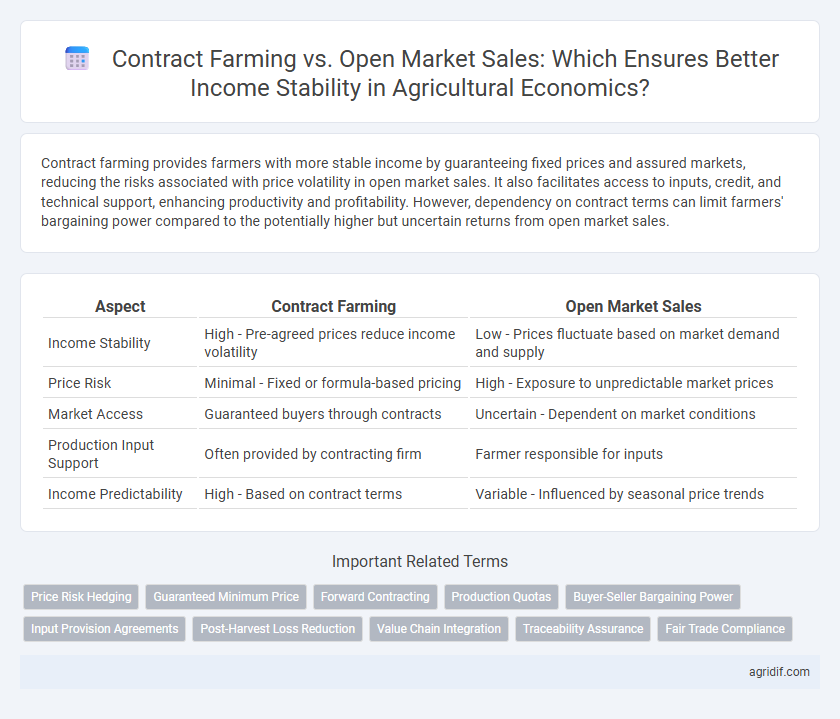
Contract farming provides farmers with more stable income by guaranteeing fixed prices and assured markets, reducing the risks associated with price volatility in open market sales. It also facilitates access to inputs, credit, and technical support, enhancing productivity and profitability. However, dependency on contract terms can limit farmers' bargaining power compared to the potentially higher but uncertain returns from open market sales.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Contract Farming | Open Market Sales |
|---|---|---|
| Income Stability | High - Pre-agreed prices reduce income volatility | Low - Prices fluctuate based on market demand and supply |
| Price Risk | Minimal - Fixed or formula-based pricing | High - Exposure to unpredictable market prices |
| Market Access | Guaranteed buyers through contracts | Uncertain - Dependent on market conditions |
| Production Input Support | Often provided by contracting firm | Farmer responsible for inputs |
| Income Predictability | High - Based on contract terms | Variable - Influenced by seasonal price trends |
Understanding Contract Farming: Definition and Mechanisms
Contract farming involves pre-agreed terms between farmers and buyers, ensuring fixed prices, input provisions, and technical support, contributing to income stability by reducing market uncertainties. This mechanism protects farmers from price volatility common in open market sales, where income fluctuates based on supply-demand dynamics and seasonal changes. By securing contractual agreements, farmers gain predictable revenue streams and improved access to resources, enhancing financial resilience in agricultural production.
Open Market Sales: Opportunities and Challenges
Open market sales offer farmers direct access to diverse buyers, enabling price negotiation and potential for higher income during favorable market conditions. However, this approach exposes farmers to price volatility and unpredictable demand, increasing income instability risks. Effective market information systems and risk management strategies are critical to maximize benefits and mitigate challenges in open market sales.
Income Stability in Contract Farming: Key Factors
Income stability in contract farming is primarily influenced by fixed pricing agreements, guaranteed market access, and risk-sharing mechanisms with buyers, reducing farmers' exposure to volatile market fluctuations. The presence of clear contract terms and timely payments further enhances income predictability for farmers. Empirical studies indicate that farmers engaged in contract farming often experience more consistent earnings compared to those relying solely on open market sales.
Income Volatility in Open Market Sales
Income volatility in open market sales poses significant risks for farmers due to fluctuating prices influenced by unpredictable demand and supply conditions. Contract farming offers income stability by providing predetermined prices and assured markets, reducing exposure to price shocks. Empirical studies indicate that contract farming mitigates income fluctuations and enhances financial security for smallholder farmers.
Price Risk Management: Contract Farming vs Open Market
Contract farming offers farmers a stable income by locking in prices through pre-agreed contracts, effectively reducing price volatility and market fluctuations. In contrast, open market sales expose farmers to significant price risk due to unpredictable demand and supply conditions, which can lead to income instability. The structured price risk management inherent in contract farming provides a financial safety net that is often absent in open market transactions.
Bargaining Power of Farmers in Different Marketing Systems
Contract farming often enhances farmers' bargaining power by providing guaranteed prices and access to inputs, reducing market uncertainties compared to open market sales. In open markets, farmers face greater price volatility and limited negotiation leverage due to asymmetric information and market fragmentation. Consequently, contract farming can lead to more stable income streams and improved financial planning for producers in agricultural economics.
Impact of Market Access and Infrastructure
Contract farming enhances income stability by providing guaranteed prices and consistent market access, reducing farmers' exposure to price volatility common in open market sales. Well-developed infrastructure, including transportation and storage facilities, improves market access, enabling farmers to meet contract conditions more efficiently and minimize post-harvest losses. In contrast, inadequate infrastructure in open markets often leads to unpredictable market access, limiting farmers' bargaining power and increasing income instability.
Role of Agribusiness Companies and Middlemen
Agribusiness companies in contract farming provide farmers with assured prices and input supplies, reducing income volatility compared to open market sales. Middlemen in open markets often exploit price fluctuations, leading to unstable farmer incomes and limited bargaining power. Reliable contracts foster financial security, while dependency on intermediaries can result in income uncertainty for small-scale producers.
Case Studies: Comparative Analysis of Farmer Incomes
Case studies in agricultural economics reveal that contract farming offers more predictable income streams for farmers compared to open market sales, reducing revenue volatility caused by price fluctuations and market uncertainties. Analysis of income data from multiple regions demonstrates that contract arrangements often include assured purchase agreements and pre-agreed prices, stabilizing farm earnings and improving financial planning. In contrast, open market sales expose farmers to price shocks and demand shifts, leading to inconsistent income and increased financial risk.
Policy Recommendations for Enhancing Income Stability
Implementing policy frameworks that promote contract farming can significantly enhance income stability by securing guaranteed prices and reducing market fluctuations for farmers. Encouraging cooperative contract negotiations and incorporating price adjustment clauses helps protect farmers against adverse market shocks. Supporting access to credit and technical assistance within contract farming arrangements further strengthens farmers' financial resilience and promotes sustainable agricultural livelihoods.
Related Important Terms
Price Risk Hedging
Contract farming provides farmers with predetermined prices, significantly reducing price volatility and ensuring more stable income compared to open market sales, where prices fluctuate unpredictably. By securing fixed agreements, contract farming acts as an effective price risk hedging mechanism, minimizing exposure to market uncertainties in agricultural economics.
Guaranteed Minimum Price
Contract farming provides income stability for farmers by ensuring a Guaranteed Minimum Price (GMP), reducing exposure to volatile market fluctuations typically experienced in open market sales. This price assurance fosters predictable revenue streams, enabling better financial planning and investment in sustainable agricultural practices.
Forward Contracting
Forward contracting in contract farming reduces income volatility by securing predetermined prices and quantities, providing farmers with financial predictability compared to open market sales. This mechanism mitigates risks associated with price fluctuations and market uncertainties, enhancing farmers' income stability and investment capacity.
Production Quotas
Production quotas in contract farming provide farmers with guaranteed income by locking in predetermined output levels and prices, reducing revenue volatility often seen in open market sales. This mechanism stabilizes income streams by ensuring consistent demand and mitigating risks associated with fluctuating market prices and unpredictable supply conditions.
Buyer-Seller Bargaining Power
Contract farming enhances income stability by reducing price volatility through pre-agreed terms, shifting significant bargaining power to buyers who secure supply and influence production decisions. Open market sales expose farmers to fluctuating prices and stronger buyer dominance during peak supply periods, often resulting in reduced farmer income stability and leverage.
Input Provision Agreements
Contract farming with input provision agreements ensures income stability by providing farmers guaranteed access to quality inputs like seeds and fertilizers at predetermined prices, reducing market uncertainties. Open market sales expose farmers to price volatility and input cost fluctuations, often resulting in inconsistent income streams and financial risks.
Post-Harvest Loss Reduction
Contract farming significantly reduces post-harvest losses by guaranteeing timely procurement and providing technical support, thereby enhancing income stability for farmers compared to open market sales, which are prone to price volatility and delayed transactions. Effective post-harvest management under contract farming ensures better quality preservation and market access, directly contributing to consistent and higher farm revenues.
Value Chain Integration
Contract farming enhances income stability by securing predetermined prices and input supplies, integrating farmers directly into the value chain, reducing market volatility risks. Open market sales expose farmers to price fluctuations and limited value chain linkages, often resulting in unstable incomes and weaker market positioning.
Traceability Assurance
Contract farming offers higher income stability for farmers due to guaranteed purchase agreements and predefined prices, enhancing traceability assurance through documented production practices and quality standards. Open market sales lack such structured traceability, exposing farmers to price volatility and reduced income predictability.
Fair Trade Compliance
Contract farming under Fair Trade Compliance provides income stability by guaranteeing minimum prices and long-term agreements for farmers, reducing exposure to volatile open market fluctuations. Open market sales often expose farmers to unpredictable price swings and lack the protective mechanisms and ethical standards promoted by Fair Trade, leading to less predictable income streams.
Contract farming vs open market sales for income stability Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com