Variable rate fertilizer application optimizes nutrient management by tailoring fertilizer amounts to the specific needs of different soil zones, enhancing crop yield and reducing waste. Uniform rate fertilizer applies the same nutrient level across the entire field, often leading to over-application in some areas and under-application in others. Precision agriculture technologies enable variable rate fertilization to improve nutrient use efficiency and minimize environmental impact compared to uniform rate strategies.
Table of Comparison
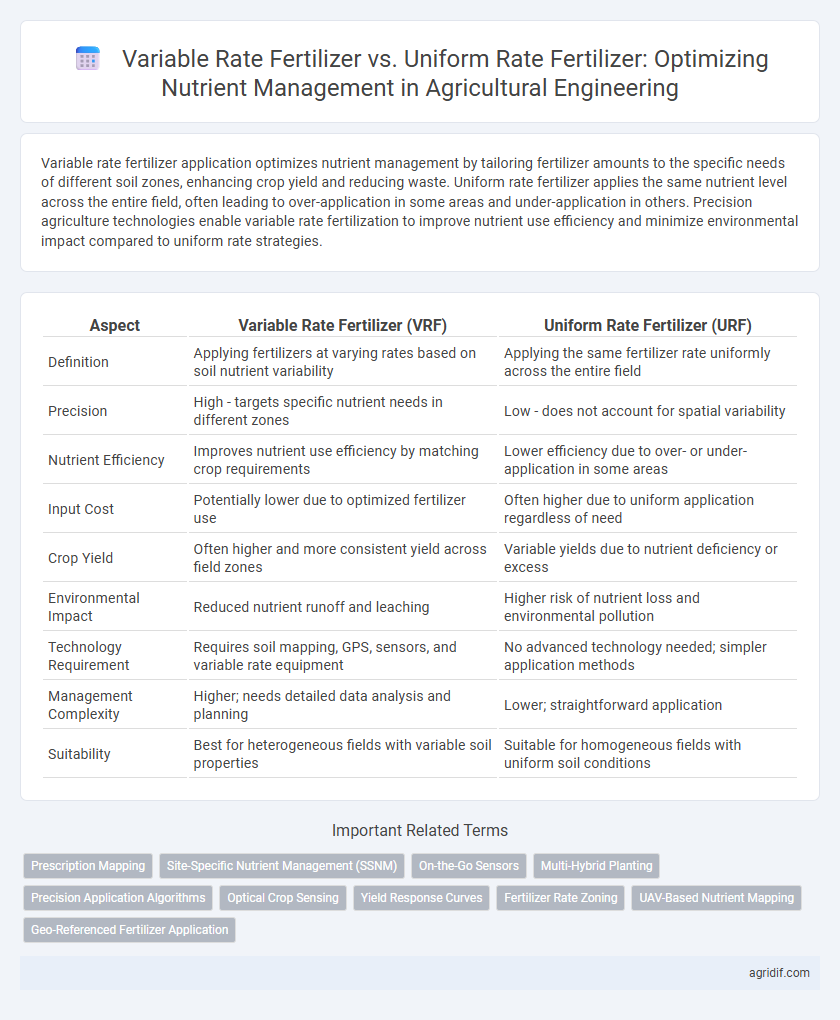
| Aspect | Variable Rate Fertilizer (VRF) | Uniform Rate Fertilizer (URF) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Applying fertilizers at varying rates based on soil nutrient variability | Applying the same fertilizer rate uniformly across the entire field |
| Precision | High - targets specific nutrient needs in different zones | Low - does not account for spatial variability |
| Nutrient Efficiency | Improves nutrient use efficiency by matching crop requirements | Lower efficiency due to over- or under-application in some areas |
| Input Cost | Potentially lower due to optimized fertilizer use | Often higher due to uniform application regardless of need |
| Crop Yield | Often higher and more consistent yield across field zones | Variable yields due to nutrient deficiency or excess |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced nutrient runoff and leaching | Higher risk of nutrient loss and environmental pollution |
| Technology Requirement | Requires soil mapping, GPS, sensors, and variable rate equipment | No advanced technology needed; simpler application methods |
| Management Complexity | Higher; needs detailed data analysis and planning | Lower; straightforward application |
| Suitability | Best for heterogeneous fields with variable soil properties | Suitable for homogeneous fields with uniform soil conditions |
Introduction to Fertilizer Application Methods
Variable rate fertilizer application optimizes nutrient distribution by adjusting inputs based on soil variability and crop requirements, enhancing fertilizer use efficiency and reducing environmental impact. Uniform rate fertilizer applies a consistent nutrient amount across a field, which may result in over- or under-fertilization in heterogeneous soils, leading to nutrient wastage and potential yield loss. Advanced technologies like GPS and soil sensors enable precise variable rate application, promoting sustainable nutrient management in modern agricultural engineering.
Principles of Variable Rate Fertilizer Application
Variable rate fertilizer application optimizes nutrient management by applying precise amounts of fertilizers based on spatial soil variability and crop needs, enhancing nutrient use efficiency and crop yield. This technology leverages GPS, soil sensors, and yield monitors to create prescription maps, ensuring site-specific nutrient delivery and minimizing environmental impacts. Compared to uniform rate fertilizer application, which applies a consistent fertilizer quantity across fields regardless of variability, variable rate application reduces waste, cost, and nutrient runoff while promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
Understanding Uniform Rate Fertilizer Application
Uniform rate fertilizer application involves delivering a consistent amount of nutrients across an entire field regardless of soil variability, which simplifies management but can lead to inefficient nutrient use and environmental runoff. This method often results in over-application in fertile zones and under-application in nutrient-deficient areas, reducing crop yield potential and increasing input costs. Advances in soil testing and precision agriculture highlight the limitations of uniform application by demonstrating the benefits of targeted nutrient management through variable rate technology.
Key Technologies Enabling Variable Rate Application
Variable rate fertilizer application relies on cutting-edge technologies such as GPS mapping, remote sensing, and soil nutrient sensors to deliver precise nutrient doses tailored to specific field zones. Advanced data analytics and machine learning algorithms process spatial and temporal field variability, enabling optimized nutrient management that improves crop yield and reduces environmental impact. In contrast, uniform rate fertilizer applies a constant nutrient level across the entire field, often leading to over- or under-fertilization in heterogeneous soil conditions.
Soil Variability and Its Impact on Fertilizer Efficiency
Variable rate fertilizer (VRF) application enhances nutrient management by adjusting input based on soil variability, improving fertilizer use efficiency compared to uniform rate fertilizer (URF) that applies a constant dose regardless of spatial differences. Soil heterogeneity in nutrient content, texture, and moisture significantly affects fertilizer uptake, making VRF more effective in addressing site-specific needs and reducing nutrient losses. Employing VRF technology optimizes crop yield, minimizes environmental impact, and increases economic returns by targeting precise nutrient requirements throughout the field.
Economic Benefits of Variable vs Uniform Rate Fertilization
Variable rate fertilization enhances nutrient use efficiency by tailoring applications to specific soil conditions, reducing waste and input costs. Studies show that variable rate strategies can increase crop yields by up to 15%, translating into higher profit margins compared to uniform rate methods. Economic benefits stem from optimized fertilizer allocation, minimizing over-application and environmental impact while maximizing return on investment in agricultural inputs.
Environmental Implications of Fertilizer Application Methods
Variable rate fertilizer application optimizes nutrient delivery by adjusting inputs according to soil variability, significantly reducing nutrient runoff and leaching compared to uniform rate methods. Precision in nutrient placement mitigates environmental impacts such as eutrophication and groundwater contamination by ensuring crops receive only the required amount of fertilizers. Research indicates that variable rate technology enhances nutrient use efficiency, leading to improved soil health and lower greenhouse gas emissions from fertilizer over-application.
Precision Agriculture Tools for Nutrient Management
Variable rate fertilizer application utilizes GPS and sensor data to deliver nutrients precisely where needed, enhancing nutrient use efficiency and reducing environmental impact. Uniform rate fertilizer applies nutrients evenly across a field, often leading to over- or under-fertilization in varying soil conditions. Precision agriculture tools, such as soil nutrient mapping and yield monitors, enable optimized nutrient management through site-specific fertilization strategies.
Challenges in Adopting Variable Rate Fertilizer Techniques
Variable rate fertilizer techniques face challenges such as high initial investment costs for precision equipment and the need for detailed soil nutrient mapping, which requires advanced data collection and analysis skills. Inconsistent field variability and equipment calibration difficulties can lead to uneven nutrient application, impacting crop yield and efficiency. Limited access to technology and lack of farmer training further hinder widespread adoption of variable rate fertilization in nutrient management.
Future Trends in Smart Fertilizer Application
Variable rate fertilizer application leverages precision agriculture technologies, such as GPS and soil sensors, to optimize nutrient delivery based on spatial variability, enhancing crop yield and minimizing environmental impact. Future trends include integrating machine learning algorithms and real-time data analytics to further refine nutrient prescriptions, enabling adaptive management in response to weather patterns and crop growth stages. This shift toward smart fertilizer application promises increased efficiency, sustainability, and reduced input costs compared to uniform rate fertilizer methods.
Related Important Terms
Prescription Mapping
Variable rate fertilizer application leverages prescription mapping technology to optimize nutrient distribution based on soil variability, crop needs, and yield potential, enhancing nutrient use efficiency and minimizing environmental impact. Uniform rate fertilizer applies nutrients evenly across fields, often resulting in over- or under-application, reducing fertilizer efficiency and increasing the risk of nutrient runoff.
Site-Specific Nutrient Management (SSNM)
Variable rate fertilizer application in Site-Specific Nutrient Management (SSNM) optimizes nutrient delivery by adjusting rates based on soil variability, enhancing crop yield and reducing environmental impact compared to uniform rate fertilizer application that applies a consistent nutrient dose regardless of spatial soil differences. Precision technologies such as GPS and remote sensing enable real-time data collection and variable rate adjustments, improving nutrient use efficiency and supporting sustainable agriculture practices.
On-the-Go Sensors
On-the-Go sensors in variable rate fertilizer application optimize nutrient management by real-time soil and crop condition assessment, significantly enhancing fertilizer use efficiency compared to uniform rate methods. This technology reduces nutrient wastage and environmental impact while improving crop yield through precise, site-specific nutrient delivery.
Multi-Hybrid Planting
Variable rate fertilizer application in multi-hybrid planting enhances nutrient use efficiency by delivering precise nutrient amounts tailored to the specific hybrid's growth requirements, leading to improved yield and reduced environmental impact. Uniform rate fertilizer often results in nutrient imbalances and suboptimal growth because it does not account for the varying nutrient demands of different hybrids within the same field.
Precision Application Algorithms
Variable rate fertilizer application leverages precision application algorithms to tailor nutrient delivery based on spatial variability in soil nutrient levels, crop type, and growth stage, optimizing input efficiency and yield outcomes. In contrast, uniform rate fertilizer applies a constant nutrient dose across the field, often leading to nutrient under- or over-application and suboptimal resource use.
Optical Crop Sensing
Variable rate fertilizer application using optical crop sensing technology enhances nutrient management by adjusting nutrient delivery precisely based on real-time crop variability and canopy reflectance data, optimizing fertilizer efficiency and minimizing environmental impact. Uniform rate fertilizer application lacks this precision, often leading to nutrient overuse or deficiency, reducing crop yield potential and increasing input costs.
Yield Response Curves
Variable rate fertilizer application optimizes nutrient distribution based on site-specific soil fertility data, resulting in more efficient nutrient utilization and a steeper yield response curve compared to uniform rate fertilizer. This tailored approach minimizes nutrient waste and enhances crop productivity by addressing spatial variability within fields, leading to increased yield and environmental sustainability.
Fertilizer Rate Zoning
Variable rate fertilizer application enhances nutrient management by tailoring fertilizer zones based on soil variability and crop nutrient requirements, leading to improved nutrient use efficiency and higher yields. Uniform rate fertilizer application often results in over- or under-application in certain zones, causing nutrient imbalances, increased input costs, and potential environmental risks such as nutrient leaching or runoff.
UAV-Based Nutrient Mapping
UAV-based nutrient mapping enables precise detection of spatial variability in crop nutrient status, allowing for variable rate fertilizer application that optimizes nutrient use efficiency and minimizes environmental impact. Uniform rate fertilizer application often leads to over- or under-fertilization in different field zones, reducing overall crop yield and increasing costs compared to site-specific management enabled by UAV technology.
Geo-Referenced Fertilizer Application
Geo-referenced variable rate fertilizer application enhances nutrient management by tailoring fertilizer inputs to spatial soil fertility variations, optimizing crop yield and reducing environmental impact compared to uniform rate fertilizer application. Precision agriculture technologies, such as GPS and remote sensing, enable accurate mapping and site-specific nutrient delivery, improving resource use efficiency and farm profitability.
Variable rate fertilizer vs Uniform rate fertilizer for nutrient management Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com