HACCP focuses on identifying and controlling specific hazards within the food production process to ensure safety, while ISO 22000 integrates HACCP principles with a comprehensive management system framework, including communication, system management, and prerequisite programs. ISO 22000 provides a more structured and scalable approach to food safety management, suitable for companies seeking certification and continuous improvement. Both systems aim to prevent food safety hazards, but ISO 22000 offers broader organizational benefits beyond hazard analysis alone.
Table of Comparison
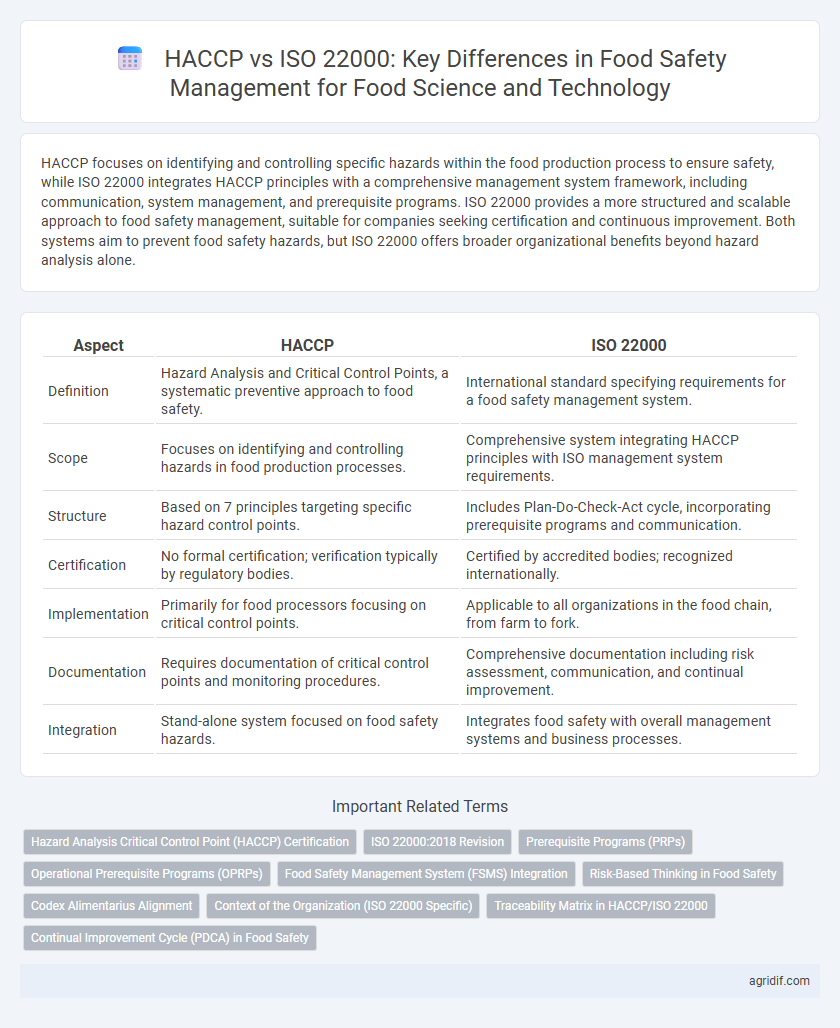
| Aspect | HACCP | ISO 22000 |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points, a systematic preventive approach to food safety. | International standard specifying requirements for a food safety management system. |
| Scope | Focuses on identifying and controlling hazards in food production processes. | Comprehensive system integrating HACCP principles with ISO management system requirements. |
| Structure | Based on 7 principles targeting specific hazard control points. | Includes Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle, incorporating prerequisite programs and communication. |
| Certification | No formal certification; verification typically by regulatory bodies. | Certified by accredited bodies; recognized internationally. |
| Implementation | Primarily for food processors focusing on critical control points. | Applicable to all organizations in the food chain, from farm to fork. |
| Documentation | Requires documentation of critical control points and monitoring procedures. | Comprehensive documentation including risk assessment, communication, and continual improvement. |
| Integration | Stand-alone system focused on food safety hazards. | Integrates food safety with overall management systems and business processes. |
Understanding HACCP: Principles and Implementation
HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) is a systematic approach focusing on identifying, evaluating, and controlling food safety hazards at specific stages in the production process. Implementation of HACCP involves seven principles: hazard analysis, critical control points identification, establishing critical limits, monitoring procedures, corrective actions, verification, and record-keeping, ensuring effective food safety management. This method prioritizes proactive risk prevention, which complements ISO 22000 by integrating HACCP principles into a broader food safety management system.
ISO 22000: Overview and Key Components
ISO 22000 is an internationally recognized food safety management system that integrates the principles of HACCP with prerequisite programs, aiming to ensure safe food production from farm to fork. Key components of ISO 22000 include interactive communication, system management, prerequisite programs, and the HACCP plan itself, which collectively enhance hazard control and regulatory compliance. This standard emphasizes continuous improvement and risk-based preventive controls, making it adaptable across various food industry sectors.
Core Differences Between HACCP and ISO 22000 Systems
HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) focuses primarily on identifying and controlling biological, chemical, and physical hazards in food production through a step-by-step preventive approach. ISO 22000 encompasses HACCP principles but integrates them within a broader food safety management system that includes interactive communication, system management, and prerequisite programs. The core difference lies in ISO 22000's comprehensive framework for continuous improvement and stakeholder communication, while HACCP strictly targets hazard control at critical points in the food supply chain.
Scope of Application in Food Science and Technology
HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) is a systematic preventive approach focusing specifically on identifying, evaluating, and controlling food safety hazards throughout production processes. ISO 22000 integrates HACCP principles within a broader food safety management system applicable to all organizations in the food chain, including feed producers, food manufacturers, and distributors. While HACCP targets specific operational control points, ISO 22000 encompasses overall management system requirements, making it suitable for diverse scopes in food science and technology industries.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements: HACCP vs ISO 22000
HACCP primarily focuses on identifying and controlling critical points in food production to meet regulatory requirements, emphasizing hazard analysis and preventive measures. ISO 22000 integrates HACCP principles within a broader management system framework, aligning with international standards and regulatory compliance across supply chains. Regulatory compliance under ISO 22000 involves documented processes, continuous improvement, and alignment with global food safety legislation, offering a more comprehensive approach than HACCP alone.
Integration with Other Food Safety Standards
HACCP provides a systematic approach to identifying, evaluating, and controlling food safety hazards, serving as a foundational component within comprehensive food safety management systems. ISO 22000 integrates the principles of HACCP with prerequisite programs and quality management system elements, enabling seamless alignment with standards such as ISO 9001 and sector-specific regulations. This integration facilitates enhanced traceability, risk management, and continuous improvement across the entire food supply chain.
Documentation and Record Keeping: Best Practices
HACCP emphasizes detailed documentation of hazard analysis, critical control points, and corrective actions to ensure traceability and compliance. ISO 22000 integrates HACCP principles with a structured management system, requiring comprehensive documentation of processes, procedures, and continuous improvement records. Best practices include maintaining clear, accessible records, regularly updating documentation, and utilizing digital tools for real-time monitoring and audit readiness.
Benefits and Challenges in Agricultural Food Processing
HACCP provides a systematic approach to identify and control hazards in agricultural food processing, enhancing product safety and consumer protection, while ISO 22000 integrates HACCP principles with a comprehensive management system, ensuring continuous improvement and compliance with international standards. Benefits of HACCP include targeted hazard control and regulatory acceptance, whereas ISO 22000 offers enhanced supplier communication and risk management across the entire supply chain. Challenges involve HACCP's limited scope on management systems and ISO 22000's complexity in implementation and resource requirements for small-scale agricultural processors.
Certification Processes and Auditing Procedures
HACCP certification emphasizes identification and control of critical points in the food production process through systematic hazard analysis and monitoring, while ISO 22000 certification integrates HACCP principles within a broader, structured Food Safety Management System encompassing interactive communication, system management, and prerequisite programs. Auditing procedures for HACCP focus primarily on verifying the control measures at critical control points (CCPs) for compliance and corrective actions, whereas ISO 22000 audits assess the complete food safety management system, including documentation, process controls, and continual improvement mechanisms. Both certifications require regular internal and external audits, but ISO 22000 audits are typically more comprehensive, involving multi-disciplinary evaluation by accredited certification bodies.
Choosing the Right Standard for Your Food Business
HACCP provides a systematic approach to identify and control hazards at specific points in the food production process, emphasizing food safety risk management. ISO 22000 integrates HACCP principles within a broader framework, including management system requirements, allowing alignment with other standards like ISO 9001. Selecting between HACCP and ISO 22000 depends on business size, regulatory requirements, customer expectations, and the need for comprehensive management system integration.
Related Important Terms
Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) Certification
Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) certification emphasizes identifying, evaluating, and controlling hazards at specific points in the food production process to ensure food safety. In contrast, ISO 22000 integrates HACCP principles within a broader food safety management system, encompassing communication, system management, and prerequisite programs for comprehensive risk mitigation.
ISO 22000:2018 Revision
ISO 22000:2018 revision integrates HACCP principles within a comprehensive food safety management system emphasizing risk-based thinking, continuous improvement, and enhanced communication along the food supply chain. This updated standard aligns with Annex SL structure, facilitating integration with other management systems while addressing prerequisite programs and operational PRPs to ensure effective hazard control and compliance in food production.
Prerequisite Programs (PRPs)
HACCP relies heavily on Prerequisite Programs (PRPs) as foundational conditions and activities to maintain a hygienic environment and prevent hazards before critical control points are identified. ISO 22000 integrates PRPs within a broader food safety management system, emphasizing continuous improvement and combining HACCP principles with other management system requirements.
Operational Prerequisite Programs (OPRPs)
HACCP focuses on identifying and controlling critical control points (CCPs) to prevent food safety hazards, while ISO 22000 integrates HACCP principles and emphasizes Operational Prerequisite Programs (OPRPs) as essential measures to maintain hygienic conditions and reduce risks before CCPs. OPRPs under ISO 22000 provide systematic control of background conditions, ensuring consistent operational practices across the food supply chain to enhance overall food safety management.
Food Safety Management System (FSMS) Integration
HACCP provides a systematic approach to hazard analysis and critical control points specifically targeting food safety risks, while ISO 22000 integrates HACCP principles into a comprehensive Food Safety Management System (FSMS) framework that includes interactive communication, system management, and prerequisite programs. Implementing ISO 22000 enables organizations to align HACCP processes with international standards, enhancing FSMS integration through structured documentation, continuous improvement, and stakeholder engagement.
Risk-Based Thinking in Food Safety
HACCP provides a foundational risk-based approach by identifying and controlling critical points to prevent food safety hazards, while ISO 22000 integrates HACCP principles into a broader management system emphasizing continual risk assessment and communication across the entire supply chain. ISO 22000 advances risk-based thinking by incorporating context analysis, stakeholder requirements, and dynamic risk controls, ensuring comprehensive food safety management beyond HACCP's hazard control focus.
Codex Alimentarius Alignment
HACCP, developed by the Codex Alimentarius Commission, serves as a fundamental food safety system emphasizing hazard analysis and critical control points, while ISO 22000 integrates HACCP principles within a broader management framework, aligning with Codex guidelines to ensure comprehensive food safety management across supply chains. ISO 22000 extends Codex Alimentarius alignment by incorporating prerequisite programs, communication, and system management requirements, facilitating certification and continuous improvement beyond HACCP's core hazard control focus.
Context of the Organization (ISO 22000 Specific)
ISO 22000 emphasizes the Context of the Organization by requiring a systematic analysis of internal and external factors affecting the food safety management system, aligning with strategic objectives and stakeholder needs. HACCP focuses specifically on hazard analysis and critical control points without integrating broader organizational context or external environment considerations.
Traceability Matrix in HACCP/ISO 22000
The Traceability Matrix in HACCP provides a detailed mapping of critical control points to hazards, ensuring direct monitoring and corrective actions in food safety management. ISO 22000 integrates this matrix within its broader framework, linking traceability to overall system processes, risk assessment, and continual improvement protocols for comprehensive food safety assurance.
Continual Improvement Cycle (PDCA) in Food Safety
HACCP focuses on hazard analysis and critical control points, emphasizing preventive measures, while ISO 22000 integrates the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) continual improvement cycle for a comprehensive food safety management system. ISO 22000 enhances HACCP principles by systematically applying PDCA to ensure ongoing refinement and effectiveness in food safety protocols.
HACCP vs ISO 22000 for Food Safety Management Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com