solutions with meter-level precision due to satellite signal variability. Fixed RTK solutions enable highly accurate field mapping essential for precise planting and resource management, while float solutions are less reliable for detailed applications requiring exact positioning.
GNSS Multipath Error
Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) GPS significantly reduces GNSS multipath error by providing centimeter-level accuracy through real-time correction signals, enhancing precise field mapping in precision agriculture. Standard GPS suffers from multipath distortions caused by signal reflections, resulting in meter-level inaccuracies that limit the effectiveness of agricultural decision-making based on spatial data.
Auto-Steer Line Recalibration
Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) GPS enhances field mapping accuracy by providing centimeter-level precision, crucial for Auto-Steer systems to recalibrate steering lines dynamically, minimizing overlaps and gaps during planting and harvesting. Standard GPS, offering meter-level accuracy, often leads to less precise Auto-Steer recalibrations, resulting in decreased efficiency and potential yield loss.
Field Boundary Geofencing
Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) GPS provides centimeter-level accuracy for field boundary geofencing, significantly reducing errors compared to standard GPS, which typically offers meter-level precision. This enhanced accuracy enables precise field demarcation, optimizing field management and minimizing crop overlap or missed areas during planting and harvesting.
Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) GPS vs Standard GPS for field mapping Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com