Autonomous tractor guidance enhances planting accuracy by using GPS and sensor technologies to maintain precise row spacing and depth, reducing seed waste and improving crop yields. Compared to manual steering, this technology minimizes operator fatigue and human error, ensuring consistent planting even in challenging field conditions. The integration of real-time data analytics further optimizes planting operations, leading to increased efficiency and cost savings in precision agriculture.
Table of Comparison
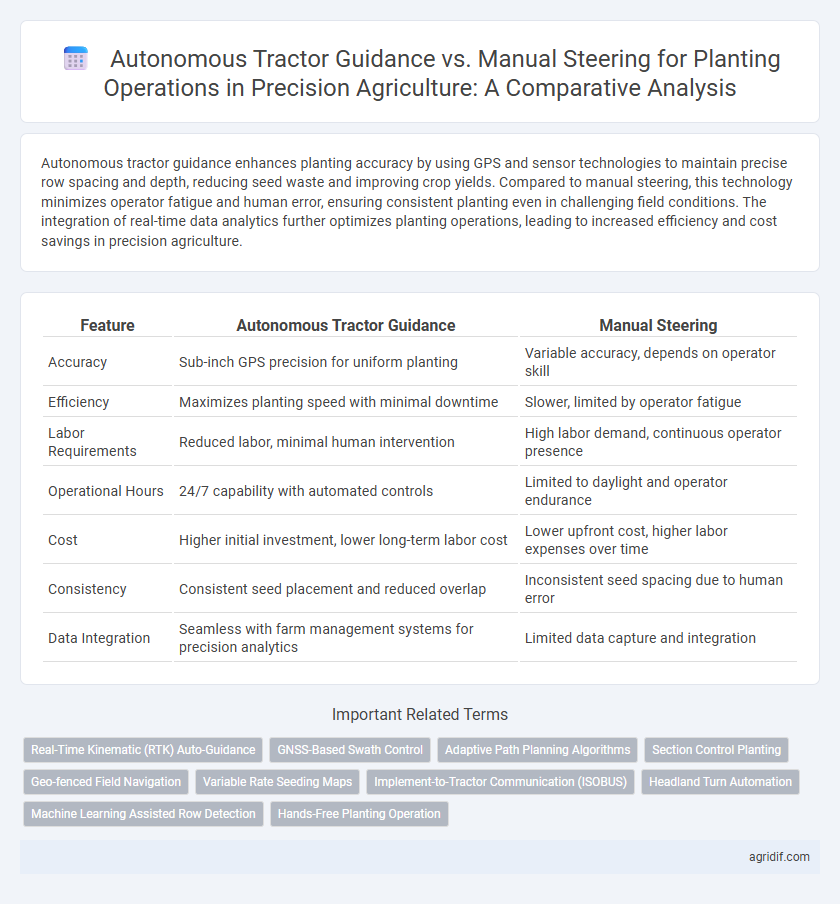
| Feature | Autonomous Tractor Guidance | Manual Steering |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Sub-inch GPS precision for uniform planting | Variable accuracy, depends on operator skill |
| Efficiency | Maximizes planting speed with minimal downtime | Slower, limited by operator fatigue |
| Labor Requirements | Reduced labor, minimal human intervention | High labor demand, continuous operator presence |
| Operational Hours | 24/7 capability with automated controls | Limited to daylight and operator endurance |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, lower long-term labor cost | Lower upfront cost, higher labor expenses over time |
| Consistency | Consistent seed placement and reduced overlap | Inconsistent seed spacing due to human error |
| Data Integration | Seamless with farm management systems for precision analytics | Limited data capture and integration |
Introduction to Precision Agriculture in Planting Operations
Autonomous tractor guidance in planting operations significantly enhances seed placement accuracy and optimizes field efficiency compared to manual steering. Precision agriculture utilizes GPS, sensors, and real-time data to automate steering, reducing human error and improving crop uniformity. Improved operational precision directly contributes to higher yields and lower input costs in modern planting practices.
Overview of Autonomous Tractor Guidance Systems
Autonomous tractor guidance systems use GPS and advanced sensors to enable precise, automated control during planting operations, significantly reducing human error and increasing efficiency. These systems integrate real-time data analytics and machine learning to adapt to field variability, optimizing seed placement and minimizing overlap. Compared to manual steering, autonomous guidance improves accuracy and consistency, leading to higher crop yields and reduced operational costs.
Manual Steering: Traditional Approach in Field Planting
Manual steering in planting operations relies on the operator's skill to guide tractors accurately along field rows, often resulting in variability and increased fatigue. This traditional approach lacks the precision of autonomous tractor guidance systems, leading to potential overlaps or gaps that can affect seed placement uniformity. Despite its widespread use, manual steering limits efficiency and consistency compared to GPS-based automated solutions in precision agriculture.
Accuracy and Consistency: Comparing Planting Results
Autonomous tractor guidance significantly enhances planting accuracy by utilizing GPS-based systems that maintain precise row spacing and seed placement, reducing human error inherent in manual steering. Studies show autonomous systems improve consistency in seed depth and distribution, leading to uniform crop emergence and higher yields. In contrast, manual steering often results in variable spacing and seed depth, which can cause uneven germination and lower overall planting efficiency.
Efficiency and Productivity Gains with Autonomous Tractors
Autonomous tractor guidance systems significantly enhance planting efficiency by enabling precise, consistent row alignment and optimal seed placement, reducing overlaps and gaps compared to manual steering. These systems increase productivity through continuous operation without operator fatigue, allowing longer working hours and faster field coverage. Data-driven adjustments from GPS and sensor inputs ensure higher accuracy, minimizing input waste and maximizing crop yield potential.
Labor Requirements: Automation vs Manual Operation
Autonomous tractor guidance significantly reduces labor requirements by enabling continuous, hands-free planting operations, which minimizes operator fatigue and increases operational efficiency. Manual steering demands constant human attention and skill, leading to higher labor costs and potential for human error during planting. Implementing automated guidance systems improves planting precision while optimizing workforce allocation in agricultural operations.
Cost Implications: Initial Investment and Long-Term Savings
Autonomous tractor guidance systems require a significant initial investment, often ranging from $20,000 to $50,000 for equipment and software integration, compared to minimal startup costs for manual steering. Long-term savings arise from reduced labor costs, increased planting accuracy, and optimized field operations, potentially boosting yield and cutting input waste by up to 15%. Over time, these efficiency gains offset the upfront expenses, making autonomous guidance a cost-effective choice for large-scale planting operations.
Impact on Crop Yields and Resource Utilization
Autonomous tractor guidance significantly enhances planting precision, resulting in optimized seed placement and uniform crop emergence that boosts overall crop yields by up to 15% compared to manual steering. Improved accuracy reduces seed overlap and skips, leading to more efficient use of seeds and fertilizers, thereby minimizing waste and lowering input costs. Enhanced operational consistency also conserves fuel and labor resources, increasing sustainability and profitability in planting operations.
Challenges and Limitations of Autonomous Tractor Guidance
Autonomous tractor guidance in planting operations faces challenges such as GPS signal interference, which can lead to reduced accuracy and inconsistent row spacing. Limitations include the high initial cost of technology integration and the need for specialized skills to manage and troubleshoot automated systems. Environmental factors like uneven terrain and unexpected obstacles further complicate autonomous navigation compared to manual steering.
Future Trends: Evolving Technologies in Tractor Guidance
Autonomous tractor guidance systems integrate advanced GPS, machine learning algorithms, and real-time sensor data to enhance planting accuracy and efficiency beyond manual steering capabilities. Future trends emphasize the development of AI-driven predictive analytics and enhanced connectivity through IoT, enabling tractors to adapt dynamically to field conditions and optimize seed placement. These evolving technologies promise to reduce operator fatigue, increase productivity, and support sustainable farming practices through precise resource management.
Related Important Terms
Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) Auto-Guidance
Autonomous tractor guidance using Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) auto-guidance achieves centimeter-level accuracy in planting operations, significantly reducing overlaps and missed rows compared to manual steering. This precision enhances seed placement uniformity, optimizes input use, and increases overall crop yield efficiency.
GNSS-Based Swath Control
GNSS-based swath control in autonomous tractor guidance significantly enhances planting accuracy by minimizing overlap and gaps between passes, leading to optimized seed placement and resource use. Manual steering lacks the precision of satellite-guided systems, resulting in increased operator fatigue and inconsistent coverage that can reduce overall crop yield efficiency.
Adaptive Path Planning Algorithms
Adaptive path planning algorithms in autonomous tractor guidance significantly enhance planting operations by optimizing route efficiency, reducing overlap, and minimizing soil compaction compared to manual steering. These algorithms dynamically adjust trajectories based on real-time field data, ensuring precise seed placement and improved crop yields.
Section Control Planting
Autonomous tractor guidance systems with section control planting optimize seed placement by automatically shutting off planting units when entering previously planted zones, significantly reducing seed overlap and input waste compared to manual steering. This technology enhances planting accuracy, improves crop uniformity, and increases operational efficiency by leveraging GPS and sensor data for precise in-field navigation.
Geo-fenced Field Navigation
Autonomous tractor guidance utilizing geo-fenced field navigation enhances planting accuracy by maintaining precise paths within predefined boundaries, reducing soil compaction and overlap. Manual steering lacks the consistency and spatial data integration of autonomous systems, often resulting in inefficient coverage and increased operator fatigue.
Variable Rate Seeding Maps
Autonomous tractor guidance systems utilize GPS and real-time data to follow Variable Rate Seeding Maps with high precision, optimizing seed placement and improving crop uniformity compared to manual steering. This technology reduces human error and enhances efficiency by automatically adjusting seeding rates based on soil variability and field conditions, leading to increased yield potential and cost savings.
Implement-to-Tractor Communication (ISOBUS)
Autonomous tractor guidance systems integrated with ISOBUS enable seamless Implement-to-Tractor communication, optimizing planting accuracy and operational efficiency compared to manual steering. This technology enhances real-time data exchange, ensuring precise control of planting depth, spacing, and rate, resulting in improved crop yields and reduced operator fatigue.
Headland Turn Automation
Autonomous tractor guidance systems enhance planting efficiency by automating headland turn maneuvers, reducing operator fatigue and maintaining consistent seed placement. In contrast, manual steering requires constant driver input, increasing variability in turn precision and potentially impacting overall field productivity.
Machine Learning Assisted Row Detection
Machine learning-assisted row detection in autonomous tractor guidance enhances planting accuracy by dynamically identifying crop rows in real-time, reducing human error and increasing operational efficiency compared to manual steering. This technology leverages advanced sensors and computer vision algorithms to adapt to varying field conditions, thereby optimizing seed placement and crop yield potential.
Hands-Free Planting Operation
Autonomous tractor guidance enables hands-free planting operations by utilizing advanced GPS and sensor technology to maintain precise row alignment and optimal seed placement, significantly reducing operator fatigue and human error. Compared to manual steering, this technology enhances planting accuracy, increases efficiency, and supports consistent field coverage, leading to higher crop yields and resource savings.
Autonomous Tractor Guidance vs Manual Steering for planting operations Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com