Site-specific management in precision agriculture tailors crop inputs based on detailed field variability data, enhancing resource efficiency and boosting yields. Blanket management applies uniform input rates across entire fields, often leading to overuse or underuse in certain areas and reduced overall productivity. Adopting site-specific approaches enables precise nutrient and water application, reducing costs and environmental impact while maximizing crop performance.
Table of Comparison
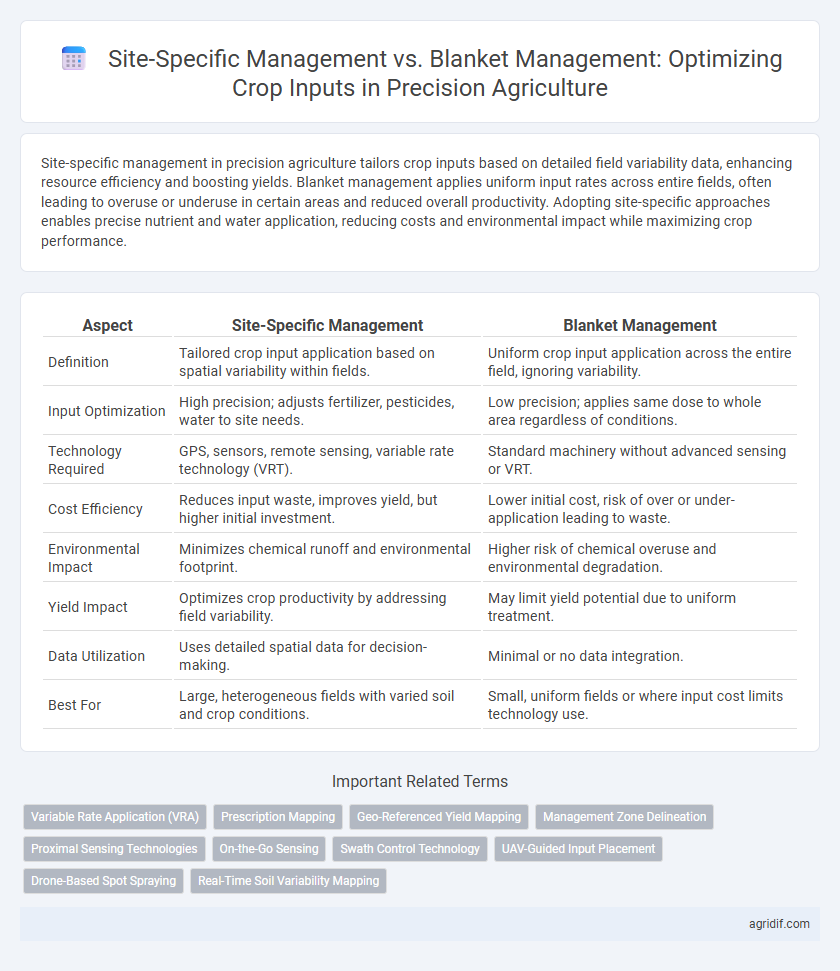
| Aspect | Site-Specific Management | Blanket Management |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tailored crop input application based on spatial variability within fields. | Uniform crop input application across the entire field, ignoring variability. |
| Input Optimization | High precision; adjusts fertilizer, pesticides, water to site needs. | Low precision; applies same dose to whole area regardless of conditions. |
| Technology Required | GPS, sensors, remote sensing, variable rate technology (VRT). | Standard machinery without advanced sensing or VRT. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces input waste, improves yield, but higher initial investment. | Lower initial cost, risk of over or under-application leading to waste. |
| Environmental Impact | Minimizes chemical runoff and environmental footprint. | Higher risk of chemical overuse and environmental degradation. |
| Yield Impact | Optimizes crop productivity by addressing field variability. | May limit yield potential due to uniform treatment. |
| Data Utilization | Uses detailed spatial data for decision-making. | Minimal or no data integration. |
| Best For | Large, heterogeneous fields with varied soil and crop conditions. | Small, uniform fields or where input cost limits technology use. |
Introduction to Crop Input Optimization
Crop input optimization in precision agriculture enhances resource efficiency by tailoring fertilizer, water, and pesticide applications to the specific needs of individual field zones. Site-specific management uses detailed soil, crop, and environmental data to apply inputs variably, reducing waste and improving yield quality compared to blanket management, which treats the entire field uniformly. Integrating GPS, remote sensing, and variable rate technology enables precise adjustments that maximize crop productivity and minimize environmental impact.
Defining Site-Specific Management
Site-Specific Management (SSM) in precision agriculture involves tailoring crop input applications such as fertilizers, pesticides, and water based on the spatial variability within fields. This approach uses data from soil sensors, GPS mapping, and remote sensing technologies to optimize inputs for specific zones, enhancing resource efficiency and crop yield. Unlike blanket management, which applies uniform treatments across entire fields, SSM enables targeted interventions that reduce waste and environmental impact.
Understanding Blanket Management Approaches
Blanket management applies uniform amounts of water, fertilizers, and pesticides across an entire field, disregarding spatial variations in soil fertility, moisture, or pest pressure. This approach simplifies operations but often leads to inefficient input use, increased costs, and potential environmental harm due to over-application in low-need areas. Understanding blanket management highlights the limitations of traditional practices, underscoring the value of precision agriculture techniques that tailor inputs to site-specific conditions for optimized crop productivity.
Key Technologies Enabling Site-Specific Management
GPS-guided machinery, remote sensing technologies like drones and satellite imagery, and variable rate technology (VRT) are key enablers of site-specific management in precision agriculture. These technologies allow precise application of fertilizers, pesticides, and water based on real-time field variability, optimizing input use and improving crop yield. Data analytics and IoT sensors further enhance decision-making by continuously monitoring soil and crop conditions at a micro-level, surpassing the uniform approach of blanket management.
Economic Impacts: Site-Specific vs Blanket Management
Site-specific management optimizes crop inputs by tailoring fertilizer, water, and pesticide applications to variable field conditions, leading to significant cost savings and increased yield efficiency. Blanket management applies uniform inputs across entire fields, often resulting in over-application, higher input costs, and resource wastage. Economic studies show that site-specific strategies can reduce input expenses by 20-30% while enhancing overall profitability compared to blanket practices.
Environmental Benefits of Precision Input Application
Site-specific management in precision agriculture optimizes crop input application by tailoring fertilizer and pesticide use to the unique conditions of each field zone, significantly reducing chemical runoff and nutrient leaching. This targeted approach enhances soil health and water quality by preventing over-application of inputs common in blanket management practices. Improved environmental sustainability results from decreased greenhouse gas emissions and minimized impact on surrounding ecosystems, promoting biodiversity alongside efficient resource use.
Case Studies: Success Stories in Site-Specific Management
Case studies in site-specific management demonstrate significant yield improvements and cost reductions by tailoring fertilizer and irrigation based on soil variability and crop needs. Farmers using precision agriculture tools, such as GPS-guided machinery and variable rate technology (VRT), reported up to 20% input savings and 15% yield increases compared to traditional blanket management. These success stories highlight the environmental benefits of reduced chemical runoff and enhanced resource efficiency in field-scale crop input optimization.
Challenges in Transitioning from Blanket to Site-Specific Management
Transitioning from blanket management to site-specific management in precision agriculture involves overcoming significant challenges such as high initial investment costs for advanced technology and data analytics tools. Farmers must acquire skills in geospatial data interpretation and variable rate technology implementation to optimize crop inputs effectively. Managing heterogeneous field variability while ensuring consistent economic returns requires ongoing adaptation and precise decision-making capabilities.
Decision-Making Tools for Crop Input Optimization
Site-specific management leverages advanced decision-making tools such as GPS mapping, sensor data, and variable rate technology to optimize crop inputs precisely where needed, enhancing resource efficiency and yield. Blanket management applies uniform input rates across entire fields, often leading to overuse or underuse of fertilizers, pesticides, and water, reducing overall efficiency. Precision agriculture decision-making tools integrate real-time data analytics and machine learning algorithms to tailor input applications, promoting sustainable practices and cost savings.
Future Trends in Precision Agriculture Management
Site-Specific Management leverages GPS technology, real-time sensor data, and variable rate application to optimize crop inputs at a micro-scale, enhancing resource efficiency and yield. Blanket Management applies uniform inputs across entire fields, often leading to over- or under-application, which future advancements aim to overcome through integration of AI-driven analytics and IoT-enabled devices. Emerging trends focus on enhanced data fusion, machine learning algorithms, and autonomous machinery to enable more precise, adaptive management strategies in precision agriculture.
Related Important Terms
Variable Rate Application (VRA)
Variable Rate Application (VRA) in Precision Agriculture enables site-specific management by adjusting inputs like fertilizers, pesticides, and water based on real-time, localized crop and soil data, leading to improved resource efficiency and crop yields. Blanket management applies uniform input rates across entire fields, often resulting in overuse or underuse of resources and reduced environmental sustainability compared to the optimized, variable input distribution achievable with VRA technology.
Prescription Mapping
Prescription mapping enables site-specific management by using GPS and sensor data to create variable-rate input applications, enhancing crop input efficiency and reducing waste compared to blanket management. This technology optimizes fertilizer and pesticide use based on field variability, leading to increased yields and sustainable resource use.
Geo-Referenced Yield Mapping
Geo-referenced yield mapping enables site-specific management by providing detailed spatial variability data that allows farmers to tailor crop inputs precisely according to field conditions, enhancing resource efficiency and yield potential. In contrast, blanket management applies uniform inputs across entire fields, often leading to over- or under-application, increased costs, and suboptimal crop performance compared to the localized precision facilitated by geo-referenced data.
Management Zone Delineation
Management zone delineation in site-specific management utilizes spatial data from soil sensors, GPS, and remote sensing to create precise input maps that address variability within fields, enhancing nutrient use efficiency and yield. In contrast, blanket management applies uniform inputs across entire fields, often leading to resource wastage and suboptimal crop performance due to ignoring intra-field heterogeneity.
Proximal Sensing Technologies
Proximal sensing technologies enable site-specific management by providing high-resolution data on soil and crop conditions, allowing farmers to apply inputs such as fertilizers and water precisely where needed, improving input efficiency and crop yield. Blanket management applies uniform inputs across entire fields, often leading to resource wastage and suboptimal plant growth, whereas proximal sensing supports variable-rate application tailored to intra-field variability.
On-the-Go Sensing
Site-specific management leverages on-the-go sensing technologies such as multispectral cameras and soil nutrient sensors to dynamically adjust fertilizer and pesticide applications, enhancing crop input efficiency and reducing environmental impacts. In contrast, blanket management applies uniform inputs across fields, often leading to overuse of resources and suboptimal crop yields due to spatial variability in soil and crop conditions.
Swath Control Technology
Swath control technology enhances site-specific management by automatically adjusting input application based on precise field zones, reducing overlap and minimizing waste of seeds, fertilizers, and pesticides. This targeted approach improves input efficiency and crop yield compared to traditional blanket management, which applies uniform inputs regardless of varying soil and crop conditions.
UAV-Guided Input Placement
UAV-guided input placement in site-specific management enables precise application of fertilizers and pesticides based on real-time spatial data, significantly reducing waste and improving crop yield compared to blanket management. This targeted approach leverages high-resolution aerial imagery and variable rate technology to optimize resource efficiency and enhance sustainable farming practices.
Drone-Based Spot Spraying
Drone-based spot spraying in site-specific management enables precise application of herbicides and pesticides on targeted crop areas, significantly reducing chemical use and minimizing environmental impact compared to blanket management. This technology leverages high-resolution aerial imagery and GPS data to identify weed patches or pest infestations, optimizing input use and enhancing crop health while lowering costs and promoting sustainable agriculture.
Real-Time Soil Variability Mapping
Site-specific management leverages real-time soil variability mapping through advanced sensors and GPS technology, enabling precise application of fertilizers, water, and pesticides tailored to distinct field zones. Blanket management applies uniform inputs across entire fields, often leading to resource inefficiencies and suboptimal crop yields compared to data-driven, variable rate management practices.
Site-Specific Management vs Blanket Management for Crop Input Optimization Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com