Drone imaging offers high-resolution, real-time data ideal for precise field scouting, enabling targeted interventions at the crop level. Satellite imaging covers larger areas with frequent revisits but may suffer from lower resolution and cloud interference, limiting detailed analysis. Integrating both technologies maximizes field monitoring efficiency by combining detailed local insights from drones with broad-scale, consistent satellite data.
Table of Comparison
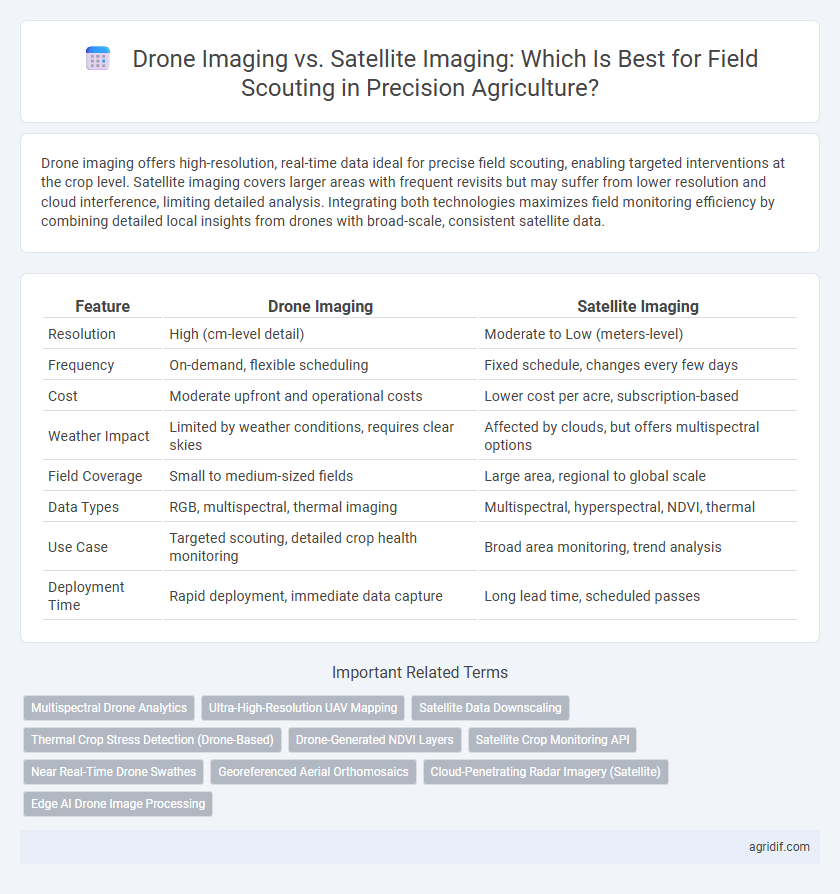
| Feature | Drone Imaging | Satellite Imaging |
|---|---|---|
| Resolution | High (cm-level detail) | Moderate to Low (meters-level) |
| Frequency | On-demand, flexible scheduling | Fixed schedule, changes every few days |
| Cost | Moderate upfront and operational costs | Lower cost per acre, subscription-based |
| Weather Impact | Limited by weather conditions, requires clear skies | Affected by clouds, but offers multispectral options |
| Field Coverage | Small to medium-sized fields | Large area, regional to global scale |
| Data Types | RGB, multispectral, thermal imaging | Multispectral, hyperspectral, NDVI, thermal |
| Use Case | Targeted scouting, detailed crop health monitoring | Broad area monitoring, trend analysis |
| Deployment Time | Rapid deployment, immediate data capture | Long lead time, scheduled passes |
Introduction to Remote Sensing in Precision Agriculture
Drone imaging provides high-resolution, real-time data for precise field scouting, enabling targeted crop management and early detection of stress factors. Satellite imaging offers broader coverage with frequent revisit times, facilitating large-scale monitoring and temporal analysis of crop health across diverse agricultural landscapes. Integrating both remote sensing technologies enhances decision-making accuracy, optimizing yield and resource efficiency in precision agriculture.
Overview of Drone Imaging Technology
Drone imaging technology in precision agriculture offers high-resolution, real-time data collection essential for accurate field scouting. Equipped with multispectral and thermal sensors, drones capture detailed crop health indicators, enabling targeted interventions and yield optimization. Their flexibility and low-altitude operation provide superior spatial resolution compared to satellite imaging, making them invaluable for monitoring small to medium-sized fields.
Overview of Satellite Imaging Technology
Satellite imaging technology utilizes high-resolution sensors aboard orbiting satellites to capture extensive, multispectral data over large agricultural fields, enabling comprehensive monitoring of crop health, soil conditions, and water stress. This method offers frequent revisits with global coverage, facilitating time-series analysis and large-scale field scouting without the constraints of local weather or terrain. Advanced satellite platforms incorporate synthetic aperture radar (SAR) and hyperspectral imaging, enhancing precision agriculture through accurate vegetation indices and early detection of crop anomalies.
Resolution and Accuracy: Drones vs Satellite Imagery
Drone imaging offers significantly higher resolution and accuracy for field scouting compared to satellite imagery, capturing detailed crop conditions at centimeter-level precision. Satellites provide broader coverage but typically at lower spatial resolutions, ranging from 10 to 30 meters per pixel, limiting fine-scale analysis. The enhanced detail from drone imagery enables precise identification of crop stress, pest infestations, and nutrient deficiencies, improving targeted interventions in precision agriculture.
Coverage and Scalability in Field Scouting
Drone imaging provides high-resolution, real-time data ideal for detailed field scouting over smaller, targeted areas, ensuring precise crop health monitoring and early pest detection. Satellite imaging covers extensive agricultural landscapes efficiently, enabling scalable analysis across vast fields but with lower spatial resolution and less frequent data collection. Combining drone and satellite imaging optimizes coverage and scalability, balancing detailed local insights with broad regional assessments for comprehensive precision agriculture management.
Temporal Frequency: How Often Can You Scout?
Drone imaging enables high temporal frequency with the ability to scout fields multiple times per week, offering real-time data for timely decision-making. Satellite imaging typically provides lower temporal frequency, with revisit times ranging from several days to weeks depending on the satellite constellation, which may delay critical interventions. Precision agriculture benefits from the complementary use of drones for frequent, targeted scouting and satellites for broader, periodic field monitoring.
Weather and Environmental Limitations
Drone imaging offers superior flexibility in precision agriculture due to its ability to capture high-resolution images under variable weather conditions, including partial cloud cover and low visibility. Satellite imaging often faces limitations from atmospheric disturbances, such as heavy clouds, fog, or precipitation, which can obstruct or degrade image quality and delay data acquisition. Environmental factors like wind speed and crop canopy height also influence drone flight capability and image clarity, whereas satellites provide broader spatial coverage but with less temporal responsiveness to immediate field scouting needs.
Data Processing and Analysis Capabilities
Drone imaging offers high-resolution, real-time data with advanced multispectral and thermal sensors, enabling precise crop health assessments and targeted interventions. Satellite imaging provides broader coverage with frequent revisit times, but data processing often involves complex algorithms for cloud removal and spatial resolution enhancement, limiting granularity. Integrated platforms combining drone data with satellite imagery enhance analysis capabilities by merging detailed field-level information with large-scale environmental trends.
Cost Considerations and ROI Comparison
Drone imaging offers lower initial investment and operational costs compared to satellite imaging, making it more accessible for small to medium-sized farms. Satellite imaging, while carrying higher subscription fees and delayed image updates, provides broader field coverage and scalability for large-scale agricultural operations. Evaluating ROI reveals drones deliver faster, detailed data for targeted interventions, whereas satellites maximize cost-efficiency over extensive acreage with less frequent but continuous monitoring.
Choosing the Right Imaging Solution for Your Farm
Drone imaging offers high-resolution, real-time data ideal for detailed crop health analysis and precise field scouting. Satellite imaging provides broader coverage and frequent revisit times, making it suitable for monitoring large-scale farms and tracking seasonal changes. Selecting the right imaging solution depends on farm size, budget, required data resolution, and specific crop management goals.
Related Important Terms
Multispectral Drone Analytics
Multispectral drone analytics provide high-resolution, real-time data crucial for precision agriculture by capturing detailed crop health indicators such as NDVI and chlorophyll levels, enabling targeted interventions and improved yield predictions. Compared to satellite imaging, drones offer greater accuracy and flexibility in field scouting, unaffected by cloud cover and capable of frequent flights to monitor dynamic crop conditions.
Ultra-High-Resolution UAV Mapping
Ultra-high-resolution UAV mapping offers precision agriculture unparalleled detail with sub-centimeter accuracy, enabling identification of crop stress, pest infestations, and nutrient deficiencies at an early stage. Unlike satellite imaging's coarse pixel resolution and limited revisit frequency, drone imaging provides flexible, on-demand flights and superior spatial granularity, allowing targeted interventions and optimizing yield potential.
Satellite Data Downscaling
Satellite data downscaling enhances the spatial resolution of broad satellite imagery, enabling more detailed and accurate field scouting compared to conventional coarse-resolution images. This technique allows precision agriculture to leverage high-frequency satellite passes combined with localized ground truth data, improving crop health monitoring and resource management efficiency.
Thermal Crop Stress Detection (Drone-Based)
Drone imaging offers high-resolution thermal sensors that enable precise detection of crop stress at the leaf level, allowing timely intervention to mitigate yield loss. Satellite imaging provides broader coverage but lacks the spatial and temporal resolution of drones, making drone-based thermal scouting more effective for localized stress detection in precision agriculture.
Drone-Generated NDVI Layers
Drone-generated NDVI layers offer higher spatial resolution and real-time data acquisition compared to satellite imaging, enabling more precise monitoring of crop health and stress patterns at the field level. This enhanced detail improves decision-making for targeted interventions, optimizing resource use and increasing crop yields in precision agriculture.
Satellite Crop Monitoring API
Satellite Crop Monitoring API delivers high-resolution multispectral data for precise crop health analysis, enabling real-time monitoring of large agricultural fields with extensive spatial coverage. Compared to drone imaging, satellite imaging offers consistent temporal data access and seamless integration into farm management systems for efficient decision-making in precision agriculture.
Near Real-Time Drone Swathes
Drone imaging offers high-resolution, near real-time swathes that enable precise monitoring of crop health and timely identification of stress zones, outperforming satellite imaging in data freshness and spatial detail. These drone-captured swathes facilitate rapid decision-making in precision agriculture by providing actionable insights within minutes, enhancing field scouting efficiency and crop management accuracy.
Georeferenced Aerial Orthomosaics
Drone imaging provides high-resolution, geo-referenced aerial orthomosaics that enable precise field scouting with centimeter-level accuracy, facilitating detailed crop health analysis and localized intervention. Satellite imaging offers broader coverage and frequent revisit times but lacks the spatial resolution and real-time data precision necessary for fine-scale agricultural management.
Cloud-Penetrating Radar Imagery (Satellite)
Cloud-penetrating radar imagery from satellites provides reliable, weather-independent data critical for precision agriculture, enabling consistent monitoring of crop health and soil moisture under diverse atmospheric conditions. Unlike drone imaging, satellite radar can cover extensive areas rapidly, offering scalable field scouting solutions that enhance decision-making accuracy and resource management.
Edge AI Drone Image Processing
Edge AI drone image processing enables real-time, high-resolution analysis of crop health and stress conditions, outperforming satellite imaging by providing detailed, localized data with minimal latency. This technology enhances precision agriculture by facilitating timely decision-making and targeted interventions while reducing dependency on cloud-based processing and large data transmission.
Drone Imaging vs Satellite Imaging for Field Scouting Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com