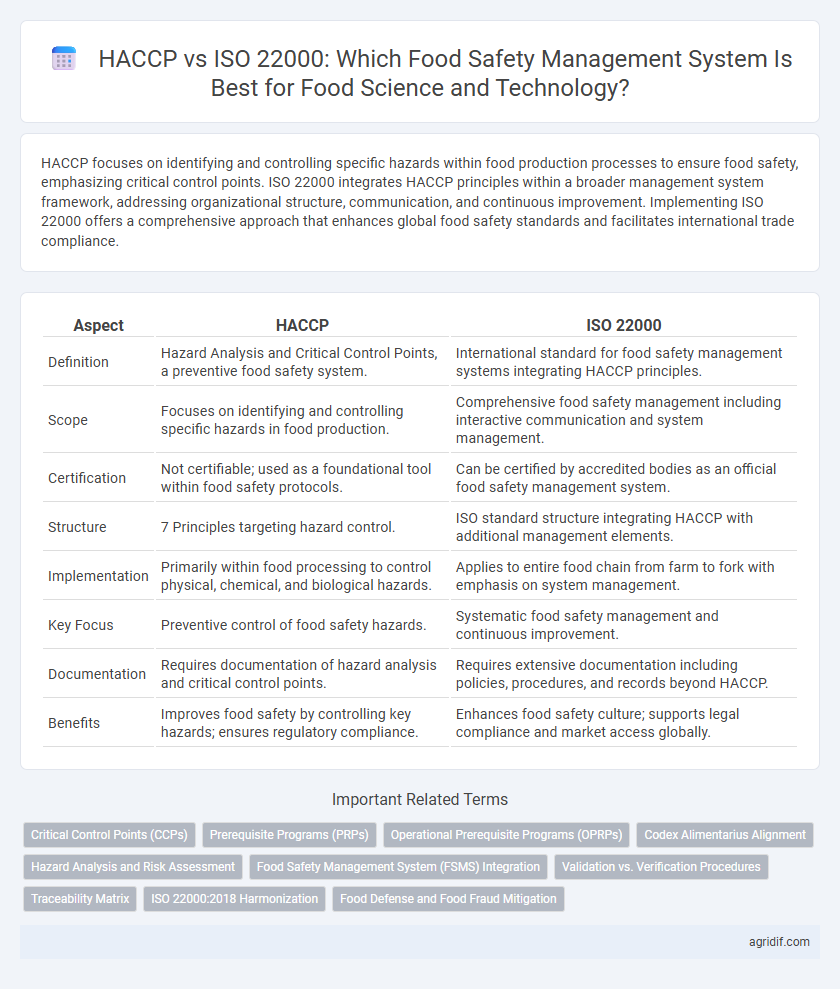
HACCP focuses on identifying and controlling specific hazards within food production processes to ensure food safety, emphasizing critical control points. ISO 22000 integrates HACCP principles within a broader management system framework, addressing organizational structure, communication, and continuous improvement. Implementing ISO 22000 offers a comprehensive approach that enhances global food safety standards and facilitates international trade compliance.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | HACCP | ISO 22000 |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points, a preventive food safety system. | International standard for food safety management systems integrating HACCP principles. |
| Scope | Focuses on identifying and controlling specific hazards in food production. | Comprehensive food safety management including interactive communication and system management. |
| Certification | Not certifiable; used as a foundational tool within food safety protocols. | Can be certified by accredited bodies as an official food safety management system. |
| Structure | 7 Principles targeting hazard control. | ISO standard structure integrating HACCP with additional management elements. |
| Implementation | Primarily within food processing to control physical, chemical, and biological hazards. | Applies to entire food chain from farm to fork with emphasis on system management. |
| Key Focus | Preventive control of food safety hazards. | Systematic food safety management and continuous improvement. |
| Documentation | Requires documentation of hazard analysis and critical control points. | Requires extensive documentation including policies, procedures, and records beyond HACCP. |
| Benefits | Improves food safety by controlling key hazards; ensures regulatory compliance. | Enhances food safety culture; supports legal compliance and market access globally. |
Understanding Food Safety Management in Agriculture
HACCP and ISO 22000 both provide frameworks for improving food safety management in agriculture by identifying critical control points and implementing preventive measures. HACCP focuses specifically on hazard analysis and critical control points within food production, ensuring contamination risks are minimized from farm to fork. ISO 22000 integrates HACCP principles with broader management system requirements, facilitating continuous improvement and compliance with international food safety standards across the agricultural supply chain.
Introduction to HACCP: Principles and Application
HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) is a systematic, preventive approach to food safety that identifies, evaluates, and controls hazards throughout the food production process. It consists of seven principles including hazard analysis, determination of critical control points, establishing critical limits, monitoring procedures, corrective actions, verification, and record-keeping. The application of HACCP ensures proactive risk management, reducing the likelihood of foodborne illnesses and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards in food manufacturing and processing.
Overview of ISO 22000: Structure and Scope
ISO 22000 integrates principles of HACCP with prerequisite programs and enhances food safety management through a structured High-Level Structure (HLS) compatible with other ISO standards, facilitating seamless integration. Its scope covers the entire food supply chain, addressing interactive communication, system management, and prerequisite programs to ensure comprehensive food safety risk control. The standard promotes continuous improvement and alignment with regulatory and customer requirements, making it a global benchmark for food safety management systems.
Key Differences Between HACCP and ISO 22000
HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) focuses specifically on identifying and controlling physical, chemical, and biological food safety hazards during production, while ISO 22000 integrates HACCP principles within a broader, systematic food safety management framework incorporating ISO standards and continuous improvement processes. ISO 22000 includes requirements for communication, management responsibility, and system evaluation, providing a more comprehensive approach compared to HACCP's hazard control emphasis. Key differences include ISO 22000's applicability across the entire food supply chain and its integration with other management systems, whereas HACCP is primarily product and process-specific.
Implementation Challenges in Agricultural Settings
Implementation challenges of HACCP in agricultural settings often stem from the system's complexity and the need for extensive hazard analysis tailored to diverse farm operations. ISO 22000 faces difficulties integrating with existing agricultural practices due to its broader scope encompassing the entire food chain and requirement for continuous communication among stakeholders. Both frameworks demand substantial training and resource allocation, often challenging small-scale farmers with limited technical expertise and financial capacity.
Benefits and Limitations of HACCP in Food Production
HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) offers precise identification and control of biological, chemical, and physical hazards in food production, enhancing product safety and regulatory compliance. Its limitations include a primary focus on hazard control without a comprehensive management system framework, potentially lacking integration with quality management practices. HACCP's structured approach supports critical control monitoring but may require additional systems like ISO 22000 for broader organizational risk management and continual improvement.
Advantages of ISO 22000 for Agricultural Enterprises
ISO 22000 integrates HACCP principles with comprehensive management system requirements, offering agricultural enterprises a structured framework for food safety that enhances consistency and compliance. The standard facilitates improved communication across the supply chain, ensuring better risk management and traceability from farm to fork. Adoption of ISO 22000 supports continuous improvement, boosts market access, and aligns with global food safety expectations, making it ideal for agricultural businesses aiming for international competitiveness.
Choosing the Right System: Factors to Consider
HACCP focuses primarily on hazard analysis and critical control points within food production, making it ideal for companies seeking compliance with specific regulatory food safety requirements. ISO 22000 incorporates HACCP principles but extends to include comprehensive management system elements, such as communication, system management, and continuous improvement, suitable for organizations aiming for international certification and broader food safety management integration. Key factors to consider when choosing between HACCP and ISO 22000 include the scope of food safety coverage, regulatory compliance needs, organizational size, and the desired level of continual food safety performance enhancement.
Regulatory Compliance: HACCP and ISO 22000 Alignment
HACCP provides a risk-based framework specifically targeting critical control points in food safety, which forms a core requirement within ISO 22000's more comprehensive food safety management system. ISO 22000 integrates HACCP principles with additional regulatory requirements and management system elements, ensuring broader compliance with international food safety standards and legal regulations. Both systems align closely, enabling companies to meet stringent regulatory compliance while enhancing operational controls and continuous improvement in food safety practices.
Future Trends in Agricultural Food Safety Standards
HACCP remains a foundational system for hazard identification and control in food safety, while ISO 22000 integrates HACCP principles with broader management processes, enhancing traceability and communication. Future trends in agricultural food safety standards emphasize digitalization, blockchain for supply chain transparency, and real-time monitoring technologies to ensure compliance and rapid response to contamination risks. The convergence of HACCP and ISO 22000 with emerging technologies supports robust, adaptive food safety management systems critical for sustainable agriculture and global food security.
Related Important Terms
Critical Control Points (CCPs)
HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) specifically emphasizes the identification and management of Critical Control Points (CCPs) to prevent food safety hazards, ensuring targeted control measures at critical stages of production. In contrast, ISO 22000 integrates the CCP concept within a broader food safety management system, combining HACCP principles with additional requirements for system management, communication, and continuous improvement.
Prerequisite Programs (PRPs)
HACCP emphasizes Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points focusing on identifying and controlling specific food safety hazards, while ISO 22000 integrates PRPs as foundational conditions essential for maintaining hygiene and preventing contamination throughout the food supply chain. PRPs in ISO 22000 provide a structured framework for facility operation, equipment maintenance, and employee training, complementing HACCP's hazard-specific approach to ensure comprehensive food safety management.
Operational Prerequisite Programs (OPRPs)
Operational Prerequisite Programs (OPRPs) in HACCP focus on specific control measures to prevent food safety hazards, whereas ISO 22000 integrates OPRPs within a broader management system framework, emphasizing continuous improvement and risk-based thinking. ISO 22000 requires documented procedures and systematic monitoring of OPRPs, enhancing traceability and operational consistency compared to the more hazard-centered HACCP approach.
Codex Alimentarius Alignment
HACCP is a systematic preventive approach to food safety hazards based on Codex Alimentarius principles, ensuring hazard analysis and critical control points are strictly managed. ISO 22000 integrates HACCP requirements with additional management system concepts, aligning closely with Codex Alimentarius to provide a comprehensive framework for food safety across the supply chain.
Hazard Analysis and Risk Assessment
HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) emphasizes systematic hazard identification and control at critical points in food production, focusing primarily on biological, chemical, and physical risks. ISO 22000 integrates HACCP principles within a broader management system framework, incorporating risk assessment alongside prerequisite programs to enhance overall food safety management and continuous improvement.
Food Safety Management System (FSMS) Integration
HACCP provides a hazard analysis and critical control points framework focused specifically on food safety risks, while ISO 22000 integrates HACCP principles within a comprehensive Food Safety Management System (FSMS) that encompasses organizational management and continual improvement. Implementing ISO 22000 ensures robust FSMS integration by combining prerequisite programs, risk control, and management system processes that enhance overall food safety performance and compliance.
Validation vs. Verification Procedures
HACCP emphasizes validation of critical control points to establish control measures' scientific and technical adequacy, ensuring food safety hazards are effectively managed. ISO 22000 incorporates both validation and verification procedures, requiring organizations to validate control measures initially and continuously verify their ongoing effectiveness through monitoring and audits.
Traceability Matrix
HACCP offers a detailed traceability matrix that identifies critical control points to prevent food safety hazards, ensuring precise monitoring of each production stage. ISO 22000 integrates this approach within a broader management system, providing a more comprehensive traceability matrix that aligns food safety with organizational processes and continuous improvement.
ISO 22000:2018 Harmonization
ISO 22000:2018 harmonizes food safety management systems by integrating the principles of HACCP with ISO standards, providing a unified framework for risk assessment, prerequisite programs, and continuous improvement. This updated standard ensures consistency across global food supply chains through structured documentation, management responsibility, and enhanced prerequisite programs, streamlining compliance and facilitating international trade.
Food Defense and Food Fraud Mitigation
HACCP primarily targets hazard analysis and critical control points focused on preventing food safety hazards, while ISO 22000 integrates HACCP principles with broader food defense and food fraud mitigation strategies, including system management and communication processes. ISO 22000 enhances food safety management systems by incorporating measures against intentional contamination and economically motivated adulteration, providing a comprehensive framework that addresses emerging threats in the global food supply chain.
HACCP vs ISO 22000 for food safety management systems Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com