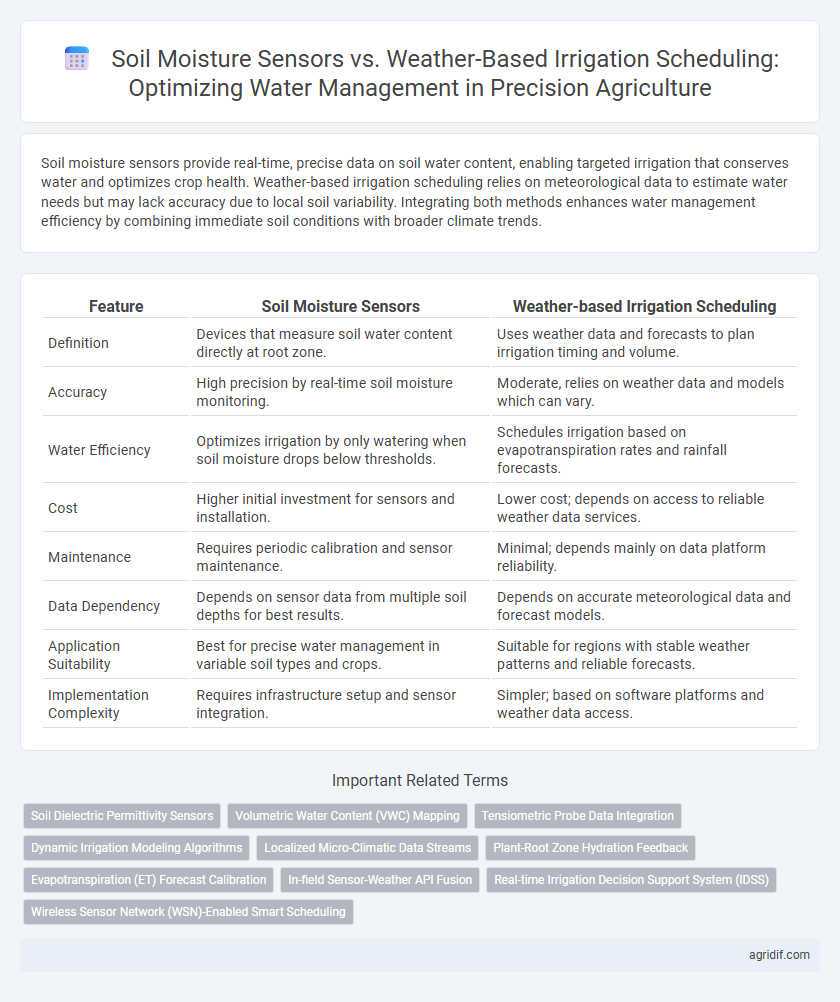
Soil moisture sensors provide real-time, precise data on soil water content, enabling targeted irrigation that conserves water and optimizes crop health. Weather-based irrigation scheduling relies on meteorological data to estimate water needs but may lack accuracy due to local soil variability. Integrating both methods enhances water management efficiency by combining immediate soil conditions with broader climate trends.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Soil Moisture Sensors | Weather-based Irrigation Scheduling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Devices that measure soil water content directly at root zone. | Uses weather data and forecasts to plan irrigation timing and volume. |
| Accuracy | High precision by real-time soil moisture monitoring. | Moderate, relies on weather data and models which can vary. |
| Water Efficiency | Optimizes irrigation by only watering when soil moisture drops below thresholds. | Schedules irrigation based on evapotranspiration rates and rainfall forecasts. |
| Cost | Higher initial investment for sensors and installation. | Lower cost; depends on access to reliable weather data services. |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic calibration and sensor maintenance. | Minimal; depends mainly on data platform reliability. |
| Data Dependency | Depends on sensor data from multiple soil depths for best results. | Depends on accurate meteorological data and forecast models. |
| Application Suitability | Best for precise water management in variable soil types and crops. | Suitable for regions with stable weather patterns and reliable forecasts. |
| Implementation Complexity | Requires infrastructure setup and sensor integration. | Simpler; based on software platforms and weather data access. |
Introduction to Precision Agriculture and Water Management
Precision agriculture integrates advanced technologies to optimize resource use and enhance crop productivity, with water management being a critical component. Soil moisture sensors provide real-time, localized data on soil water content, enabling precise irrigation tailored to crop needs. Weather-based irrigation scheduling uses meteorological information to predict water demand, supporting efficient irrigation timing and reducing water waste.
Understanding Soil Moisture Sensors: Technology and Benefits
Soil moisture sensors utilize technologies such as capacitance, resistance, and time-domain reflectometry to provide real-time data on soil water content, enabling precise irrigation decisions. These sensors improve water management by reducing over-irrigation, enhancing crop yield, and conserving water resources through accurate moisture monitoring at various root zone depths. Integration with automated irrigation systems allows farmers to optimize water usage based on actual soil conditions rather than relying on weather forecasts alone.
Overview of Weather-based Irrigation Scheduling Systems
Weather-based irrigation scheduling systems leverage real-time and forecasted meteorological data to optimize water application, reducing wastage and enhancing crop health. These systems integrate parameters such as temperature, humidity, rainfall, and evapotranspiration rates to predict irrigation needs accurately. By utilizing weather data, farmers achieve more efficient water management compared to traditional timer-based methods, although soil moisture sensors provide direct feedback from the root zone.
Key Differences Between Soil Moisture Sensors and Weather-based Scheduling
Soil moisture sensors provide real-time, localized data on soil water content, enabling precise irrigation decisions tailored to specific field conditions. Weather-based irrigation scheduling relies on forecasted rainfall and evapotranspiration rates to estimate crop water needs, which may not account for microclimate variations or soil heterogeneity. The key difference lies in the direct measurement of soil moisture versus the predictive nature of weather data, impacting irrigation accuracy and water use efficiency.
Accuracy and Real-time Data in Water Management
Soil moisture sensors provide precise, real-time data on soil water content, enabling targeted irrigation that prevents overwatering and conserves water resources. In contrast, weather-based irrigation scheduling relies on predictive models and historical climate data, which may lack the immediacy and localized accuracy required for optimal water management. Deploying soil moisture sensors enhances irrigation efficiency by directly measuring field conditions, resulting in improved crop health and reduced water waste.
Efficiency and Water Conservation Impact
Soil moisture sensors provide real-time, localized data enabling precise irrigation scheduling, significantly improving water use efficiency and reducing wastage by targeting crop water needs directly. Weather-based irrigation scheduling relies on forecast data and historical climate patterns to estimate irrigation timing, which may result in less accurate water application due to variability in microclimates and soil conditions. Studies indicate that integrating soil moisture sensors can enhance water conservation by up to 30% compared to weather-based methods, optimizing both crop yield and sustainability in precision agriculture systems.
Cost Implications and Economic Analysis
Soil moisture sensors provide real-time, field-specific data that optimize irrigation schedules, reducing water waste and energy costs but involve higher initial investment and maintenance expenses. Weather-based irrigation scheduling relies on external meteorological data, offering a lower upfront cost yet risks less precise water use that can lead to crop stress or over-irrigation, impacting overall yield and economic returns. Economic analysis shows soil moisture sensors can yield higher long-term savings and improved crop performance, justifying their cost for high-value crops and water-scarce regions.
Integration with Smart Farming Platforms
Soil moisture sensors provide real-time, localized data on water availability in the root zone, enabling precise irrigation decisions that reduce water waste and enhance crop health. Weather-based irrigation scheduling relies on meteorological data to estimate irrigation needs but may lack the granularity required for field-specific conditions, potentially leading to inefficiencies. Integrating soil moisture sensors with smart farming platforms allows for automated irrigation adjustments based on accurate soil data combined with weather forecasts, optimizing water management and improving overall farm productivity.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Soil moisture sensors offer precise, real-time data on soil water content, but they face challenges such as sensor calibration, installation costs, and limited spatial coverage. Weather-based irrigation scheduling relies on regional climate data, which can lead to inaccuracies due to microclimate variability and unpredictable rainfall patterns. Both approaches require integration with robust decision-support systems to overcome limitations in data accuracy and ensure efficient water management in precision agriculture.
Choosing the Right Irrigation Strategy for Precision Agriculture
Soil moisture sensors provide real-time, site-specific data that enables precise irrigation scheduling by directly measuring the water content in the root zone, enhancing water use efficiency and crop yield. Weather-based irrigation scheduling relies on meteorological data and evapotranspiration models to estimate crop water needs but may lack accuracy in heterogeneous field conditions. Selecting the right irrigation strategy involves assessing factors such as crop type, soil variability, and available technology to optimize water management in precision agriculture.
Related Important Terms
Soil Dielectric Permittivity Sensors
Soil dielectric permittivity sensors offer precise, real-time soil moisture data by measuring the soil's ability to store and transmit electrical signals, enabling optimized irrigation scheduling that reduces water waste and improves crop yield. Unlike weather-based irrigation scheduling, which relies on external climatic conditions and predictive models, these sensors provide site-specific soil moisture insights critical for efficient water management in precision agriculture.
Volumetric Water Content (VWC) Mapping
Soil moisture sensors provide precise Volumetric Water Content (VWC) mapping by directly measuring water levels in the root zone, enabling targeted irrigation decisions that improve water efficiency and crop yield. In contrast, weather-based irrigation scheduling relies on evapotranspiration data and climatic forecasts, which can lack spatial resolution and result in less accurate VWC estimates for optimal irrigation management.
Tensiometric Probe Data Integration
Tensiometric probes provide precise soil moisture measurements critical for optimizing irrigation timing, enhancing water use efficiency in precision agriculture. Integrating data from these sensors into irrigation scheduling systems improves decision-making accuracy compared to weather-based models alone, reducing overwatering and conserving water resources.
Dynamic Irrigation Modeling Algorithms
Soil moisture sensors provide real-time, field-specific data that enhances the accuracy of dynamic irrigation modeling algorithms by directly measuring soil water content, leading to optimized water application and improved crop yield. Weather-based irrigation scheduling relies on predictive climate data but may lack the granularity and responsiveness offered by sensor-driven models, which adjust irrigation dynamically based on immediate soil moisture variations.
Localized Micro-Climatic Data Streams
Soil moisture sensors provide real-time, localized micro-climatic data streams that enable precise irrigation scheduling based on actual soil water content, reducing water waste and enhancing crop yield. In contrast, weather-based irrigation scheduling relies on regional forecasts and models, which may overlook field-specific soil moisture variability and microclimatic conditions essential for optimizing water management.
Plant-Root Zone Hydration Feedback
Soil moisture sensors provide real-time, precise measurements of water levels directly within the plant-root zone, enabling targeted irrigation that optimizes water use efficiency and enhances crop health. In contrast, weather-based irrigation scheduling relies on external climatic data, which may not accurately reflect the actual hydration status of the root zone, potentially leading to under- or over-irrigation.
Evapotranspiration (ET) Forecast Calibration
Soil moisture sensors provide real-time, site-specific data that enables precise calibration of evapotranspiration (ET) forecasts, improving irrigation scheduling accuracy and water use efficiency. In contrast, weather-based irrigation scheduling relies on generalized ET models that may lack local soil moisture feedback, potentially leading to over- or under-irrigation in variable field conditions.
In-field Sensor-Weather API Fusion
In-field sensor-weather API fusion enhances water management in precision agriculture by integrating real-time soil moisture sensor data with localized weather forecasts, enabling dynamic irrigation scheduling that optimizes water use efficiency and crop health. This hybrid approach improves decision-making accuracy over standalone soil moisture sensors or weather-based systems by accounting for both immediate soil conditions and predictive environmental factors.
Real-time Irrigation Decision Support System (IDSS)
Soil moisture sensors provide precise, real-time data on soil water content, enabling irrigation decision support systems (IDSS) to optimize water application based on actual crop needs, reducing water waste and improving yield. Weather-based irrigation scheduling relies on predictive data from meteorological forecasts, which can be less accurate for immediate irrigation decisions compared to sensor-driven IDSS that adjust watering dynamically based on in-field conditions.
Wireless Sensor Network (WSN)-Enabled Smart Scheduling
Wireless Sensor Network (WSN)-enabled soil moisture sensors provide real-time, precise soil water content data, enhancing irrigation scheduling accuracy compared to traditional weather-based models that rely on forecasted conditions. This technology reduces water waste and improves crop yield by enabling site-specific irrigation adjustments, optimizing water use efficiency under variable environmental conditions.
Soil Moisture Sensors vs Weather-based Irrigation Scheduling for Water Management Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com