Rotary tillers provide finer soil texture and better weed control, making them ideal for precise seedbed preparation in various soil types. Disc harrows excel in breaking up clods and incorporating crop residues, facilitating faster soil drying and nutrient mixing. Choosing between the two depends on soil condition, crop requirements, and tillage depth for optimal seed germination and growth.
Table of Comparison
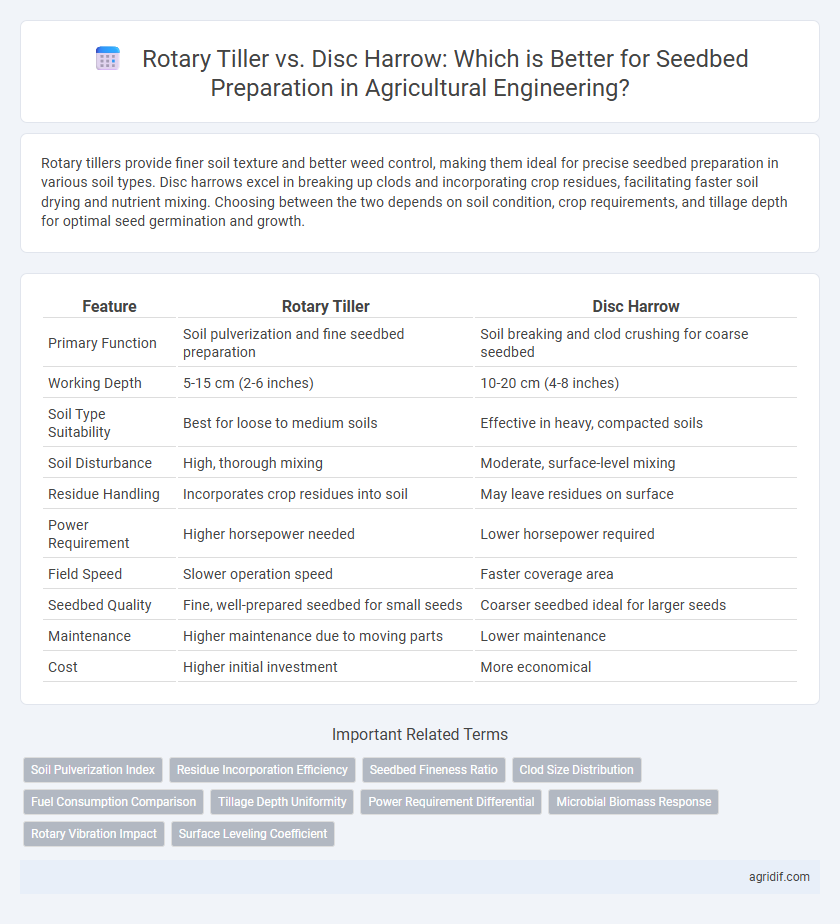
| Feature | Rotary Tiller | Disc Harrow |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Soil pulverization and fine seedbed preparation | Soil breaking and clod crushing for coarse seedbed |
| Working Depth | 5-15 cm (2-6 inches) | 10-20 cm (4-8 inches) |
| Soil Type Suitability | Best for loose to medium soils | Effective in heavy, compacted soils |
| Soil Disturbance | High, thorough mixing | Moderate, surface-level mixing |
| Residue Handling | Incorporates crop residues into soil | May leave residues on surface |
| Power Requirement | Higher horsepower needed | Lower horsepower required |
| Field Speed | Slower operation speed | Faster coverage area |
| Seedbed Quality | Fine, well-prepared seedbed for small seeds | Coarser seedbed ideal for larger seeds |
| Maintenance | Higher maintenance due to moving parts | Lower maintenance |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | More economical |
Introduction to Seedbed Preparation Techniques
Rotary tillers and disc harrows are essential seedbed preparation tools in agricultural engineering, each offering unique soil conditioning benefits. Rotary tillers provide fine soil pulverization ideal for small to medium-sized fields, enhancing seed-soil contact and moisture retention. Disc harrows excel in breaking up heavy clods and managing crop residues, making them suitable for large-scale operations requiring efficient residue incorporation and soil aeration.
Overview of Rotary Tiller and Disc Harrow
Rotary tillers use rotating blades to finely pulverize soil, creating a smooth seedbed ideal for small-scale and precision farming. Disc harrows consist of concave metal discs arranged in gangs, effectively breaking up clods and incorporating crop residues for medium to large-scale soil preparation. Both tools optimize soil aeration and moisture retention but differ in soil disturbance intensity and operational efficiency.
Principle of Operation: Rotary Tiller vs Disc Harrow
Rotary tillers operate using rotating blades that actively dig and churn the soil, breaking it into fine particles ideal for seedbed preparation. Disc harrows use concave metal discs arranged in gangs that slice and turn the soil, creating a rougher seedbed suitable for heavier residue conditions. The rotary tiller's principle of mechanical mixing contrasts with the disc harrow's slicing and cutting action, influencing soil texture and aeration differently during seedbed preparation.
Soil Texture and Suitability for Each Implement
Rotary tillers are highly effective for fine-textured soils like sandy loams and silts, where their rotating blades break up clods to create a smooth seedbed ideal for small-seeded crops. Disc harrows better suit heavier soils such as clay and loam, cutting through dense, compacted layers to improve aeration and drainage without excessive soil disturbance. Selecting the appropriate implement based on soil texture maximizes seedbed quality, promotes uniform germination, and enhances crop establishment.
Depth and Uniformity of Seedbed Preparation
Rotary tillers achieve greater depth in seedbed preparation, typically reaching 6 to 12 inches, ensuring thorough soil aeration and residue incorporation. Disc harrows generally work at shallower depths of 3 to 6 inches but provide uniform soil mixing by cutting and lifting soil clods for even seed placement. Uniformity in seedbed preparation is often superior with disc harrows due to consistent soil slicing, while rotary tillers excel in creating a finely pulverized, deeper seedbed for optimal root development.
Impact on Soil Structure and Compaction
Rotary tillers break soil into fine particles improving seedbed uniformity but risk over-disruption leading to soil compaction and reduced pore space. Disc harrows maintain better soil structure by cutting and lifting soil, limiting compaction and preserving aggregates essential for aeration and water infiltration. Choosing between rotary tillers and disc harrows depends on soil type and moisture, balancing seedbed quality with minimal soil disturbance.
Residue Management Capabilities
Rotary tillers excel in residue management by finely chopping and incorporating crop residues into the soil, promoting faster decomposition and improving soil organic matter. Disc harrows primarily cut and mix surface residues, which can leave larger debris on the field, potentially slowing down residue breakdown but aiding in erosion control. For intensive residue incorporation and seedbed uniformity, rotary tillers provide superior performance compared to disc harrows.
Fuel Efficiency and Power Requirements
Rotary tillers generally consume more fuel and require higher power due to their intensive soil engagement, making them suitable for heavy-duty seedbed preparation. Disc harrows, with lower power demands and better fuel efficiency, are preferred for lighter soil conditions and faster field coverage. Choosing between the two depends on balancing fuel consumption with the power availability of the tractor and specific soil management goals.
Maintenance and Durability Considerations
Rotary tillers require frequent maintenance due to their complex moving parts, such as blades and gearboxes, which demand regular lubrication and inspection to prevent wear and tear. Disc harrows, constructed with robust steel discs and simpler mechanisms, generally offer greater durability and lower maintenance costs, making them suitable for tougher soil conditions and prolonged use. Selecting between rotary tiller and disc harrow depends on the balance between maintenance capacity and durability needs for efficient seedbed preparation.
Cost-Effectiveness and Practical Recommendations
Rotary tillers offer superior soil pulverization for seedbed preparation but involve higher initial costs and maintenance compared to disc harrows, which are more cost-effective for larger, less-intensive applications. Disc harrows perform well in breaking up clods and managing crop residues, making them practical for dryland and coarse soil conditions. For optimal cost-effectiveness, producers should match rotary tiller use to smaller, well-managed fields requiring fine seedbeds, while leveraging disc harrows for extensive acreage and preliminary soil conditioning.
Related Important Terms
Soil Pulverization Index
The Rotary tiller achieves a higher Soil Pulverization Index compared to the Disc harrow, resulting in finer soil particles and improved seedbed conditions. Enhanced pulverization from rotary tillers promotes better seed-to-soil contact and uniform moisture distribution, crucial for optimal germination and crop establishment.
Residue Incorporation Efficiency
Rotary tillers provide superior residue incorporation efficiency compared to disc harrows by finely chopping and thoroughly mixing crop residues into the soil, enhancing organic matter decomposition and soil fertility. Disc harrows tend to leave larger residue fragments on the surface, resulting in slower breakdown and less uniform seedbed conditions.
Seedbed Fineness Ratio
Rotary tillers achieve a higher Seedbed Fineness Ratio compared to disc harrows, producing finer soil particles essential for optimal seed germination and uniform seedling emergence. The aggressive soil fragmentation by rotary tillers enhances aeration and moisture retention, whereas disc harrows tend to leave larger clods, reducing seedbed uniformity and potentially impacting crop yield.
Clod Size Distribution
Rotary tillers produce finer and more uniform clod size distribution compared to disc harrows, resulting in an ideal seedbed for optimal seed-to-soil contact and improved germination rates. Disc harrows tend to leave larger clods and uneven soil texture, which can hinder seedling emergence and reduce overall crop uniformity.
Fuel Consumption Comparison
Rotary tillers typically consume more fuel than disc harrows due to their intensive soil agitation and deeper tillage capabilities, averaging around 12-15 liters per hectare compared to disc harrows' 8-10 liters per hectare. Fuel efficiency in disc harrows is enhanced by their simpler mechanical design and lighter operational load, making them more cost-effective for large-scale seedbed preparation.
Tillage Depth Uniformity
Rotary tillers provide superior tillage depth uniformity due to their rotating blades that break soil evenly, promoting consistent seedbed conditions essential for optimal crop growth. Disc harrows, while effective in soil mixing, often create variable tillage depths because of uneven disc penetration, leading to less uniform seedbeds and potential issues in seed germination.
Power Requirement Differential
Rotary tillers typically require higher power input than disc harrows due to their intensive soil fragmentation and mixing action, which enhances seedbed uniformity and aeration. Disc harrows, benefiting from their simpler design and rolling disc mechanism, consume less energy, making them more fuel-efficient but potentially less effective in breaking compacted soils compared to rotary tillers.
Microbial Biomass Response
Rotary tillers enhance microbial biomass by creating finer soil particles and improving aeration, which accelerates organic matter decomposition and nutrient cycling. Disc harrows, while effective for residue incorporation, tend to disrupt microbial habitats less intensively, resulting in a slower but steadier increase in microbial biomass during seedbed preparation.
Rotary Vibration Impact
Rotary tillers generate intense rotary vibration impact that effectively breaks soil clods, resulting in a finer seedbed structure compared to the disc harrow's shearing action, which primarily fractures soil along planes without significant vibration. The enhanced soil pulverization and uniform seedbed preparation by rotary tillers improve seed-to-soil contact and promote better germination rates in agricultural engineering applications.
Surface Leveling Coefficient
Rotary tillers achieve a higher surface leveling coefficient compared to disc harrows, providing a finer and more uniform seedbed crucial for optimal seed germination. Disc harrows often create a coarser surface with uneven soil clods, which can negatively impact seed placement and moisture retention.
Rotary tiller vs Disc harrow for seedbed preparation Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com