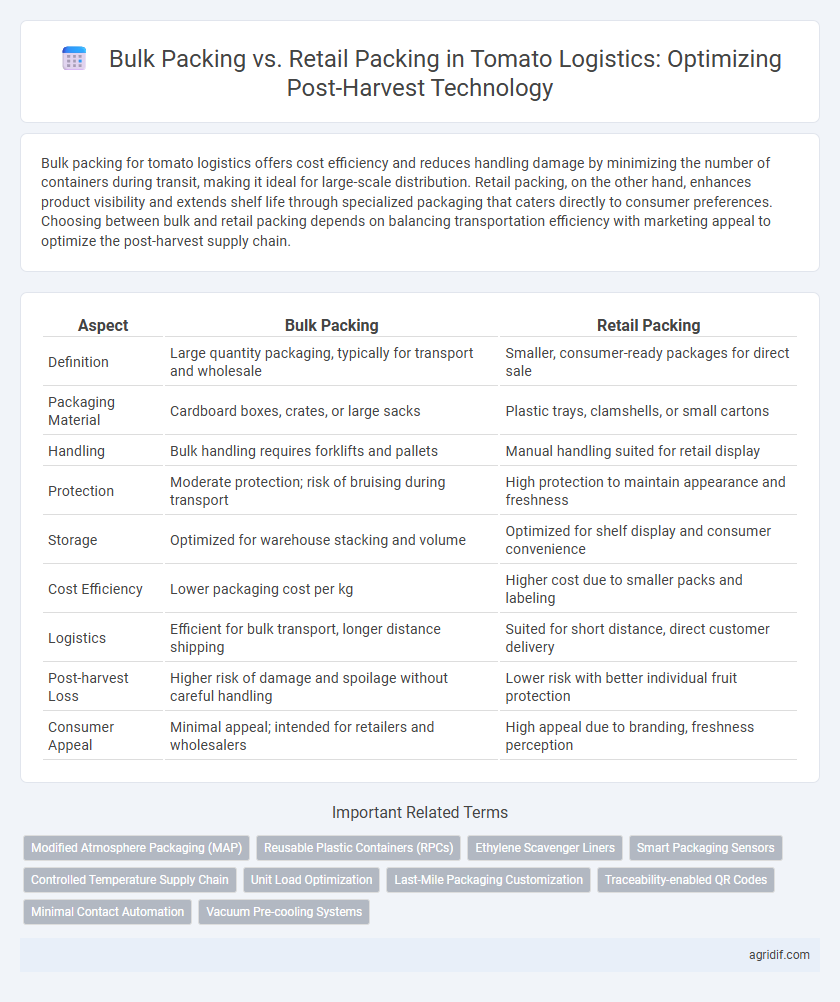
Bulk packing for tomato logistics offers cost efficiency and reduces handling damage by minimizing the number of containers during transit, making it ideal for large-scale distribution. Retail packing, on the other hand, enhances product visibility and extends shelf life through specialized packaging that caters directly to consumer preferences. Choosing between bulk and retail packing depends on balancing transportation efficiency with marketing appeal to optimize the post-harvest supply chain.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Bulk Packing | Retail Packing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Large quantity packaging, typically for transport and wholesale | Smaller, consumer-ready packages for direct sale |
| Packaging Material | Cardboard boxes, crates, or large sacks | Plastic trays, clamshells, or small cartons |
| Handling | Bulk handling requires forklifts and pallets | Manual handling suited for retail display |
| Protection | Moderate protection; risk of bruising during transport | High protection to maintain appearance and freshness |
| Storage | Optimized for warehouse stacking and volume | Optimized for shelf display and consumer convenience |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower packaging cost per kg | Higher cost due to smaller packs and labeling |
| Logistics | Efficient for bulk transport, longer distance shipping | Suited for short distance, direct customer delivery |
| Post-harvest Loss | Higher risk of damage and spoilage without careful handling | Lower risk with better individual fruit protection |
| Consumer Appeal | Minimal appeal; intended for retailers and wholesalers | High appeal due to branding, freshness perception |
Introduction to Tomato Post-Harvest Logistics
Bulk packing in tomato post-harvest logistics involves grouping large quantities of tomatoes in crates or bins, optimizing space and reducing transportation costs for wholesale distribution. Retail packing focuses on smaller, consumer-ready packages that enhance product protection, shelf appeal, and ease of handling during last-mile delivery. Efficient packaging strategies balance reducing post-harvest losses and maintaining tomato quality throughout the supply chain.
Overview of Bulk Packing and Retail Packing Methods
Bulk packing involves grouping large quantities of tomatoes in crates or bins designed for transport and storage efficiency, minimizing handling and reducing bruising during logistics. Retail packing focuses on consumer-ready packaging like trays or clamshells, enhancing product visibility and convenience but increasing packaging costs and complexity. Proper selection between bulk and retail packing methods impacts shelf life, transportation efficiency, and market presentation in tomato supply chains.
Impact on Tomato Quality and Shelf Life
Bulk packing in tomato logistics significantly reduces handling damage by minimizing the number of touchpoints, preserving firmness and color while extending shelf life by up to 5-7 days compared to retail packing. Retail packing, although convenient for consumer access, increases mechanical injuries due to repeated handling and exposure to varying temperatures, accelerating ripening and spoilage. Optimizing post-harvest conditions such as temperature control and humidity in bulk packing further enhances tomato quality by maintaining higher antioxidant levels and reducing microbial decay.
Packaging Materials: Bulk vs Retail
Bulk packing for tomatoes typically uses robust materials such as ventilated plastic crates or wooden boxes that ensure protection during large-scale transport and minimize damage by facilitating airflow. Retail packing employs lightweight, visually appealing materials like clamshell containers or cardboard trays designed for consumer convenience and display while maintaining tomato freshness. Choosing appropriate packaging materials directly impacts product quality, shelf-life, and cost-efficiency throughout the tomato supply chain.
Cost Comparison: Bulk vs Retail Packing
Bulk packing of tomatoes significantly reduces logistics costs due to lower material expenses and increased packing efficiency, enabling transportation of larger quantities per shipment with reduced labor input. Retail packing increases per-unit costs as it requires individual packaging, enhanced handling, and additional labeling, leading to higher labor and material expenditures. The overall cost-effectiveness of bulk packing is amplified for long-distance transportation and large-scale distribution, offering economies of scale not achievable with retail packing formats.
Transportation Efficiency in Tomato Logistics
Bulk packing for tomato logistics enhances transportation efficiency by maximizing cargo space utilization and reducing packaging material weight, leading to lower fuel consumption and transportation costs. In contrast, retail packing, although providing better protection and immediate shelf readiness, often increases volume per unit weight and complicates stacking, resulting in less efficient space usage during transit. Optimizing transportation routes and load configurations with bulk-packed tomatoes significantly improves overall logistics performance.
Handling and Labor Requirements
Bulk packing of tomatoes reduces handling frequency by consolidating produce into larger units, minimizing labor costs during loading and unloading stages. Retail packing demands more intensive manual sorting and careful placement to maintain aesthetic quality, increasing labor time and skill requirements. Efficient logistics balance bulk packing's labor efficiency with retail packing's quality control for optimal supply chain performance.
Market Preferences and Consumer Demands
Bulk packing of tomatoes is favored in large-scale supply chains due to cost efficiency and reduced handling damage during transportation, addressing the needs of wholesalers and retailers requiring high-volume storage. Retail packing, on the other hand, caters to consumer demands for convenience, freshness, and portion control with attractive packaging formats that enhance shelf appeal and reduce spoilage. Market preferences increasingly lean towards retail-ready packaging in urban settings where consumer purchasing behavior prioritizes quality, hygiene, and ease of use.
Environmental Sustainability and Packaging Waste
Bulk packing for tomatoes significantly reduces packaging waste and lowers the environmental footprint by minimizing the use of materials compared to retail packing. Using bulk containers enables more efficient transport, decreasing carbon emissions per kilogram of produce through optimized space utilization. Retail packing, while consumer-friendly, increases packaging waste and resource consumption, posing greater challenges for sustainability in tomato logistics.
Recommendations for Optimizing Tomato Logistics
Bulk packing of tomatoes enhances efficiency by reducing handling damage and lowering transportation costs, suitable for large-scale distribution centers. Retail packing prioritizes consumer convenience and product visibility, making it ideal for direct sales but often increasing packaging waste and logistical complexity. Optimizing tomato logistics involves a hybrid approach that leverages bulk packing for initial transport and retail packing closer to the point of sale to maintain quality and meet market demands.
Related Important Terms
Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP)
Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP) in tomato logistics significantly extends shelf life by reducing oxygen and increasing carbon dioxide levels, which slows respiration and delays ripening in both bulk and retail packing. Bulk packing with MAP enhances efficiency in transportation and storage by maintaining quality over larger volumes, while retail packing focuses on consumer convenience and protection, ensuring freshness and reducing waste at the point of sale.
Reusable Plastic Containers (RPCs)
Reusable Plastic Containers (RPCs) significantly improve tomato logistics efficiency by offering enhanced protection, stackability, and ventilation compared to traditional bulk packing methods. Their durability and reusability reduce post-harvest losses, maintain tomato quality during transit, and support sustainable supply chain practices in retail packing.
Ethylene Scavenger Liners
Ethylene scavenger liners in bulk packing for tomato logistics significantly reduce ethylene accumulation, slowing ripening and extending shelf life compared to retail packing. This technology enhances quality retention during transportation and storage, minimizing spoilage and improving overall supply chain efficiency.
Smart Packaging Sensors
Smart packaging sensors in bulk packing for tomato logistics enhance real-time monitoring of temperature, humidity, and ethylene levels, significantly reducing spoilage and extending shelf-life during transportation. In contrast, retail packing employs advanced smart labels that provide consumers with freshness indicators and authenticity verification, improving traceability and reducing food waste at the point of sale.
Controlled Temperature Supply Chain
Bulk packing of tomatoes in controlled temperature supply chains reduces temperature fluctuations and minimizes mechanical damage during transit, enhancing shelf life and quality retention. Retail packing, while providing individual consumer convenience, often compromises thermal stability and increases spoilage risk due to frequent handling and exposure to variable temperatures.
Unit Load Optimization
Bulk packing in tomato logistics enhances unit load optimization by maximizing pallet space utilization and reducing packaging costs, which streamlines handling and transport efficiency. Retail packing, while improving consumer presentation and minimizing product damage, typically results in lower load density and higher transportation expenses due to increased packaging complexity.
Last-Mile Packaging Customization
Bulk packing for tomato logistics enhances cost-efficiency and reduces handling damage during transportation, while retail packing offers customized last-mile packaging that improves consumer appeal and extends shelf life. Tailored packaging solutions in last-mile delivery optimize product quality, minimize spoilage, and boost marketability by addressing specific retailer and consumer requirements.
Traceability-enabled QR Codes
Bulk packing of tomatoes maximizes handling efficiency but limits individual fruit traceability, whereas retail packing integrated with traceability-enabled QR codes allows precise tracking from farm to consumer, enhancing supply chain transparency and quality control. QR code technology facilitates real-time data access on origin, handling conditions, and freshness, critical for reducing post-harvest losses and ensuring compliance with safety standards in tomato logistics.
Minimal Contact Automation
Bulk packing in tomato logistics reduces handling by using automated systems that minimize physical contact, preserving fruit integrity and extending shelf life. Retail packing involves more manual handling, increasing the risk of bruising and contamination, making bulk packing with minimal contact automation a superior choice for maintaining quality during transportation.
Vacuum Pre-cooling Systems
Vacuum Pre-cooling Systems significantly enhance the efficacy of Bulk Packing in tomato logistics by rapidly reducing temperature and preserving freshness during transport, minimizing spoilage risks. In contrast, Retail Packing often limits this technology's impact due to smaller batch sizes and increased handling, making Bulk Packing more suitable for maintaining tomato quality through the supply chain.
Bulk Packing vs Retail Packing for tomato logistics Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com