IoT devices in precision agriculture enable real-time data collection and seamless integration across various farming operations, enhancing decision-making and resource management. Standalone equipment provides specific functionalities but often lacks connectivity and interoperability, limiting the scope of data-driven insights. Leveraging IoT connectivity facilitates comprehensive, automated monitoring and control, driving efficiency and sustainability in modern farming practices.
Table of Comparison
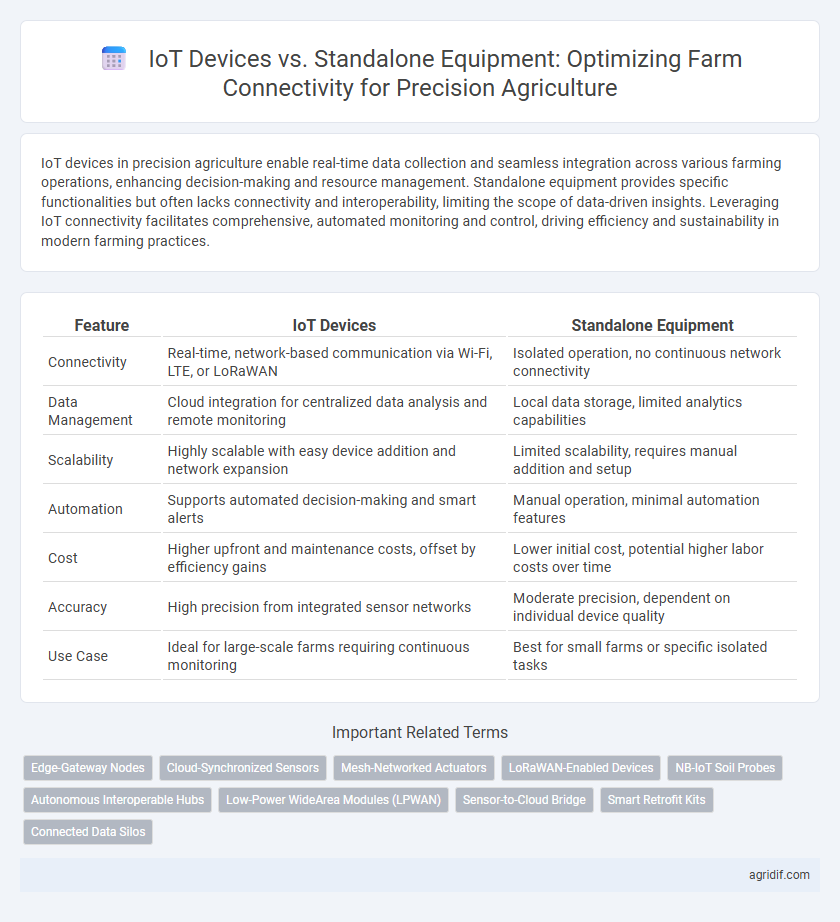
| Feature | IoT Devices | Standalone Equipment |
|---|---|---|
| Connectivity | Real-time, network-based communication via Wi-Fi, LTE, or LoRaWAN | Isolated operation, no continuous network connectivity |
| Data Management | Cloud integration for centralized data analysis and remote monitoring | Local data storage, limited analytics capabilities |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with easy device addition and network expansion | Limited scalability, requires manual addition and setup |
| Automation | Supports automated decision-making and smart alerts | Manual operation, minimal automation features |
| Cost | Higher upfront and maintenance costs, offset by efficiency gains | Lower initial cost, potential higher labor costs over time |
| Accuracy | High precision from integrated sensor networks | Moderate precision, dependent on individual device quality |
| Use Case | Ideal for large-scale farms requiring continuous monitoring | Best for small farms or specific isolated tasks |
Introduction to Farm Connectivity in Precision Agriculture
IoT devices enable real-time data collection and remote monitoring in precision agriculture, enhancing farm connectivity by linking sensors, machinery, and environmental controls through wireless networks. Standalone equipment operates independently, often requiring manual data retrieval and lacking seamless integration with other farm systems, limiting overall efficiency. Integrating IoT devices within farm connectivity frameworks improves decision-making, resource management, and crop yield optimization.
Overview of IoT Devices in Modern Farming
IoT devices in modern farming enable real-time monitoring of soil moisture, weather conditions, and crop health through interconnected sensors and drones, enhancing data-driven decision-making. These devices facilitate automated irrigation, pest control, and nutrient management, improving resource efficiency and crop yield. Integration with cloud platforms allows seamless data analytics and remote farm management, surpassing the capabilities of standalone equipment.
Standalone Agricultural Equipment: Features and Limitations
Standalone agricultural equipment operates independently without requiring internet connectivity, offering reliable functionality in remote areas with limited network access. These devices often include sensors and automated controls tailored to specific farming tasks but lack real-time data integration and remote monitoring capabilities. While standalone systems enhance operational efficiency locally, they do not provide the comprehensive data analytics and connectivity benefits available through IoT-enabled farm devices.
Data Collection Capabilities: IoT vs Standalone Devices
IoT devices in precision agriculture offer real-time data collection through interconnected sensors, enabling comprehensive monitoring of soil moisture, weather conditions, and crop health across large fields. Standalone equipment, while capable of collecting specific data points, often lacks continuous connectivity and integration, limiting its ability to provide holistic farm insights. The superior data aggregation and remote access capabilities of IoT devices make them more effective for dynamic decision-making and optimizing farm productivity.
Connectivity and Integration Across Farm Operations
IoT devices enable seamless connectivity by integrating sensors, drones, and machinery through cloud-based platforms, facilitating real-time data exchange across diverse farm operations. Standalone equipment often operates in isolation, limiting the ability to synchronize data for optimized decision-making and resource management. Comprehensive connectivity through IoT fosters precision agriculture by enhancing equipment interoperability and enabling holistic farm management systems.
Real-Time Monitoring and Remote Management
IoT devices enable seamless real-time monitoring and remote management of farm conditions through interconnected sensors and wireless communication, allowing farmers to track soil moisture, weather, and crop health continuously. Standalone equipment, while effective for specific tasks like automated irrigation or drone surveillance, lacks the integrated data flow and remote accessibility provided by IoT networks. The use of IoT technology enhances decision-making efficiency by delivering instant insights and control over farm operations from any location, improving precision and resource management.
Scalability and Future-Proofing Farm Technologies
Internet of Things (IoT) devices offer unparalleled scalability for farm connectivity by enabling seamless integration of sensors, drones, and machinery across extensive agricultural operations. Standalone equipment, while reliable for specific tasks, often lacks the flexibility to adapt or expand with advancing technologies, limiting long-term usability. Embracing IoT platforms ensures future-proofing by supporting real-time data analytics, remote management, and interoperability essential for precision agriculture's evolving demands.
Cost Comparison: Initial Investment and Long-term Value
Internet of Things (IoT) devices typically require a higher initial investment due to costs associated with sensors, connectivity infrastructure, and data platforms, whereas standalone equipment has a lower upfront cost but limited integration capabilities. Over the long term, IoT devices offer greater value by enabling real-time data collection, remote monitoring, and predictive analytics, which improve farm efficiency and reduce input waste. Standalone equipment may incur additional expenses later due to maintenance and lack of scalability, limiting overall return on investment compared to IoT solutions.
Security and Data Privacy Considerations
IoT devices in precision agriculture enable real-time farm monitoring but introduce cybersecurity risks, including data breaches and unauthorized access due to network vulnerabilities. Standalone equipment reduces exposure to external threats by operating independently, yet limits data integration and remote management capabilities crucial for optimizing farm operations. Ensuring robust encryption, secure authentication protocols, and regular firmware updates are essential for protecting sensitive agricultural data across both connectivity approaches.
Choosing the Right Solution: Factors for Farmers to Consider
Farmers selecting between IoT devices and standalone equipment for farm connectivity should evaluate factors such as compatibility with existing systems, scalability, and data integration capabilities. IoT devices offer real-time data collection and remote monitoring, enhancing decision-making through interconnected sensors, while standalone equipment provides simpler, often more cost-effective solutions with limited connectivity. Prioritizing factors like network reliability, power availability, and ease of maintenance ensures optimal technology adoption tailored to specific farm operations.
Related Important Terms
Edge-Gateway Nodes
Edge-gateway nodes in precision agriculture enable seamless integration of IoT devices by processing data locally, reducing latency and bandwidth usage compared to standalone equipment. These nodes enhance real-time decision-making, improve farm connectivity, and support scalable deployment of sensors for optimized crop management.
Cloud-Synchronized Sensors
Cloud-synchronized sensors in IoT devices enable real-time data collection and seamless integration with farm management platforms, enhancing precision agriculture through improved monitoring of soil moisture, crop health, and weather conditions. Standalone equipment lacks this continuous connectivity and centralized data access, limiting responsiveness and scalability in farm operations.
Mesh-Networked Actuators
Mesh-networked actuators within IoT devices enable seamless communication across extensive farm areas, optimizing precision agriculture through real-time data exchange and coordinated control of irrigation and fertilization. Standalone equipment lacks this interconnected capability, often resulting in isolated data points and less efficient resource management on large-scale farms.
LoRaWAN-Enabled Devices
LoRaWAN-enabled IoT devices offer extensive farm connectivity by providing long-range, low-power communication crucial for precise monitoring of soil moisture, crop health, and weather conditions across large agricultural fields. Unlike standalone equipment, these devices integrate seamlessly into a network, enabling real-time data collection and remote management, which enhances decision-making accuracy and operational efficiency in precision agriculture.
NB-IoT Soil Probes
NB-IoT soil probes offer enhanced farm connectivity by providing low-power, wide-area network capabilities that enable real-time soil moisture and nutrient monitoring, outperforming standalone equipment in data accuracy and transmission range. These IoT devices integrate seamlessly with precision agriculture platforms, optimizing irrigation schedules and crop management through continuous, reliable field data.
Autonomous Interoperable Hubs
Autonomous interoperable hubs in precision agriculture enable seamless integration of diverse Internet of Things (IoT) devices, enhancing real-time data sharing and operational efficiency across farm connectivity networks. Unlike standalone equipment, these hubs centralize communication protocols, facilitating synchronized sensor data analysis and automated decision-making critical for optimizing crop management and resource utilization.
Low-Power WideArea Modules (LPWAN)
Low-Power Wide-Area Network (LPWAN) modules in Internet of Things (IoT) devices offer extensive farm connectivity with minimal energy consumption, enabling real-time monitoring and management of agricultural parameters over vast areas. Standalone equipment often lacks the scalable, low-power communication capabilities of LPWAN-enabled IoT systems, limiting efficient data transmission and integration needed for precision agriculture advancements.
Sensor-to-Cloud Bridge
Sensor-to-cloud bridge technology enhances farm connectivity by linking IoT devices directly to cloud platforms, enabling real-time data transmission for precise monitoring and management. Unlike standalone equipment, IoT-based solutions facilitate seamless integration of multiple sensors, delivering comprehensive insights to optimize crop yields and resource usage.
Smart Retrofit Kits
Smart retrofit kits transform traditional standalone farming equipment into interconnected IoT devices, enabling real-time data collection and remote management that enhance precision agriculture practices. These kits offer seamless integration with existing machinery, improving efficiency and reducing costs compared to investing in fully new IoT-enabled equipment.
Connected Data Silos
Internet of Things (IoT) devices in precision agriculture enable seamless integration of diverse farm data streams, breaking down connected data silos by providing real-time, centralized monitoring and control. In contrast, standalone equipment often generates isolated data sets that hinder comprehensive analysis and limit the potential for optimized decision-making in farm management.
Internet of Things (IoT) Devices vs Standalone Equipment for Farm Connectivity Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com