Antioxidant capacity in food additives primarily protects against oxidative degradation, extending shelf life and preserving nutritional quality by neutralizing free radicals. Antimicrobial activity, on the other hand, inhibits the growth of spoilage and pathogenic microorganisms, ensuring food safety and reducing spoilage. The optimal food additive balances both antioxidant and antimicrobial properties to enhance food preservation and safety effectively.
Table of Comparison
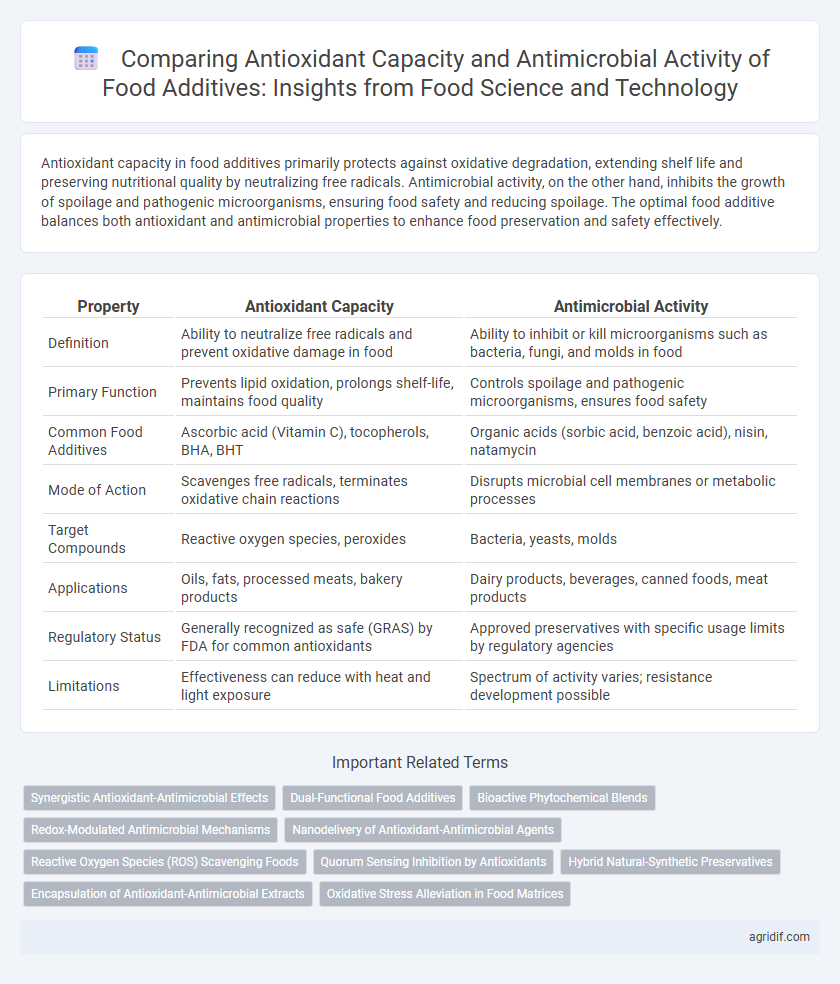
| Property | Antioxidant Capacity | Antimicrobial Activity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to neutralize free radicals and prevent oxidative damage in food | Ability to inhibit or kill microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, and molds in food |
| Primary Function | Prevents lipid oxidation, prolongs shelf-life, maintains food quality | Controls spoilage and pathogenic microorganisms, ensures food safety |
| Common Food Additives | Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C), tocopherols, BHA, BHT | Organic acids (sorbic acid, benzoic acid), nisin, natamycin |
| Mode of Action | Scavenges free radicals, terminates oxidative chain reactions | Disrupts microbial cell membranes or metabolic processes |
| Target Compounds | Reactive oxygen species, peroxides | Bacteria, yeasts, molds |
| Applications | Oils, fats, processed meats, bakery products | Dairy products, beverages, canned foods, meat products |
| Regulatory Status | Generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by FDA for common antioxidants | Approved preservatives with specific usage limits by regulatory agencies |
| Limitations | Effectiveness can reduce with heat and light exposure | Spectrum of activity varies; resistance development possible |
Introduction: Importance of Food Additives in Modern Agriculture
Food additives play a crucial role in modern agriculture by enhancing food preservation and safety through their antioxidant capacity and antimicrobial activity. Antioxidants prevent oxidative spoilage by neutralizing free radicals, thereby extending shelf life and maintaining nutritional quality. Antimicrobial agents inhibit the growth of pathogens and spoilage microorganisms, reducing foodborne illnesses and post-harvest losses in agricultural products.
Defining Antioxidant Capacity in Food Science
Antioxidant capacity in food science refers to the ability of food additives to neutralize free radicals and prevent oxidative damage, thereby enhancing food preservation and nutritional quality. This capacity is quantified through methods such as DPPH, ABTS, and ORAC assays, which measure the scavenging activity of antioxidants against reactive oxygen species. While a high antioxidant capacity often correlates with improved antimicrobial activity, these properties are distinct, as antimicrobial activity specifically targets the inhibition of microbial growth and spoilage in food systems.
Exploring Antimicrobial Activity of Food Additives
Food additives with high antioxidant capacity often exhibit enhanced antimicrobial activity by inhibiting microbial growth and extending food shelf life. Phenolic compounds and essential oils derived from natural sources demonstrate significant antimicrobial effects against foodborne pathogens such as Listeria monocytogenes and Escherichia coli. Evaluating the synergistic impact of antioxidant capacity on antimicrobial efficacy is critical for developing safer, more effective preservative systems in food technology.
Key Differences Between Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Functions
Antioxidant capacity in food additives primarily targets the prevention of oxidative degradation by neutralizing free radicals, thereby extending shelf life and preserving nutritional quality. In contrast, antimicrobial activity focuses on inhibiting or destroying pathogenic and spoilage microorganisms to ensure food safety and prevent contamination. These distinct mechanisms are critical in food preservation, with antioxidants safeguarding chemical stability, while antimicrobials protect biological integrity.
Common Additives with Dual Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties
Common food additives such as rosemary extract, green tea polyphenols, and oregano oil exhibit significant antioxidant capacity while simultaneously providing antimicrobial activity, making them valuable for food preservation. These additives inhibit lipid oxidation and microbial growth, enhancing shelf-life and safety of perishable products. Their dual functionality is attributed to bioactive compounds like phenolics and flavonoids, which disrupt microbial cell membranes and scavenge free radicals effectively.
Evaluating Antioxidant Efficiency in Food Preservation
Evaluating antioxidant efficiency in food preservation involves measuring the antioxidant capacity of additives, which reflects their ability to neutralize free radicals and prevent lipid oxidation, thereby maintaining food quality and shelf life. Antimicrobial activity, while crucial for inhibiting pathogenic and spoilage microorganisms, operates through distinct mechanisms targeting microbial cell structures or metabolism, and does not directly indicate antioxidant potential. A comprehensive assessment of food additives requires quantifying both antioxidant capacity using assays like DPPH or ORAC, and antimicrobial efficacy through microbial inhibition tests to ensure synergistic protection in food systems.
Assessing Antimicrobial Efficacy Against Foodborne Pathogens
Evaluating antimicrobial efficacy of food additives against foodborne pathogens involves measuring their ability to inhibit or kill microorganisms such as Salmonella, Listeria monocytogenes, and Escherichia coli. While antioxidant capacity contributes to food preservation by preventing oxidative spoilage, antimicrobial activity directly targets pathogen control to enhance food safety. Methods like minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) assays and time-kill studies quantify the antimicrobial potential, critical for selecting effective natural or synthetic additives in food formulations.
Impact of Additive Selection on Food Safety and Shelf Life
Antioxidant capacity in food additives primarily prevents lipid oxidation, thereby extending shelf life by maintaining product quality and nutritional value. Antimicrobial activity targets spoilage and pathogenic microorganisms, directly enhancing food safety by reducing microbial growth and contamination risks. Selecting additives with balanced antioxidant and antimicrobial properties is crucial for optimizing both food safety and shelf life, as this dual functionality minimizes spoilage while preserving sensory attributes.
Regulatory Considerations in Food Additive Approval
Regulatory authorities require comprehensive evaluation of both antioxidant capacity and antimicrobial activity when approving food additives to ensure safety and efficacy. Antioxidants must demonstrate effective free radical scavenging without adverse toxicological effects, while antimicrobial agents require validated inhibition of pathogenic microorganisms without promoting resistance. Documentation must include standardized assays like ORAC or DPPH for antioxidant assessment and MIC determination for antimicrobial potential, adhering to guidelines by agencies such as the FDA, EFSA, or Codex Alimentarius.
Future Trends: Innovations in Multifunctional Food Additives
Emerging research in food science emphasizes the development of multifunctional food additives that combine high antioxidant capacity with potent antimicrobial activity, enhancing food preservation and safety. Nanotechnology and bioengineering approaches enable the creation of novel compounds that inhibit microbial growth while scavenging free radicals, extending shelf life and improving nutritional value. Future trends highlight the integration of natural extracts and synthetic agents to optimize these dual functionalities in clean-label food formulations.
Related Important Terms
Synergistic Antioxidant-Antimicrobial Effects
Synergistic antioxidant-antimicrobial effects in food additives enhance preservation by simultaneously inhibiting oxidative spoilage and microbial growth, improving shelf life stability. Combining natural polyphenols and essential oils demonstrates increased efficacy in reducing lipid oxidation and suppressing pathogenic bacteria in food matrices.
Dual-Functional Food Additives
Dual-functional food additives exhibiting both antioxidant capacity and antimicrobial activity enhance food preservation by simultaneously inhibiting oxidative spoilage and microbial growth, thereby extending shelf life and ensuring food safety. Incorporating natural compounds such as polyphenols and essential oils in food formulations maximizes efficacy against lipid oxidation and pathogenic bacteria, aligning with clean-label and health-conscious consumer demands.
Bioactive Phytochemical Blends
Bioactive phytochemical blends exhibit a synergistic enhancement of antioxidant capacity, effectively neutralizing free radicals and preventing lipid oxidation in food systems. These blends concurrently demonstrate potent antimicrobial activity by disrupting microbial cell membranes and inhibiting pathogen growth, ensuring extended shelf life and improved food safety.
Redox-Modulated Antimicrobial Mechanisms
Redox-modulated antimicrobial mechanisms in food additives leverage antioxidant capacity to disrupt microbial redox balance, generating oxidative stress that impairs pathogen viability. This interplay enhances food preservation by simultaneously neutralizing free radicals and inhibiting microbial growth through redox cycling and reactive oxygen species production.
Nanodelivery of Antioxidant-Antimicrobial Agents
Nanodelivery systems enhance the stability and bioavailability of antioxidant-antimicrobial agents in food additives, significantly improving their efficacy against oxidative spoilage and microbial contamination. These nanoscale carriers optimize controlled release, targeting pathogens while preserving food quality by simultaneously boosting antioxidant capacity and antimicrobial activity.
Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Scavenging Foods
Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) scavenging foods exhibit high antioxidant capacity by neutralizing free radicals, thereby reducing oxidative stress and prolonging food shelf life. These foods often display complementary antimicrobial activity by inhibiting the growth of spoilage and pathogenic microorganisms, enhancing food safety and preservation.
Quorum Sensing Inhibition by Antioxidants
Antioxidants in food additives exhibit significant quorum sensing inhibition, disrupting microbial communication and reducing pathogenic biofilm formation, which enhances antimicrobial efficacy beyond direct oxidative stress reduction. The dual role of antioxidants in scavenging free radicals and modulating quorum sensing pathways positions them as promising agents for controlling foodborne pathogens and extending shelf life.
Hybrid Natural-Synthetic Preservatives
Hybrid natural-synthetic preservatives combine the antioxidant capacity of natural extracts with the strong antimicrobial activity of synthetic agents, effectively enhancing food shelf life and safety. These additives leverage polyphenols and flavonoids from natural sources alongside synthetic compounds such as benzoates or sorbates to inhibit oxidative spoilage and microbial growth simultaneously.
Encapsulation of Antioxidant-Antimicrobial Extracts
Encapsulation of antioxidant-antimicrobial extracts enhances the stability and controlled release of bioactive compounds, significantly improving their efficacy in food preservation by maintaining antioxidant capacity and inhibiting microbial growth. This technology optimizes the functional performance of natural additives, extending shelf life while preserving sensory qualities and nutritional value in food products.
Oxidative Stress Alleviation in Food Matrices
Antioxidant capacity in food additives plays a critical role in mitigating oxidative stress by neutralizing free radicals, thereby preserving the nutritional quality and shelf life of food matrices. While antimicrobial activity targets spoilage and pathogenic microorganisms, antioxidant properties specifically alleviate lipid oxidation and protein degradation, ensuring enhanced food stability and safety.
Antioxidant capacity vs Antimicrobial activity for food additives Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com