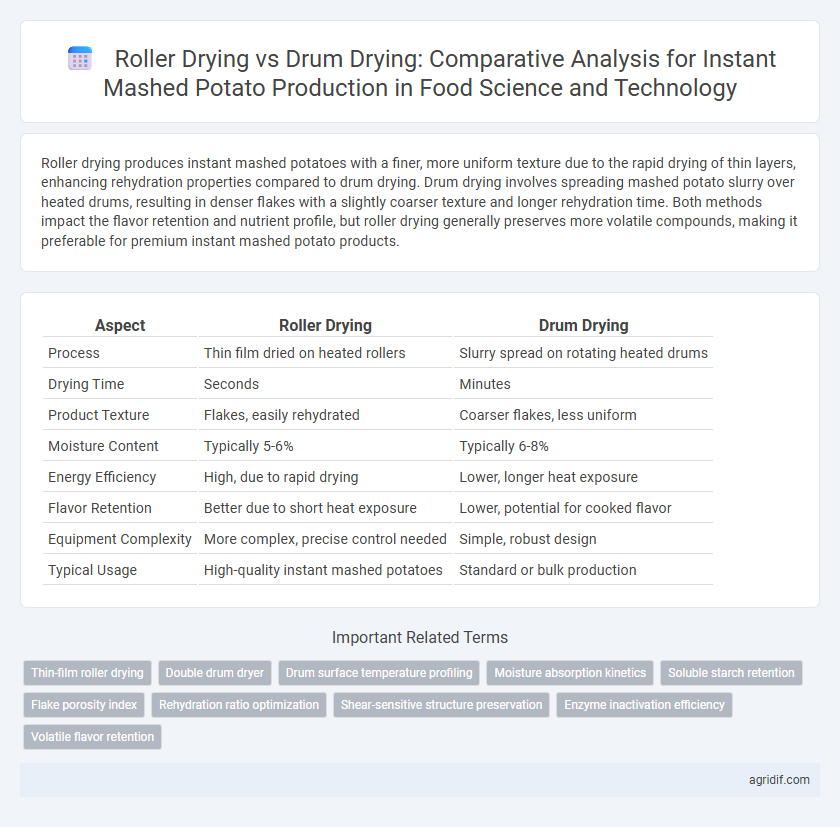
Roller drying produces instant mashed potatoes with a finer, more uniform texture due to the rapid drying of thin layers, enhancing rehydration properties compared to drum drying. Drum drying involves spreading mashed potato slurry over heated drums, resulting in denser flakes with a slightly coarser texture and longer rehydration time. Both methods impact the flavor retention and nutrient profile, but roller drying generally preserves more volatile compounds, making it preferable for premium instant mashed potato products.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Roller Drying | Drum Drying |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Thin film dried on heated rollers | Slurry spread on rotating heated drums |
| Drying Time | Seconds | Minutes |
| Product Texture | Flakes, easily rehydrated | Coarser flakes, less uniform |
| Moisture Content | Typically 5-6% | Typically 6-8% |
| Energy Efficiency | High, due to rapid drying | Lower, longer heat exposure |
| Flavor Retention | Better due to short heat exposure | Lower, potential for cooked flavor |
| Equipment Complexity | More complex, precise control needed | Simple, robust design |
| Typical Usage | High-quality instant mashed potatoes | Standard or bulk production |
Introduction to Drying Technologies in Instant Mashed Potato Production
Roller drying and drum drying are key technologies in the production of instant mashed potatoes, each affecting texture and rehydration properties differently. Roller drying uses heated drums to rapidly dry potato slurry into thin flakes, preserving starch gelatinization and enhancing solubility. Drum drying involves spreading the slurry over a rotating drum surface, producing thicker flakes with a distinct texture but potentially longer drying times and higher energy consumption.
Overview of Roller Drying and Drum Drying Principles
Roller drying and drum drying are thermal dehydration techniques used to produce instant mashed potatoes, where roller drying involves spreading the potato slurry as a thin film over heated rotating drums for rapid moisture evaporation. Drum drying operates by applying the potato puree onto the surface of large, heated drums that rotate, allowing the product to dry into thin sheets that are subsequently milled into flakes or powder. Both methods leverage heat transfer principles to efficiently remove moisture while preserving the starch gelatinization critical for instant rehydration quality.
Comparative Analysis: Process Mechanisms
Roller drying utilizes a thin film of potato slurry applied to heated drums that rapidly evaporate moisture, producing flakes with uniform thickness and high rehydration rates. Drum drying involves spreading the potato puree over large rotating drums where heat conduction dries the product into sheets, often resulting in coarser texture and longer drying times. The controlled heat transfer in roller drying typically enhances product consistency and nutrient retention compared to the broader thermal exposure in drum drying.
Effects on Nutritional Quality and Retention
Roller drying preserves higher levels of vitamins and antioxidants in instant mashed potatoes compared to drum drying due to lower thermal exposure and faster moisture removal. Drum drying often leads to greater nutrient degradation, including loss of heat-sensitive vitamins like vitamin C and B-complex, resulting from prolonged contact with hot surfaces. Consequently, roller drying enhances nutritional retention and maintains better functional properties in the final product.
Impact on Instant Mashed Potato Texture and Sensory Properties
Roller drying produces instant mashed potatoes with a finer, more uniform particle size, resulting in smoother rehydrated texture and consistent creaminess preferred in sensory evaluations. Drum drying often leads to coarser flakes that can create a grainier mouthfeel and less uniform hydration, negatively affecting overall palatability. Texture attributes such as cohesiveness and smoothness are enhanced by roller drying due to higher surface area contact and more controlled moisture evaporation during processing.
Energy Efficiency and Operational Costs
Roller drying offers higher energy efficiency compared to drum drying due to its low moisture evaporation rate and shorter drying time, significantly reducing fuel consumption. Operational costs are lower with roller drying since it requires less maintenance and offers a continuous process, minimizing labor expenses. Drum drying, while effective for certain textures, typically incurs higher energy use and increased downtime, raising overall production costs for instant mashed potatoes.
Scalability and Industrial Applications
Roller drying offers higher scalability for instant mashed potato production due to its continuous processing capability and uniform thin-film drying, enabling consistent product quality at large volumes. Drum drying, while suitable for smaller batches, is less efficient in mass production but advantageous for its simplicity and lower initial investment costs in industrial applications. Industrial plants prefer roller drying for high-throughput operations, whereas drum drying serves niche markets with moderate-scale demands.
Influence on Starch Gelatinization and Rehydration Properties
Roller drying promotes uniform starch gelatinization by applying consistent heat and pressure, resulting in instant mashed potatoes with superior rehydration properties and smooth texture. Drum drying, while effective for starch gelatinization, often leads to uneven heating, causing partial gelatinization and reduced solubility in the final product. The controlled environment of roller drying enhances starch swelling and water absorption, thereby improving instant potato flakes' rehydration rate and overall quality.
Food Safety and Microbial Control in Drying Processes
Roller drying ensures rapid dehydration at controlled temperatures, effectively reducing microbial load in instant mashed potatoes by minimizing exposure to contaminants. Drum drying, while efficient for high-moisture foods, may present challenges in uniformly eliminating pathogens due to potential temperature inconsistencies on the drum surface. Both methods require stringent monitoring of processing parameters to uphold food safety standards and prevent microbial growth during drying.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Roller drying for instant mashed potatoes offers lower energy consumption and reduced water usage compared to drum drying, enhancing overall sustainability. The roller drying process generates less wastewater and emits fewer greenhouse gases, making it a more environmentally friendly option. Furthermore, its efficient heat transfer minimizes nutrient loss, contributing to both product quality and resource conservation.
Related Important Terms
Thin-film roller drying
Thin-film roller drying offers superior control over film thickness and drying temperature compared to drum drying, resulting in instant mashed potatoes with enhanced rehydration properties and consistent texture. The precise thin-film spreading minimizes nutrient loss and Maillard reaction, preserving flavor and color more effectively than traditional drum drying methods.
Double drum dryer
Double drum dryers offer precise temperature control and rapid dehydration, preserving the nutritional quality and texture of instant mashed potatoes better than traditional roller drying methods. Their efficient heat transfer and uniform drying surfaces reduce product stickiness and enhance rehydration properties, making them ideal for high-quality instant mashed potato production.
Drum surface temperature profiling
Drum surface temperature profiling during drum drying of instant mashed potatoes critically influences starch gelatinization and moisture evaporation, enhancing product texture and solubility. Precise control of surface temperature gradients ensures uniform drying, preventing overheating and nutrient degradation compared to roller drying methods.
Moisture absorption kinetics
Roller drying exhibits faster moisture absorption kinetics in instant mashed potatoes compared to drum drying, resulting from its thinner product sheet and increased surface area, which enhance water rehydration efficiency. Drum-dried mashed potatoes have slower moisture uptake due to their denser structure and thicker dried layers, affecting reconstitution time and texture quality.
Soluble starch retention
Roller drying for instant mashed potatoes demonstrates higher soluble starch retention compared to drum drying due to its rapid dehydration process and minimal thermal degradation. This enhanced retention improves the rehydration quality and texture of the final product, making roller drying a preferred method in food science technology for maximizing starch functionality.
Flake porosity index
Roller drying produces instant mashed potato flakes with a higher porosity index compared to drum drying, enhancing rehydration speed and texture quality. The increased porosity from roller drying results from the controlled film formation and rapid moisture removal, which creates a more porous and fragile flake structure ideal for instant applications.
Rehydration ratio optimization
Roller drying produces instant mashed potatoes with a higher rehydration ratio due to its thin film formation and rapid moisture removal, enhancing porosity and water uptake. Drum drying's thicker flakes often result in lower rehydration efficiency, affecting texture and cooking performance negatively.
Shear-sensitive structure preservation
Roller drying preserves the shear-sensitive structure of instant mashed potatoes more effectively than drum drying by applying gentle, uniform heat and pressure, minimizing cellular damage and maintaining texture integrity. The controlled drying environment of roller dryers results in improved rehydration properties and retention of starch granule functionality compared to the higher shear forces experienced in drum drying.
Enzyme inactivation efficiency
Roller drying demonstrates superior enzyme inactivation efficiency compared to drum drying in the production of instant mashed potatoes, primarily due to its rapid heat transfer and controlled drying environment. This enhanced inactivation minimizes enzymatic browning and preserves the quality and shelf life of the final product.
Volatile flavor retention
Roller drying preserves volatile flavors in instant mashed potatoes more effectively than drum drying due to its rapid drying process and minimal heat exposure, which reduces the loss of aroma compounds. Drum drying typically results in greater flavor degradation as extended heat contact promotes volatilization and oxidation of delicate flavor molecules.
Roller drying vs drum drying for instant mashed potatoes Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com