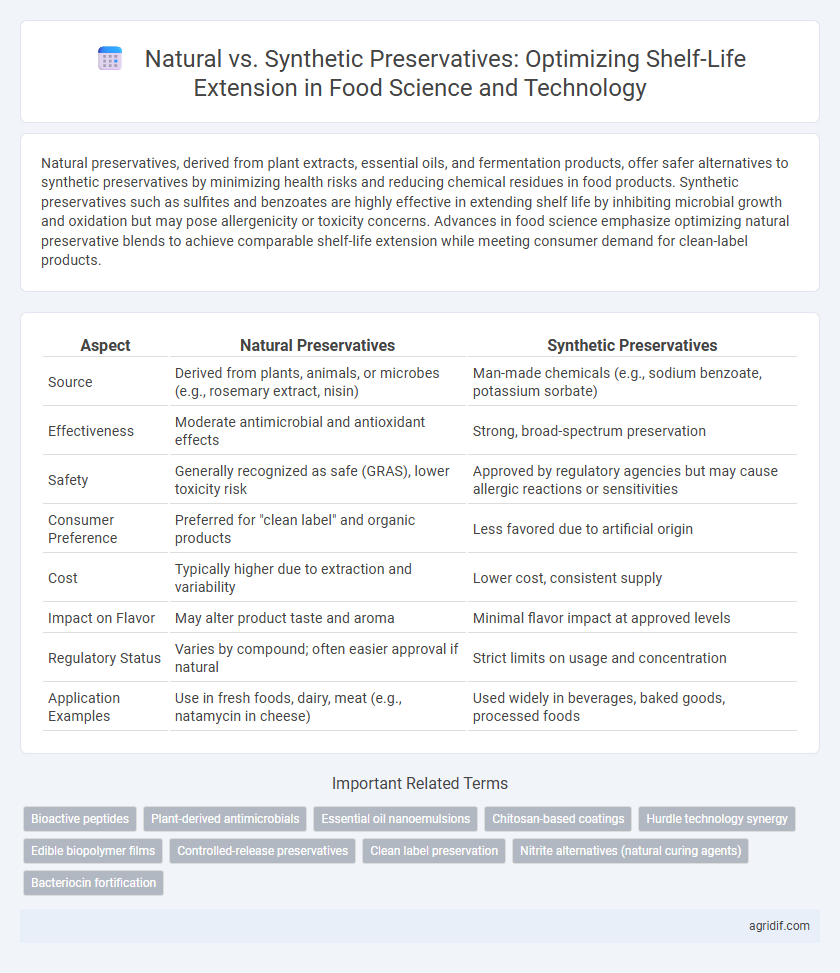
Natural preservatives, derived from plant extracts, essential oils, and fermentation products, offer safer alternatives to synthetic preservatives by minimizing health risks and reducing chemical residues in food products. Synthetic preservatives such as sulfites and benzoates are highly effective in extending shelf life by inhibiting microbial growth and oxidation but may pose allergenicity or toxicity concerns. Advances in food science emphasize optimizing natural preservative blends to achieve comparable shelf-life extension while meeting consumer demand for clean-label products.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Natural Preservatives | Synthetic Preservatives |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Derived from plants, animals, or microbes (e.g., rosemary extract, nisin) | Man-made chemicals (e.g., sodium benzoate, potassium sorbate) |
| Effectiveness | Moderate antimicrobial and antioxidant effects | Strong, broad-spectrum preservation |
| Safety | Generally recognized as safe (GRAS), lower toxicity risk | Approved by regulatory agencies but may cause allergic reactions or sensitivities |
| Consumer Preference | Preferred for "clean label" and organic products | Less favored due to artificial origin |
| Cost | Typically higher due to extraction and variability | Lower cost, consistent supply |
| Impact on Flavor | May alter product taste and aroma | Minimal flavor impact at approved levels |
| Regulatory Status | Varies by compound; often easier approval if natural | Strict limits on usage and concentration |
| Application Examples | Use in fresh foods, dairy, meat (e.g., natamycin in cheese) | Used widely in beverages, baked goods, processed foods |
Overview of Food Preservation Methods
Natural preservatives such as rosemary extract, chitosan, and essential oils offer antimicrobial and antioxidant properties that enhance shelf-life while maintaining food safety and quality. Synthetic preservatives like sodium benzoate, potassium sorbate, and BHA provide consistent, long-lasting inhibition of microbial growth and oxidation but may raise health concerns among consumers. Combining natural and synthetic methods in food preservation optimizes shelf-life extension by balancing efficacy, safety, and consumer preference.
Understanding Natural Preservatives in Agriculture
Natural preservatives in agriculture, such as essential oils, plant extracts, and fermentation-derived compounds, offer eco-friendly alternatives for shelf-life extension by inhibiting microbial growth and oxidative spoilage. These bioactive substances enhance food safety and quality without the synthetic chemical residues, aligning with consumer demand for clean-label products. Research emphasizes optimizing extraction methods and application techniques to maximize the efficacy of natural preservatives in extending the shelf life of agricultural products.
Common Types of Synthetic Preservatives
Common types of synthetic preservatives used for shelf-life extension include sodium benzoate, potassium sorbate, and calcium propionate, known for their effectiveness in inhibiting mold, yeast, and bacterial growth. These preservatives are widely applied in beverages, baked goods, and dairy products due to their stability and cost-efficiency. Despite concerns about potential health risks, synthetic preservatives provide consistent antimicrobial activity and are strictly regulated by food safety authorities.
Mechanisms of Shelf-Life Extension
Natural preservatives extend shelf life by inhibiting microbial growth through antimicrobial compounds like essential oils, organic acids, and phenolic compounds that disrupt cell membranes and metabolic pathways. Synthetic preservatives, such as sodium benzoate and potassium sorbate, function by interfering with microbial enzymatic activity and maintaining product pH to prevent spoilage. Both types act by reducing oxidation, microbial contamination, and enzymatic degradation, thereby preserving food quality and safety over extended periods.
Efficacy of Natural vs Synthetic Preservatives
Natural preservatives such as rosemary extract, nisin, and essential oils often exhibit strong antimicrobial properties against specific foodborne pathogens, but their efficacy can vary with concentration and food matrix. Synthetic preservatives like sodium benzoate and potassium sorbate provide consistent, broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, often resulting in longer shelf-life extension under diverse storage conditions. Comparative studies indicate that while natural preservatives are favored for consumer health and clean-label trends, synthetic options generally ensure more reliable and prolonged preservation in food products.
Impact on Food Quality and Safety
Natural preservatives such as essential oils, antioxidants, and fermentates enhance food quality by maintaining flavor, texture, and nutritional value while exhibiting antimicrobial properties that inhibit spoilage and pathogenic microorganisms. Synthetic preservatives like sodium benzoate and potassium sorbate provide effective, consistent shelf-life extension but may alter sensory attributes and pose potential health risks due to chemical residues and allergenicity. Balancing efficacy and consumer safety requires evaluating the impact of preservative types on microbial stability, sensory integrity, and regulatory compliance within food safety frameworks.
Consumer Perception and Market Trends
Natural preservatives such as rosemary extract, vitamin E, and nisin are increasingly favored by consumers seeking clean-label products and minimal chemical additives, driving market demand for natural alternatives in food preservation. Synthetic preservatives like sodium benzoate and potassium sorbate continue to offer effective shelf-life extension but face growing scrutiny due to potential health concerns and negative consumer perception. Market trends indicate a shift towards natural preservatives, with innovation in plant-based antimicrobials and antioxidants shaping product development and labeling strategies for food manufacturers.
Regulatory Frameworks for Preservative Usage
Regulatory frameworks for preservative usage in food science enforce strict safety evaluations and permissible limits to ensure consumer protection. Natural preservatives, such as essential oils and plant extracts, often face different regulatory requirements compared to synthetic preservatives like sodium benzoate or potassium sorbate due to variability in composition and efficacy. Compliance with agencies such as the FDA, EFSA, and CODEX Alimentarius is essential for validating preservative claims and ensuring product shelf-life extension aligns with legal standards.
Environmental Sustainability Considerations
Natural preservatives such as rosemary extract, citric acid, and essential oils offer biodegradable and renewable alternatives to synthetic preservatives like butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) and sodium benzoate, reducing environmental pollution and chemical residues in ecosystems. The production of natural preservatives typically involves less energy-intensive processes and lower greenhouse gas emissions, supporting sustainable agricultural practices and minimizing ecological footprints. Synthetic preservatives often rely on petrochemical derivatives and generate hazardous waste during manufacturing, raising concerns about long-term environmental sustainability and bioaccumulation in food chains.
Future Directions in Food Preservation Technology
Emerging trends in food preservation technology emphasize natural preservatives like plant extracts, essential oils, and probiotics due to their biodegradability and consumer preference for clean labels. Advances in nanotechnology and encapsulation methods are enhancing the efficacy and controlled release of natural antimicrobials, addressing challenges of stability and flavor impact. Integration of these innovations with smart packaging and predictive analytics is poised to revolutionize shelf-life extension while reducing reliance on synthetic preservatives.
Related Important Terms
Bioactive peptides
Bioactive peptides derived from natural sources exhibit potent antimicrobial and antioxidant properties, making them effective natural preservatives for shelf-life extension in food products. These peptides offer a safer alternative to synthetic preservatives by inhibiting spoilage microorganisms and oxidative reactions while maintaining food quality and consumer safety.
Plant-derived antimicrobials
Plant-derived antimicrobials such as essential oils, phenolic compounds, and flavonoids exhibit potent antimicrobial activity against foodborne pathogens, making them effective natural preservatives for extending shelf-life in various food products. These natural preservatives offer advantages over synthetic counterparts by reducing chemical residues and consumer health risks while enhancing food safety and quality through their antioxidant and antimicrobial properties.
Essential oil nanoemulsions
Essential oil nanoemulsions serve as effective natural preservatives by enhancing antimicrobial and antioxidant properties, thereby extending food shelf-life without compromising safety or sensory qualities. Compared to synthetic preservatives, they offer biocompatibility and reduced toxicity risks, aligning with clean-label trends and consumer demand for natural food additives.
Chitosan-based coatings
Chitosan-based coatings derived from natural sources offer antimicrobial and antioxidant properties that effectively extend food shelf life while reducing reliance on synthetic preservatives like sorbates and benzoates, which may pose health risks. These biodegradable coatings form edible films that inhibit microbial growth and moisture loss, enhancing food quality and safety in a sustainable manner.
Hurdle technology synergy
Natural preservatives such as essential oils, organic acids, and plant extracts demonstrate enhanced efficacy in shelf-life extension when combined with synthetic preservatives through Hurdle Technology, exploiting multiple antimicrobial mechanisms simultaneously. This synergy disrupts microbial growth more effectively, improving food safety and quality without compromising sensory attributes.
Edible biopolymer films
Edible biopolymer films derived from natural preservatives such as chitosan, alginate, and gelatin exhibit antimicrobial and antioxidant properties that enhance food shelf-life without harmful chemical residues. Compared to synthetic preservatives, these biopolymer films improve food quality by providing biodegradable, non-toxic barriers that reduce microbial growth and moisture loss, aligning with consumer demand for clean-label and sustainable packaging solutions.
Controlled-release preservatives
Controlled-release preservatives in food science utilize encapsulation techniques to gradually release natural antimicrobial agents like essential oils, enhancing shelf-life while minimizing sensory alterations. Compared to synthetic preservatives such as sodium benzoate, these controlled systems offer targeted microbial inhibition and reduce chemical residues, aligning with consumer demand for clean-label products.
Clean label preservation
Natural preservatives such as rosemary extract, nisin, and citric acid effectively extend shelf-life while aligning with consumer demand for clean label products due to their recognizable ingredients and minimal chemical additives. Synthetic preservatives like sodium benzoate and potassium sorbate offer strong antimicrobial properties and longer shelf stability but often face consumer resistance due to perceived health concerns and artificial ingredient labeling.
Nitrite alternatives (natural curing agents)
Natural curing agents such as celery powder, beet extract, and rosemary extract serve as effective nitrite alternatives, providing antimicrobial properties and antioxidant benefits that extend meat product shelf-life while minimizing health risks associated with synthetic nitrites. These natural preservatives enhance food safety and quality by inhibiting pathogenic bacteria growth, reducing nitrosamine formation, and maintaining color stability in processed meats.
Bacteriocin fortification
Bacteriocin fortification, a natural preservative derived from lactic acid bacteria, effectively inhibits pathogenic and spoilage bacteria, enhancing shelf-life while reducing reliance on synthetic additives. Its targeted antimicrobial activity and biocompatibility offer a safer and consumer-preferred alternative in food preservation technologies.
Natural preservatives vs synthetic preservatives for shelf-life extension Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com