Stifling and reeling are two essential methods for cocoon processing in sericulture, each impacting silk quality differently. Stifling involves killing the pupa inside the cocoon by heat, preventing damage from emerging moths but potentially weakening fiber strength. Reeling extracts silk filaments from intact cocoons, preserving fiber continuity and resulting in finer and higher-quality silk threads ideal for textile production.
Table of Comparison
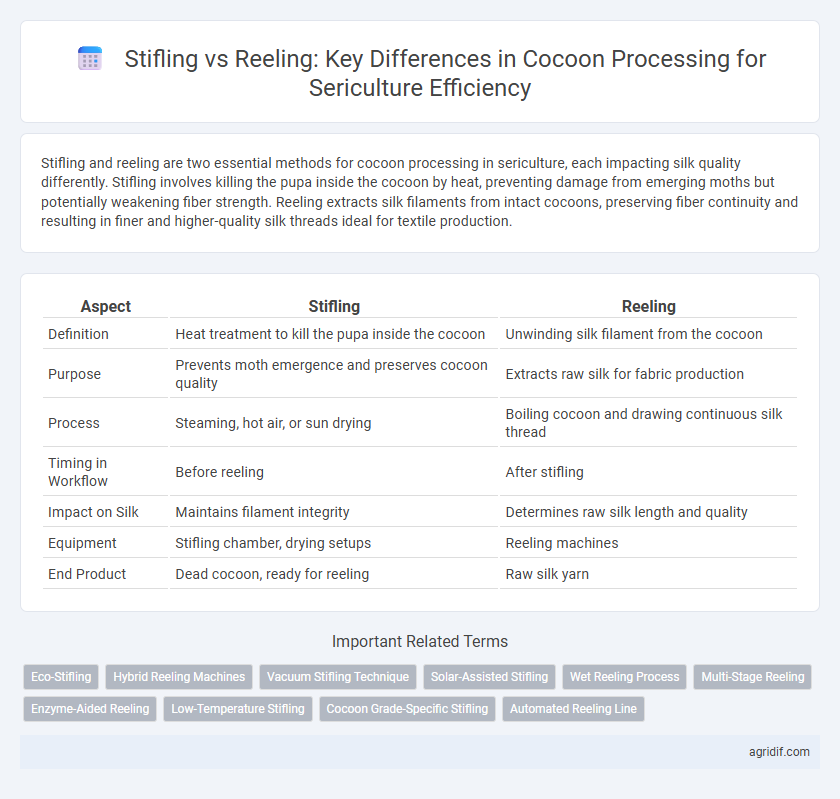
| Aspect | Stifling | Reeling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Heat treatment to kill the pupa inside the cocoon | Unwinding silk filament from the cocoon |
| Purpose | Prevents moth emergence and preserves cocoon quality | Extracts raw silk for fabric production |
| Process | Steaming, hot air, or sun drying | Boiling cocoon and drawing continuous silk thread |
| Timing in Workflow | Before reeling | After stifling |
| Impact on Silk | Maintains filament integrity | Determines raw silk length and quality |
| Equipment | Stifling chamber, drying setups | Reeling machines |
| End Product | Dead cocoon, ready for reeling | Raw silk yarn |
Understanding Stifling and Reeling in Sericulture
Stifling in sericulture involves killing the pupa inside the cocoon by applying heat, typically through hot air, steam, or boiling water, to preserve cocoon quality and prevent moth emergence. Reeling is the process of unwinding the silk filament from the stifled cocoon, requiring precise handling to maintain filament length and strength, which directly impacts the quality of raw silk. Effective stifling and controlled reeling are critical steps that influence fiber uniformity, silk yield, and downstream textile production in sericulture.
Key Differences Between Stifling and Reeling Methods
Stifling involves exposing cocoons to heat or chemicals to kill the pupae and preserve the silk quality, while reeling is the process of unwinding silk filaments from the cocoon to produce raw silk threads. Stifling primarily focuses on ensuring pupae termination to prevent damage to the silk, whereas reeling emphasizes the careful extraction of continuous silk fibers to maintain thread strength and uniformity. Key differences include the purpose--stifling for preservation and pest control, reeling for silk extraction--and their sequential roles in sericulture processing.
Importance of Cocoon Processing in Silk Production
Cocoon processing is crucial in sericulture, where stifling and reeling serve distinct roles to ensure high-quality silk fibers. Stifling involves killing the pupae to prevent damage to the silk filament, preserving the cocoon's integrity, while reeling extracts continuous silk threads essential for weaving fine textiles. Efficient cocoon processing directly impacts the filament length, tensile strength, and overall silk yield, underscoring its importance in producing premium silk products.
Traditional vs Modern Techniques in Cocoon Handling
Traditional stifling techniques involve exposing cocoons to hot air or steam to kill pupae, preserving filament quality but often resulting in inconsistent fiber strength. Modern stifling uses controlled temperature and humidity chambers, enhancing cocoon freshness and preventing filament damage for higher silk yield. Reeling advances with mechanized reeling machines ensure uniform filament extraction, while traditional hand-reeling requires skilled labor and yields variable filament length and thickness.
Step-by-Step Guide to Stifling Silk Cocoons
Stifling silk cocoons involves killing the pupae inside to preserve the quality of silk fibers by exposing them to heat, typically through sun drying, hot air, or steam. After collecting cocoons in batches, sericulturists arrange them on trays or racks and apply controlled heat for several hours to halt pupal development without damaging the cocoon structure. This step-by-step stifling process ensures easy unwinding during reeling while maintaining the tensile strength and luster of raw silk threads.
Essential Equipment for Cocoon Reeling
Essential equipment for cocoon reeling includes a stifling chamber for precise temperature control, which ensures the cocoons are dried adequately to prevent premature pupal development. Reeling machines with adjustable tension systems and high-speed spinning reels are crucial to efficiently unwind the delicate silk fibers without breakage. Proper water tanks and motorized reeling frames facilitate consistent silk filament extraction, optimizing fiber quality for textile production.
Impact of Stifling on Silk Yarn Quality
Stifling involves killing silkworm pupae by heat or chemicals before reeling, significantly affecting silk yarn quality by altering fiber strength and texture. Heat stifling methods preserve fiber length and tensile strength better than chemical methods, which may introduce impurities and weaken the silk threads. Proper stifling ensures easier cocoon unwinding but requires careful control to maintain optimal silk luster, smoothness, and durability in the final yarn.
Reeling Process: Techniques and Best Practices
Reeling is a critical process in sericulture that involves unwinding silk filament from the stifled cocoons, requiring precise temperature and humidity control to maintain filament strength and quality. Techniques include boiling the cocoons in water to loosen the sericin, careful handling to prevent filament breakage, and using mechanical reeling devices for consistent yarn thickness. Best practices emphasize maintaining optimal water temperature around 70-80degC, continuous monitoring of filament tension, and employing skilled operators to ensure high-quality silk thread production.
Challenges Faced in Stifling and Reeling Operations
Stifling in sericulture presents challenges such as achieving uniform temperature control to prevent premature pupal development and minimizing damage to the delicate silk fibers, which affects cocoon quality. Reeling operations often face difficulties in handling fragile cocoons without causing filament breakage, maintaining consistent filament tension, and optimizing water temperature for smooth unwinding. Both processes demand precision and careful monitoring to ensure high-quality silk production and reduce material loss.
Innovations and Future Trends in Cocoon Processing
Innovations in stifling techniques, such as controlled atmosphere stifling and low-temperature drying, enhance cocoon quality by minimizing damage and preserving sericin content. Advances in automated reeling machines equipped with sensors and AI algorithms optimize silk filament extraction, increasing yield and uniformity. Future trends focus on integrating sustainable energy sources and IoT-enabled smart processing systems to improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact in cocoon processing.
Related Important Terms
Eco-Stifling
Eco-Stifling in sericulture involves using solar or natural heat methods to kill silkworm pupae within cocoons, preserving cocoon quality while reducing environmental impact. This green alternative to traditional stifling enhances silk filament length and strength, contributing to sustainable silk production and lower carbon emissions.
Hybrid Reeling Machines
Hybrid reeling machines enhance cocoon processing by combining the efficiency of traditional stifling methods with advanced automated reeling techniques, resulting in higher silk filament strength and reduced fiber breakage. These machines optimize filament extraction by precisely controlling temperature and tension during reeling, improving raw silk quality and boosting overall productivity in sericulture operations.
Vacuum Stifling Technique
Vacuum stifling technique enhances sericulture by efficiently killing pupae inside cocoons without damaging silk fibers, maintaining high filament quality compared to traditional heat-based stifling. This method reduces moisture content and microbial growth, improving reelability and resulting in superior silk reeling performance.
Solar-Assisted Stifling
Solar-assisted stifling harnesses solar energy to effectively kill pupae inside silkworm cocoons, preserving filament quality while reducing environmental impact and energy consumption compared to conventional stifling methods. This eco-friendly approach enhances reelability by maintaining optimal moisture levels and minimizing filament breakage during the subsequent reeling process.
Wet Reeling Process
Wet reeling is a cocoon processing technique used in sericulture where softened cocoons are unwound in hot water to extract continuous raw silk fibers with minimal damage, preserving the fiber's strength and gloss. This method contrasts with stifling, which kills the pupa through heat or chemicals before reeling, often leading to lower silk quality and shorter fiber lengths.
Multi-Stage Reeling
Multi-stage reeling enhances silk filament extraction by progressively unwinding cocoons through a series of calibrated tension adjustments, improving fiber uniformity and reducing breakage compared to traditional stifling methods that kill pupae via heat or chemicals before reeling. This advanced reeling technique increases raw silk yield and quality, supporting sustainable sericulture practices by optimizing filament length and strength.
Enzyme-Aided Reeling
Enzyme-aided reeling enhances silk extraction from cocoons by softening sericin proteins, improving filament integrity and reelability compared to traditional stifling methods that rely on heat or chemical treatment to kill pupae. This biological approach reduces fiber breakage and increases silk yield, making it a more efficient and sustainable process in sericulture.
Low-Temperature Stifling
Low-temperature stifling preserves the delicate fibroin structure of cocoons by using temperatures typically below 60degC, minimizing fiber damage compared to high-temperature stifling. This method enhances silk quality during reeling by reducing filament breakage and maintaining tensile strength, leading to superior raw silk output in sericulture processing.
Cocoon Grade-Specific Stifling
Cocoon grade-specific stifling optimizes silk quality by applying precise temperature and duration controls tailored to the cocoon's grade, preventing premature pupal mortality and maintaining filament strength. This targeted approach enhances subsequent reeling efficiency, resulting in higher yield and superior raw silk texture compared to generic stifling methods.
Automated Reeling Line
Automated reeling lines enhance sericulture efficiency by precisely extracting silk threads from stifled cocoons, minimizing labor and maximizing fiber quality. Unlike stifling, which kills larvae by heat or chemical treatment, automated reeling ensures consistent thread tension and speeds, improving overall silk yield and reducing wastage.
Stifling vs Reeling for cocoon processing Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com