Cold extraction preserves the delicate flavors and nutrients of olive oil by avoiding high temperatures that can degrade antioxidants and polyphenols. Hot extraction increases oil yield but often compromises quality, resulting in a less flavorful and less nutritious product. Choosing cold extraction techniques ensures a superior olive oil rich in health-promoting compounds and natural aroma.
Table of Comparison
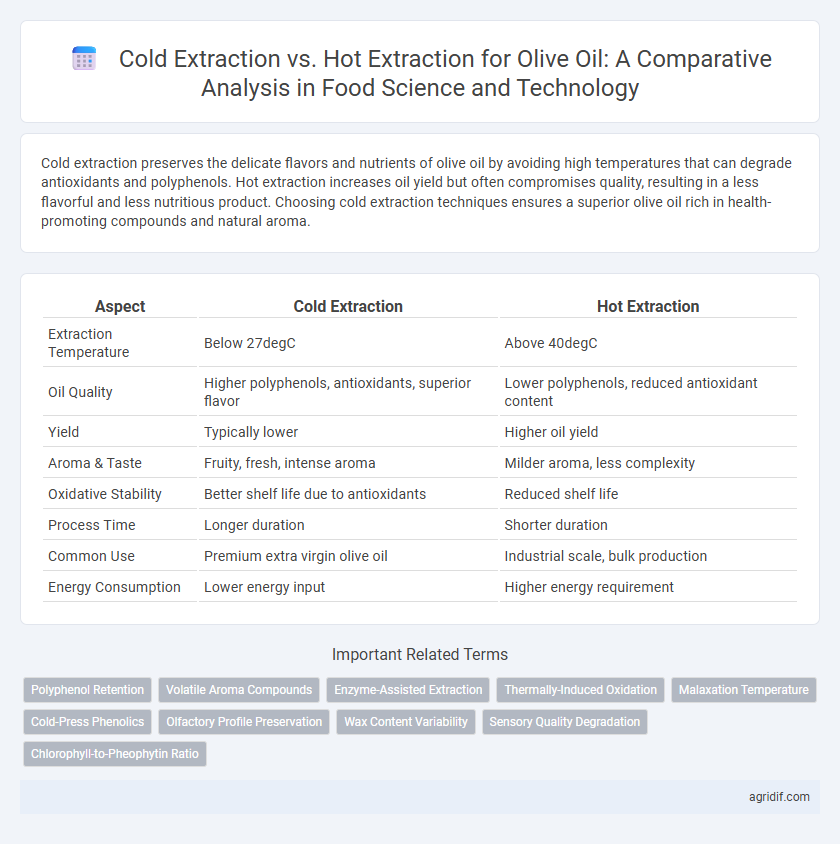
| Aspect | Cold Extraction | Hot Extraction |
|---|---|---|
| Extraction Temperature | Below 27degC | Above 40degC |
| Oil Quality | Higher polyphenols, antioxidants, superior flavor | Lower polyphenols, reduced antioxidant content |
| Yield | Typically lower | Higher oil yield |
| Aroma & Taste | Fruity, fresh, intense aroma | Milder aroma, less complexity |
| Oxidative Stability | Better shelf life due to antioxidants | Reduced shelf life |
| Process Time | Longer duration | Shorter duration |
| Common Use | Premium extra virgin olive oil | Industrial scale, bulk production |
| Energy Consumption | Lower energy input | Higher energy requirement |
Introduction to Olive Oil Extraction Methods
Cold extraction of olive oil involves pressing olives at temperatures below 27degC to preserve antioxidants, polyphenols, and volatile compounds, resulting in higher quality extra virgin olive oil with enhanced flavor and health benefits. Hot extraction uses controlled heating above 27degC to increase oil yield by reducing viscosity but may degrade sensitive nutrients and alter sensory properties. The choice between cold and hot extraction significantly impacts the oil's chemical composition, nutritional value, and sensory profile, making it crucial in olive oil production technology.
What is Cold Extraction in Olive Oil Production?
Cold extraction in olive oil production refers to the process of mechanically pressing olives without applying external heat, typically maintaining temperatures below 27degC (80degF) to preserve the oil's natural flavor, aroma, and nutritional compounds such as polyphenols and antioxidants. This method ensures higher quality oil with enhanced sensory characteristics and health benefits compared to hot extraction, which involves heat that can degrade sensitive compounds. Cold extraction is preferred in premium olive oil production for producing extra virgin olive oil with superior chemical and sensory profiles.
Understanding Hot Extraction for Olive Oil
Hot extraction for olive oil involves heating the olive paste to temperatures typically between 35degC and 45degC, which facilitates higher oil yield by breaking down cell membranes more effectively. This method can accelerate the extraction process and enhance certain phenolic compounds, but it may also reduce the oil's overall antioxidant content and alter its flavor profile due to heat exposure. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for producers aiming to balance yield efficiency with the preservation of olive oil quality and nutritional properties.
Key Differences Between Cold and Hot Extraction Processes
Cold extraction of olive oil preserves the highest levels of antioxidants and polyphenols by maintaining temperatures below 27degC, which enhances flavor and nutritional quality. In contrast, hot extraction uses elevated temperatures to increase yield but can degrade sensitive compounds, resulting in lower antioxidant content and altered sensory profiles. Cold extraction is preferred for premium extra virgin olive oils, while hot extraction suits industrial-scale production prioritizing volume over quality.
Impact on Olive Oil Nutrient Retention
Cold extraction preserves higher levels of phenolic compounds and antioxidants in olive oil, enhancing its nutritional quality and health benefits. Hot extraction increases oil yield but leads to significant degradation of sensitive nutrients such as polyphenols and vitamin E due to heat exposure. The nutrient retention in cold-extracted olive oil contributes to superior antioxidant activity and longer shelf life compared to hot-extracted counterparts.
Flavor and Aroma Profiles: Cold vs Hot Extracted Olive Oil
Cold extraction of olive oil preserves delicate phenolic compounds and volatile aromatics, resulting in a robust flavor profile with fruity, grassy, and peppery notes. Hot extraction tends to degrade these sensitive compounds, leading to a milder flavor and reduced aromatic complexity. The choice between cold and hot extraction directly affects the intensity, freshness, and sensory experience of the olive oil.
Yield and Efficiency Comparison
Cold extraction of olive oil preserves delicate phenolic compounds and antioxidants but typically results in lower oil yield compared to hot extraction methods. Hot extraction increases yield and overall efficiency by using controlled heat to facilitate oil release from olive paste, though it may degrade some bioactive compounds. The choice between these methods balances maximum oil recovery with retention of nutritional quality, where hot extraction offers superior yield but cold extraction maintains higher antioxidant levels.
Quality and Purity: Assessing Extraction Methods
Cold extraction preserves the highest levels of phenolic compounds and antioxidants in olive oil, ensuring superior quality and purity by minimizing oxidation and thermal degradation. Hot extraction, while increasing yield, often compromises oil quality through heat-induced loss of volatile flavors and beneficial bioactive components. Choosing cold extraction results in a more stable, nutrient-rich olive oil with enhanced sensory attributes and extended shelf life.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Cold extraction of olive oil, often labeled as "extra virgin" and retaining higher levels of polyphenols and antioxidants, aligns with consumer preferences for health benefits and premium quality. Hot extraction methods, while yielding larger quantities, typically result in lower antioxidant content and may be perceived as less natural, influencing market demand toward cold-extracted oils. Market trends show increasing consumer focus on cold-extracted olive oil due to growing awareness of its superior nutritional profile and flavor complexity.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations in Extraction Methods
Cold extraction of olive oil utilizes lower temperatures, preserving more antioxidants and phenolic compounds while significantly reducing energy consumption compared to hot extraction methods. Hot extraction demands higher energy inputs, increasing greenhouse gas emissions and environmental impact due to prolonged heating and processing times. Prioritizing cold extraction aligns with sustainable food technology goals by minimizing carbon footprint and enhancing the nutritional quality of olive oil.
Related Important Terms
Polyphenol Retention
Cold extraction of olive oil preserves higher levels of polyphenols compared to hot extraction, as elevated temperatures cause degradation of these antioxidant compounds. Maintaining low temperatures during the extraction process maximizes polyphenol retention, enhancing the oil's nutritional quality and oxidative stability.
Volatile Aroma Compounds
Cold extraction of olive oil preserves a higher concentration of volatile aroma compounds such as aldehydes, esters, and terpenes, which contribute to the oil's fresh, fruity aroma and enhanced sensory quality. Hot extraction methods tend to degrade these delicate volatile compounds due to increased temperatures, resulting in diminished aroma intensity and altered flavor profiles.
Enzyme-Assisted Extraction
Enzyme-assisted extraction in olive oil production enhances oil yield and quality by breaking down cell walls, enabling more efficient cold extraction compared to traditional hot extraction methods. This enzymatic process preserves phenolic compounds and antioxidants, resulting in superior flavor and higher nutritional value in the cold-extracted olive oil.
Thermally-Induced Oxidation
Cold extraction of olive oil minimizes thermally-induced oxidation by maintaining temperatures below 27degC, preserving phenolic compounds and antioxidants that enhance oil stability and flavor. In contrast, hot extraction exposes the oil to elevated temperatures, accelerating oxidative degradation and reducing the concentration of health-promoting bioactive compounds.
Malaxation Temperature
Cold extraction of olive oil involves malaxation at temperatures below 27degC, preserving phenolic compounds and antioxidants for higher nutritional value and superior flavor. Hot extraction uses malaxation temperatures above 27degC, increasing oil yield but reducing the concentration of heat-sensitive bioactive compounds.
Cold-Press Phenolics
Cold extraction of olive oil preserves higher levels of phenolic compounds compared to hot extraction methods, enhancing the oil's antioxidant properties and health benefits. Phenolics such as hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein are better retained through cold-press techniques, resulting in superior flavor, stability, and nutritional quality.
Olfactory Profile Preservation
Cold extraction of olive oil preserves volatile compounds and delicate aromatic notes, resulting in a richer and more complex olfactory profile compared to hot extraction. Hot extraction often degrades these sensitive compounds due to higher temperatures, leading to a loss of freshness and diminished sensory quality.
Wax Content Variability
Cold extraction of olive oil preserves low wax content due to minimal heat exposure, resulting in higher quality and purer oil with enhanced sensory attributes. Hot extraction increases wax content by promoting the solubilization of lipophilic compounds, which can affect clarity, stability, and shelf life of the olive oil.
Sensory Quality Degradation
Cold extraction of olive oil preserves phenolic compounds and volatile aroma molecules, maintaining superior sensory quality with fresh, fruity, and bitter notes. Hot extraction accelerates oxidation and enzymatic degradation, leading to diminished flavor complexity and the loss of desirable sensory attributes.
Chlorophyll-to-Pheophytin Ratio
Cold extraction of olive oil preserves a higher Chlorophyll-to-Pheophytin ratio due to minimal heat exposure, maintaining better pigment integrity and antioxidant properties. Hot extraction accelerates chlorophyll degradation to pheophytin, resulting in a lower Chlorophyll-to-Pheophytin ratio and altered oil quality and color characteristics.
Cold extraction vs hot extraction for olive oil Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com