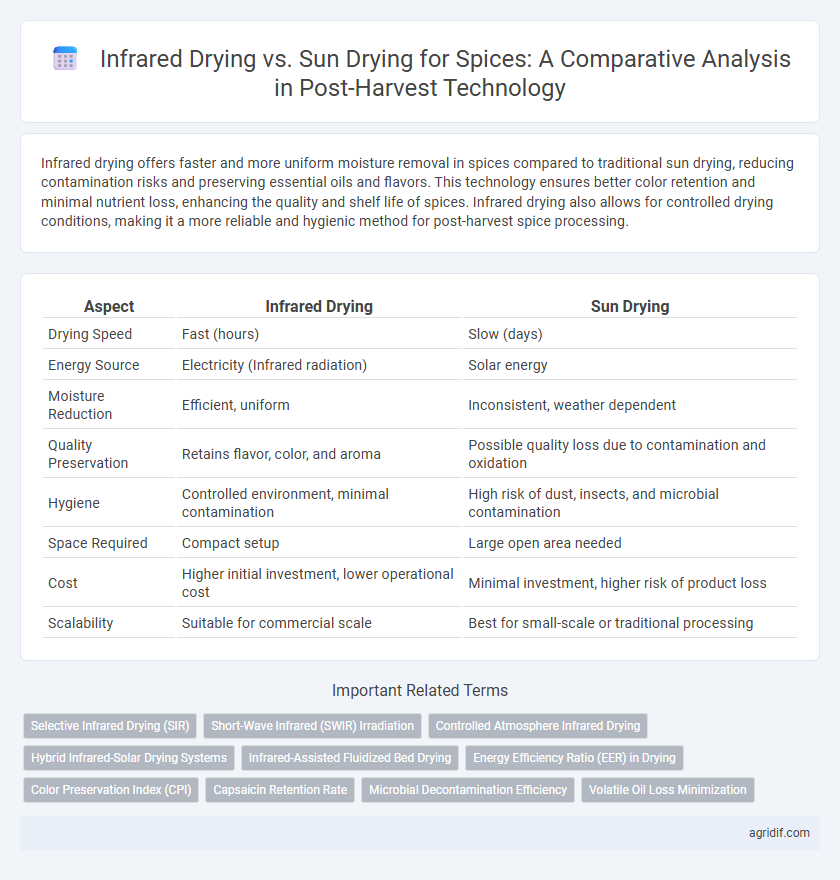
Infrared drying offers faster and more uniform moisture removal in spices compared to traditional sun drying, reducing contamination risks and preserving essential oils and flavors. This technology ensures better color retention and minimal nutrient loss, enhancing the quality and shelf life of spices. Infrared drying also allows for controlled drying conditions, making it a more reliable and hygienic method for post-harvest spice processing.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Infrared Drying | Sun Drying |
|---|---|---|
| Drying Speed | Fast (hours) | Slow (days) |
| Energy Source | Electricity (Infrared radiation) | Solar energy |
| Moisture Reduction | Efficient, uniform | Inconsistent, weather dependent |
| Quality Preservation | Retains flavor, color, and aroma | Possible quality loss due to contamination and oxidation |
| Hygiene | Controlled environment, minimal contamination | High risk of dust, insects, and microbial contamination |
| Space Required | Compact setup | Large open area needed |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, lower operational cost | Minimal investment, higher risk of product loss |
| Scalability | Suitable for commercial scale | Best for small-scale or traditional processing |
Introduction to Post-Harvest Drying Techniques for Spices
Post-harvest drying techniques for spices are crucial to preserving quality, flavor, and shelf life by reducing moisture content to safe levels. Infrared drying offers a controlled, faster, and more energy-efficient alternative compared to traditional sun drying, which is weather-dependent and often leads to inconsistent drying results. By minimizing microbial growth and enzymatic activity, infrared drying enhances the overall safety and market value of spices versus sun drying methods.
Principles of Infrared Drying in Spice Processing
Infrared drying in spice processing utilizes electromagnetic radiation to penetrate spice particles, causing rapid internal water molecule vibration and evaporation. This technique offers uniform heat distribution, leading to faster drying rates and better retention of essential oils and bioactive compounds compared to sun drying. Optimized infrared wavelengths enhance moisture removal efficiency while preserving spice quality and aroma.
Sun Drying: Traditional Method in Spice Preservation
Sun drying, a traditional method in spice preservation, relies on natural solar energy to reduce moisture content and inhibit microbial growth. This process is cost-effective and widely practiced, especially in regions with abundant sunlight, but it is susceptible to environmental contaminants and inconsistent drying conditions. Compared to infrared drying, sun drying requires longer durations and offers less uniform moisture removal, which can impact spice quality and shelf life.
Comparative Drying Efficiency: Infrared vs Sun Drying
Infrared drying offers significantly higher drying efficiency for spices compared to sun drying by providing uniform heat distribution and faster moisture removal, reducing drying time by up to 50%. Sun drying depends on ambient conditions, leading to uneven drying and increased risk of contamination or spoilage. Infrared drying also maintains spice quality by minimizing nutrient loss and preserving volatile oils, crucial for flavor and aroma retention.
Quality Retention of Spices: Color, Flavor, and Aroma
Infrared drying preserves the vibrant color, intense flavor, and rich aroma of spices more effectively than traditional sun drying by minimizing exposure to contaminants and reducing drying time. By delivering controlled heat uniformly, infrared drying prevents enzymatic and microbial degradation that typically diminishes spice quality during prolonged sun exposure. This advanced post-harvest technology enhances overall spice quality retention, ensuring superior sensory attributes for market and culinary use.
Microbial Safety in Infrared and Sun-Dried Spices
Infrared drying significantly reduces microbial load in spices by rapidly lowering moisture content and inactivating pathogens through controlled heat exposure, enhancing microbial safety compared to traditional sun drying. Sun drying exposes spices to environmental contaminants such as dust, insects, and microorganisms, increasing the risk of microbial contamination and spoilage. The uniform heat distribution and shorter drying time in infrared drying ensure safer spice products with improved shelf life and reduced health hazards.
Energy Consumption and Environmental Impact
Infrared drying significantly reduces energy consumption compared to sun drying, utilizing targeted radiation that accelerates moisture removal within a controlled environment. This method minimizes environmental impact by reducing greenhouse gas emissions associated with prolonged sun drying, which relies on fossil-fuel-powered machinery for auxiliary processes like transportation and mechanized turning. Infrared drying offers a more sustainable and energy-efficient solution for post-harvest spice processing by lowering carbon footprints and conserving natural resources.
Cost Analysis: Infrared Drying versus Sun Drying
Infrared drying offers a higher initial investment cost compared to sun drying, which is virtually free but requires substantial labor and time. Operational expenses for infrared drying include energy consumption but result in faster drying times, reducing labor costs and minimizing post-harvest losses. Sun drying depends heavily on weather conditions, potentially increasing overall costs due to spoilage and inconsistent quality during prolonged drying periods.
Challenges and Limitations in Spice Drying Methods
Infrared drying offers faster moisture removal and better microbial control compared to traditional sun drying, yet it faces challenges such as high energy consumption and initial equipment costs. Sun drying remains cost-effective but suffers from prolonged drying times, inconsistent drying due to weather dependence, and increased risks of contamination and spoilage. Both methods require careful management of drying parameters to preserve spice quality and prevent loss of essential oils and flavor compounds.
Future Prospects in Spice Drying Technologies
Infrared drying offers precise temperature control and reduced drying time compared to traditional sun drying, minimizing quality loss and microbial contamination in spices. Emerging technologies integrating infrared with solar energy or continuous flow dryers present sustainable solutions for large-scale spice processing. These advancements promise improved efficiency, energy savings, and preservation of essential oils, enhancing the overall value and shelf life of dried spices.
Related Important Terms
Selective Infrared Drying (SIR)
Selective Infrared Drying (SIR) enhances spice drying efficiency by targeting specific wavelengths that penetrate spice tissues, resulting in uniform moisture removal and preservation of essential oils compared to conventional sun drying. This method reduces drying time by up to 50%, minimizes microbial contamination, and maintains higher quality parameters such as color, aroma, and antioxidant content in spices like turmeric and black pepper.
Short-Wave Infrared (SWIR) Irradiation
Short-Wave Infrared (SWIR) irradiation significantly enhances the drying rate of spices compared to traditional sun drying by providing uniform heat distribution and reducing microbial contamination. This method preserves essential oils and bioactive compounds more effectively, resulting in higher quality and prolonged shelf life of the dried spices.
Controlled Atmosphere Infrared Drying
Controlled Atmosphere Infrared Drying (CAID) offers precise temperature and humidity control, significantly reducing drying time for spices compared to traditional sun drying and minimizing quality degradation such as color loss and essential oil evaporation. This advanced method enhances microbial safety and preserves the bioactive compounds, improving overall spice shelf life and market value.
Hybrid Infrared-Solar Drying Systems
Hybrid infrared-solar drying systems combine the rapid moisture removal efficiency of infrared radiation with the cost-effectiveness and environmental benefits of solar drying, resulting in improved spice quality and reduced drying times compared to traditional sun drying alone. These systems enhance color retention, flavor preservation, and microbial safety in spices by maintaining controlled drying conditions and minimizing exposure to contaminants.
Infrared-Assisted Fluidized Bed Drying
Infrared-assisted fluidized bed drying significantly reduces drying time and enhances the retention of color, aroma, and bioactive compounds in spices compared to traditional sun drying. This advanced post-harvest technology ensures uniform heat distribution and minimizes microbial contamination, improving overall spice quality and shelf life.
Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER) in Drying
Infrared drying demonstrates a significantly higher Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER) compared to traditional sun drying methods for spices, reducing drying time while minimizing energy consumption. This method enhances moisture removal rates and preserves spice quality by using targeted infrared radiation, leading to more sustainable and cost-effective post-harvest processing.
Color Preservation Index (CPI)
Infrared drying demonstrates a significantly higher Color Preservation Index (CPI) compared to sun drying for spices, maintaining vibrant hues by reducing enzymatic browning and oxidation. This enhanced CPI ensures superior visual quality and market value, making infrared drying a preferred method for preserving the natural color of spices post-harvest.
Capsaicin Retention Rate
Infrared drying retains a higher percentage of capsaicin in spices compared to sun drying, preserving up to 90% of the compound versus 60-70% retention in traditional sun drying methods. This enhanced retention is attributed to the controlled temperature and reduced drying time in infrared drying, minimizing capsaicin degradation and maintaining spice potency.
Microbial Decontamination Efficiency
Infrared drying significantly enhances microbial decontamination efficiency in spices by rapidly penetrating and heating the moisture, leading to effective reduction of microbial load compared to traditional sun drying, which is slower and more prone to contamination from environmental exposure. Studies demonstrate that infrared drying achieves higher log reductions of bacteria and fungi, thereby improving spice safety and shelf life.
Volatile Oil Loss Minimization
Infrared drying significantly minimizes volatile oil loss in spices compared to traditional sun drying by providing rapid, uniform heat that reduces exposure time and prevents oil degradation. Controlled temperature and shorter drying periods in infrared drying preserve essential oils, enhancing flavor retention and overall spice quality.
Infrared drying vs Sun drying for spices Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com