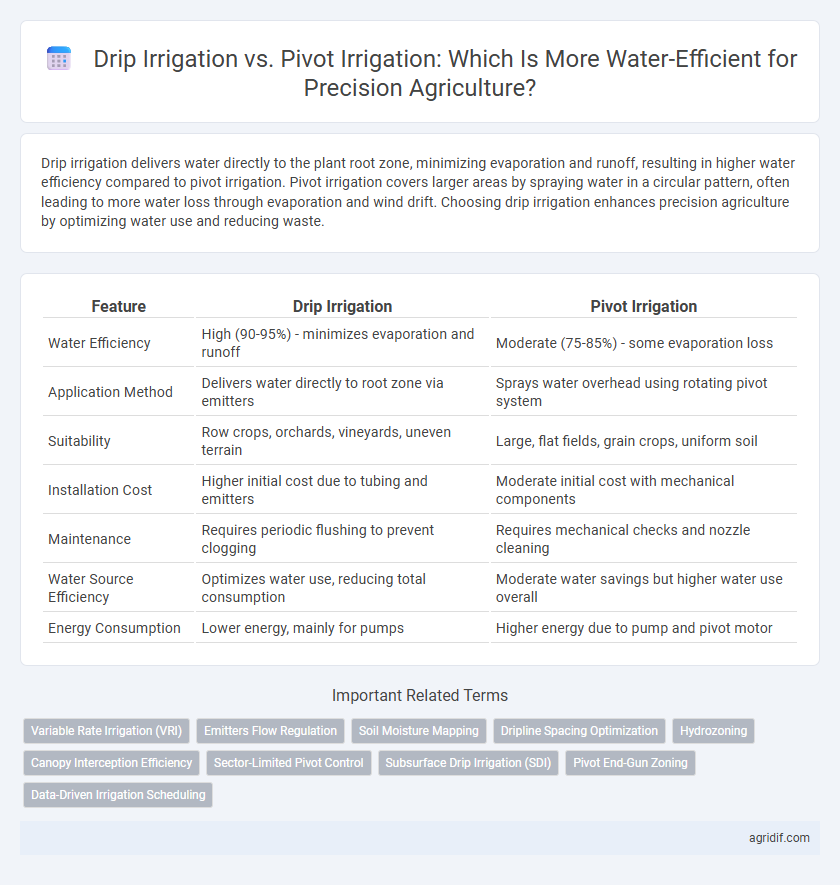
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the plant root zone, minimizing evaporation and runoff, resulting in higher water efficiency compared to pivot irrigation. Pivot irrigation covers larger areas by spraying water in a circular pattern, often leading to more water loss through evaporation and wind drift. Choosing drip irrigation enhances precision agriculture by optimizing water use and reducing waste.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Drip Irrigation | Pivot Irrigation |
|---|---|---|
| Water Efficiency | High (90-95%) - minimizes evaporation and runoff | Moderate (75-85%) - some evaporation loss |
| Application Method | Delivers water directly to root zone via emitters | Sprays water overhead using rotating pivot system |
| Suitability | Row crops, orchards, vineyards, uneven terrain | Large, flat fields, grain crops, uniform soil |
| Installation Cost | Higher initial cost due to tubing and emitters | Moderate initial cost with mechanical components |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic flushing to prevent clogging | Requires mechanical checks and nozzle cleaning |
| Water Source Efficiency | Optimizes water use, reducing total consumption | Moderate water savings but higher water use overall |
| Energy Consumption | Lower energy, mainly for pumps | Higher energy due to pump and pivot motor |
Introduction to Precision Agriculture and Water Management
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the plant roots through a network of valves and pipes, significantly reducing water loss from evaporation and runoff, making it highly efficient for precision agriculture. Pivot irrigation uses a rotating sprinkler system that covers large circular fields, offering moderate efficiency but often resulting in higher water usage compared to drip systems. Effective water management in precision agriculture prioritizes drip irrigation to optimize water conservation and enhance crop yield while minimizing resource waste.
Overview of Drip Irrigation Technology
Drip irrigation technology delivers water directly to the root zone through a network of valves, pipes, tubing, and emitters, significantly reducing water wastage compared to traditional methods. This precision watering approach enhances water efficiency by minimizing evaporation and runoff, making it ideal for arid regions and high-value crops. Studies show drip irrigation can reduce water usage by up to 50% while improving crop yield quality and uniformity.
Overview of Pivot Irrigation Systems
Pivot irrigation systems use a central rotating arm to distribute water evenly across large fields, enhancing water use efficiency by minimizing runoff and evaporation. These systems can be precisely controlled with sensors and automation to match crop water needs, reducing waste compared to traditional flood irrigation. Pivot irrigation is particularly effective for uniform terrain and large-scale farming, optimizing water application and improving crop yield.
Comparative Water Use Efficiency: Drip vs Pivot
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the root zone with minimal evaporation and runoff, achieving water use efficiency rates of up to 90-95%, significantly outperforming pivot irrigation, which typically operates at 75-85% efficiency. Pivot irrigation applies water over a larger area but often experiences higher losses due to wind drift and evaporation, especially in arid regions. Precision agriculture leverages sensor data and automated controls to optimize both systems, yet drip irrigation remains the preferred choice for maximizing water conservation in water-scarce environments.
Soil Moisture Distribution in Drip and Pivot Methods
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the root zone through a network of tubes and emitters, resulting in uniform soil moisture distribution and reduced evaporation losses. Pivot irrigation applies water in a circular pattern from a central pivot, often creating uneven moisture levels due to spray dispersion and wind drift. The precise control of drip systems enhances water efficiency by maintaining optimal soil moisture, while pivots may require supplemental irrigation to address dry spots.
Crop Health and Yield Impacts of Each System
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the plant root zone, minimizing evaporation and runoff, which enhances crop health by maintaining consistent soil moisture and reducing disease risk. Pivot irrigation covers larger areas with overhead watering, which might cause uneven moisture distribution and increase water waste but supports rapid growth in high-density crops. Studies show drip systems improve water use efficiency by up to 40%, leading to higher yield quality and healthier plants in water-scarce environments, while pivot irrigation can maximize yield on expansive fields with moderate water efficiency.
Energy and Resource Inputs Required
Drip irrigation significantly reduces water and energy consumption by delivering water directly to the root zone, minimizing evaporation and runoff, and requiring lower pump pressures compared to pivot irrigation systems. Pivot irrigation demands higher energy inputs due to large-scale water lifting and distribution, often making it less efficient in terms of resource use for water application. Optimizing energy use in drip systems enhances sustainability in precision agriculture by conserving both water and operational costs.
Cost Analysis: Installation and Maintenance
Drip irrigation typically involves higher initial installation costs due to the need for extensive tubing and emitters but offers lower maintenance expenses by minimizing water waste and reducing energy use. Pivot irrigation systems usually have lower upfront costs for equipment but incur higher ongoing maintenance costs related to mechanical parts and frequent adjustments. Cost efficiency depends on farm size and crop type, with drip systems favored for water-sensitive crops and pivots more suitable for large-scale cereal or row crop farming.
Suitability for Different Crop Types and Terrains
Drip irrigation offers superior water efficiency for row crops, orchards, and uneven terrains by delivering water directly to plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff. Pivot irrigation suits large, flat fields with crops such as corn and wheat, enabling uniform water application but often results in higher water loss due to evaporation and wind drift. Crop type, field size, and topography critically influence the choice, with drip systems favoring water-sensitive plants and complex terrains, while pivot systems optimize irrigation for extensive, uniform crops on leveled land.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Drip irrigation significantly reduces water wastage by delivering water directly to plant roots, enhancing water use efficiency by up to 90% compared to conventional methods. Pivot irrigation, while effective for large-scale fields, often results in considerable evaporation and runoff, leading to lower overall efficiency and increased water resource strain. Implementing drip irrigation aligns better with sustainable agriculture goals by minimizing water depletion and reducing the environmental impact associated with excessive groundwater extraction.
Related Important Terms
Variable Rate Irrigation (VRI)
Drip irrigation with Variable Rate Irrigation (VRI) technology delivers precise water application tailored to crop and soil variability, significantly enhancing water use efficiency compared to traditional pivot irrigation. Employing VRI in pivot systems improves uniformity but typically cannot match the localized, low-volume water delivery accuracy of drip systems in precision agriculture.
Emitters Flow Regulation
Drip irrigation systems offer superior water efficiency through precise emitter flow regulation, delivering water directly to plant roots and minimizing evaporation and runoff. Pivot irrigation often faces challenges in maintaining consistent emitter flow rates, leading to uneven water distribution and higher overall water usage compared to drip systems.
Soil Moisture Mapping
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to plant roots with minimal evaporation, significantly enhancing water efficiency based on precise soil moisture mapping data. In contrast, pivot irrigation applies water over large areas, often leading to uneven soil moisture distribution and decreased water use efficiency in precision agriculture systems.
Dripline Spacing Optimization
Drip irrigation with optimized dripline spacing maximizes water efficiency by delivering targeted moisture directly to the root zone, reducing evaporation and runoff compared to pivot irrigation systems. Precise spacing adjustments tailored to crop type and soil conditions enhance uniform water distribution and minimize resource waste in precision agriculture practices.
Hydrozoning
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the root zone with minimal evaporation, maximizing water efficiency especially in hydrozoned fields where precise moisture levels are essential for crop health. Pivot irrigation covers larger areas but can lead to water loss through evaporation and runoff, making it less efficient for managing distinct hydrozones that require variable watering schedules.
Canopy Interception Efficiency
Drip irrigation offers superior canopy interception efficiency by delivering water directly to the root zone, minimizing evaporation and runoff compared to pivot irrigation systems that spray water overhead, often resulting in significant water loss through canopy interception. Studies indicate drip irrigation can improve water use efficiency by up to 40%, optimizing soil moisture retention and enhancing crop yield under precision agriculture practices.
Sector-Limited Pivot Control
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the root zone with high precision, minimizing evaporation and runoff to optimize water efficiency, especially for row crops and orchards. Sector-limited pivot control enhances traditional center pivot systems by targeting irrigation to specific field sectors, reducing overwatering and runoff, thus improving water use efficiency in large-scale, uniform crop fields.
Subsurface Drip Irrigation (SDI)
Subsurface Drip Irrigation (SDI) delivers water directly to plant root zones with minimal evaporation and runoff, improving water use efficiency by up to 90% compared to traditional pivot irrigation systems. SDI reduces deep percolation losses and enables precise nutrient application, making it a superior choice for conserving water in precision agriculture practices.
Pivot End-Gun Zoning
Pivot irrigation with end-gun zoning enhances water efficiency by targeting specific field areas, reducing runoff and evaporation compared to traditional drip irrigation systems. This technology enables precise application rates and improved uniformity, optimizing water use in large-scale precision agriculture operations.
Data-Driven Irrigation Scheduling
Drip irrigation achieves superior water efficiency by delivering precise amounts directly to plant roots, reducing evaporation and runoff, while pivot irrigation covers larger fields with uniform water distribution but tends to use more water overall. Data-driven irrigation scheduling leverages soil moisture sensors and weather forecasts to optimize watering times and quantities, significantly enhancing the efficacy of both drip and pivot systems in precision agriculture.
Drip Irrigation vs Pivot Irrigation for water efficiency Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com