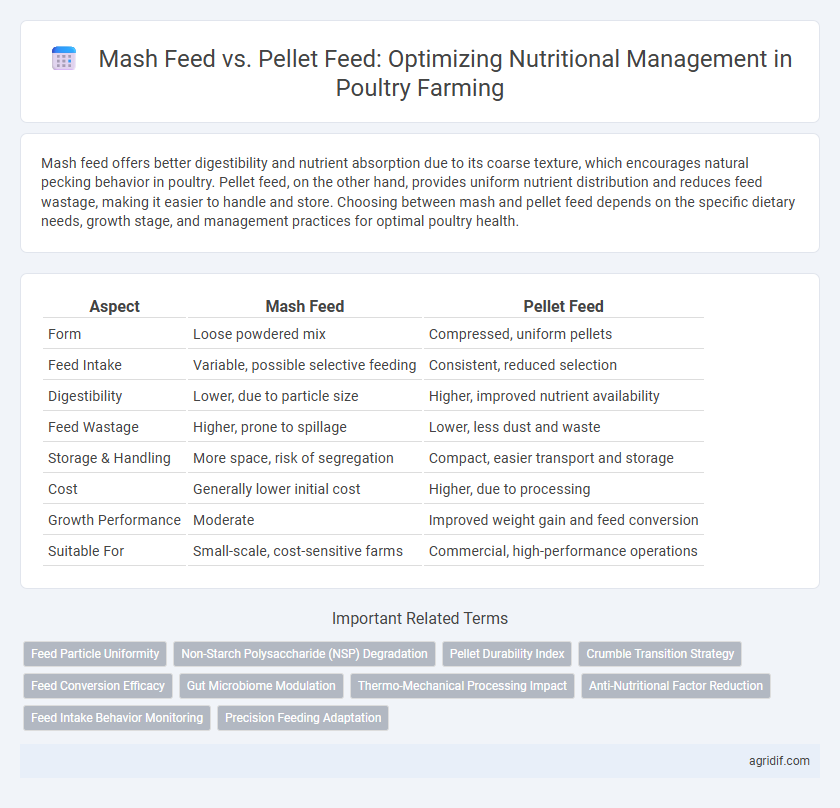
Mash feed offers better digestibility and nutrient absorption due to its coarse texture, which encourages natural pecking behavior in poultry. Pellet feed, on the other hand, provides uniform nutrient distribution and reduces feed wastage, making it easier to handle and store. Choosing between mash and pellet feed depends on the specific dietary needs, growth stage, and management practices for optimal poultry health.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Mash Feed | Pellet Feed |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Loose powdered mix | Compressed, uniform pellets |
| Feed Intake | Variable, possible selective feeding | Consistent, reduced selection |
| Digestibility | Lower, due to particle size | Higher, improved nutrient availability |
| Feed Wastage | Higher, prone to spillage | Lower, less dust and waste |
| Storage & Handling | More space, risk of segregation | Compact, easier transport and storage |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher, due to processing |
| Growth Performance | Moderate | Improved weight gain and feed conversion |
| Suitable For | Small-scale, cost-sensitive farms | Commercial, high-performance operations |
Introduction to Mash Feed and Pellet Feed
Mash feed consists of a loose mixture of ground grains, protein sources, vitamins, and minerals designed for easy consumption in poultry diets, promoting consistent nutrient intake and digestive efficiency. Pellet feed is formed by compressing mash ingredients into dense, uniform shapes that reduce feed waste and improve palatability, enhancing feed conversion ratios in poultry production. Both feed types play crucial roles in optimizing nutritional management tailored to poultry growth stages and production goals.
Nutritional Composition: Mash vs Pellet Feeds
Mash feed retains more intact nutrients like vitamins and enzymes, providing better digestibility for poultry, while pellet feed undergoes heat and pressure that can slightly reduce heat-sensitive vitamins but improves feed intake and nutrient utilization efficiency. Pellet feed often contains higher energy density due to compacting ingredients, promoting faster growth rates but may have lower fiber content compared to mash feed. Nutritionally, mash feed offers variability for targeted micronutrient supplementation, whereas pellet feed ensures uniform nutrient distribution essential for consistent poultry performance.
Digestibility and Feed Conversion Efficiency
Mash feed offers higher digestibility due to its coarse texture, promoting better enzyme activity and nutrient absorption in poultry. Pellet feed enhances feed conversion efficiency by reducing feed wastage and encouraging uniform intake, leading to improved growth rates and weight gain. Optimizing dietary formulations with pellet feed can maximize nutrient utilization and overall production performance in poultry farming.
Impact on Poultry Growth and Productivity
Mash feed enhances feed intake and digestion due to its loose texture, promoting steady poultry growth and efficient nutrient absorption. Pellet feed improves feed conversion ratio and weight gain by reducing feed wastage and increasing uniform nutrient consumption. Optimizing feed form according to poultry age and production goals significantly boosts overall productivity and profitability in poultry farming.
Feed Uniformity and Palatability
Pellet feed offers superior feed uniformity compared to mash feed, ensuring consistent nutrient intake essential for optimal poultry growth and health. The processing of pellet feed enhances palatability by improving texture and reducing feed wastage, leading to higher feed consumption rates. Mash feed, while less uniform, allows for easier inclusion of certain additives but may result in selective feeding and nutrient imbalance.
Storage, Handling, and Feed Wastage
Mash feed requires more careful storage to prevent moisture absorption and contamination, while pellet feed's compact form enhances durability and reduces spoilage during handling. Pellets minimize feed wastage due to their uniform shape and reduced dust, improving feed intake efficiency in poultry. Proper handling of pellet feed also decreases the likelihood of feed segregation, ensuring consistent nutritional delivery to poultry.
Cost Implications in Mash and Pellet Feeding
Mash feed typically incurs lower initial processing costs but can lead to higher feed wastage, increasing overall expenses in poultry farming. Pellet feed, despite higher production and equipment costs, enhances feed conversion efficiency and reduces waste, potentially lowering long-term feeding costs. Economic decisions in mash versus pellet feeding hinge on balancing upfront investments against feed utilization and poultry growth performance.
Disease Control and Hygiene Factors
Mash feed in poultry farming promotes better disease control by reducing the risk of feed contamination, as its coarse texture discourages mold and bacteria growth compared to pellet feed. Pellet feed, while nutritionally balanced and energy-dense, can retain moisture leading to higher hygiene risks if not stored properly, increasing the chance of pathogen proliferation. Effective nutritional management requires selecting feed types that minimize microbial hazards; thus, mash feed offers improved hygiene advantages critical for maintaining flock health.
Suitability for Different Poultry Ages and Breeds
Mash feed offers flexibility in particle size and nutrient composition, making it suitable for young chicks and small breeds that require gradual adaptation to solid feed. Pellet feed provides uniform density and higher energy concentration, ideal for fast-growing broilers and larger breeds to support rapid weight gain and efficient digestion. Selecting the appropriate feed form based on poultry age and breed optimizes nutrient absorption and enhances overall flock performance.
Practical Recommendations for Nutritional Management
Mash feed offers flexibility in ingredient adjustment and is ideal for young poultry requiring gradual dietary transitions, while pellet feed ensures uniform nutrient intake and boosts feed efficiency in mature birds. Nutritional management should prioritize pellet feed to enhance growth rates, digestibility, and reduce feed wastage, especially in large-scale operations. Implementing a phase-feeding strategy with pellet feed can optimize nutrient utilization, minimize feed costs, and improve overall flock performance.
Related Important Terms
Feed Particle Uniformity
Feed particle uniformity in poultry farming directly influences nutrient digestibility and intake efficiency, with pellet feed generally providing more consistent particle size compared to mash feed. Uniform pellets reduce selective feeding and feed wastage, enhancing overall nutritional management and bird performance.
Non-Starch Polysaccharide (NSP) Degradation
Pellet feed enhances Non-Starch Polysaccharide (NSP) degradation more effectively than mash feed due to its higher digestibility and uniform nutrient composition, promoting better enzyme interaction in the gut. Improved NSP breakdown in pellet feed supports enhanced nutrient absorption and growth performance in poultry, optimizing overall nutritional management.
Pellet Durability Index
Pellet Feed offers superior nutritional management in poultry farming due to its high Pellet Durability Index (PDI), which ensures less feed fines and reduced nutrient segregation during handling and feeding. A higher PDI enhances feed conversion efficiency and minimizes wastage compared to Mash Feed, supporting optimal growth and health in poultry.
Crumble Transition Strategy
Crumble feed offers an effective transition strategy from mash to pellet feed by combining the nutritional benefits of pellets with the ease of consumption found in mash, promoting better digestion and growth in poultry. Implementing crumble feed during early stages enhances feed intake consistency and nutrient absorption, crucial for optimizing poultry health and production efficiency.
Feed Conversion Efficacy
Pellet feed significantly improves feed conversion efficacy by reducing wastage and promoting uniform nutrient intake compared to mash feed, which often results in selective feeding and uneven nutrient consumption. Research shows poultry fed with pellet feed exhibit higher weight gain and better feed efficiency ratios, enhancing overall growth performance and cost-effectiveness in poultry farming.
Gut Microbiome Modulation
Pellet feed enhances nutrient digestibility and supports beneficial gut microbiota growth more effectively than mash feed, promoting a balanced gut microbiome in poultry. Improved microbial diversity from pellet feed contributes to better immune response and overall poultry health compared to mash feed counterparts.
Thermo-Mechanical Processing Impact
Thermo-mechanical processing in pellet feed enhances nutrient digestibility and feed intake by altering the physical structure, offering improved energy utilization compared to mash feed. While mash feed retains original ingredient textures, pellet feed's processing increases starch gelatinization and protein denaturation, optimizing nutrient absorption in poultry farming.
Anti-Nutritional Factor Reduction
Pellet feed enhances nutrient bioavailability by reducing anti-nutritional factors such as phytates and tannins through heat processing, leading to improved digestibility and growth performance in poultry. Conversely, mash feed retains higher levels of these compounds, potentially limiting nutrient absorption and overall flock productivity.
Feed Intake Behavior Monitoring
Mash feed allows chickens to exhibit natural pecking behavior, facilitating more precise monitoring of individual feed intake and reducing wastage, whereas pellet feed promotes uniform consumption but can mask subtle variations in feeding patterns. Effective feed intake behavior monitoring through mash diets can enhance nutritional management by enabling timely adjustments to feeding strategies that optimize growth and health.
Precision Feeding Adaptation
Mash feed enables tailored nutrient blending for precise poultry diet formulations, enhancing individual bird performance through customized ingredient ratios. Pellet feed offers uniform nutrient distribution and reduces feed wastage, supporting automated precision feeding systems that optimize growth and feed conversion efficiency.
Mash Feed vs Pellet Feed for Nutritional Management Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com