Hermetic storage offers superior grain protection by creating an oxygen-deficient environment that inhibits pest development and mold growth, preserving grain quality for extended periods. Traditional storage methods often rely on physical barriers and chemical treatments, which may be less effective against infestations and increase health risks. Implementing hermetic technology enhances post-harvest losses reduction and maintains grain viability without harmful residues.
Table of Comparison
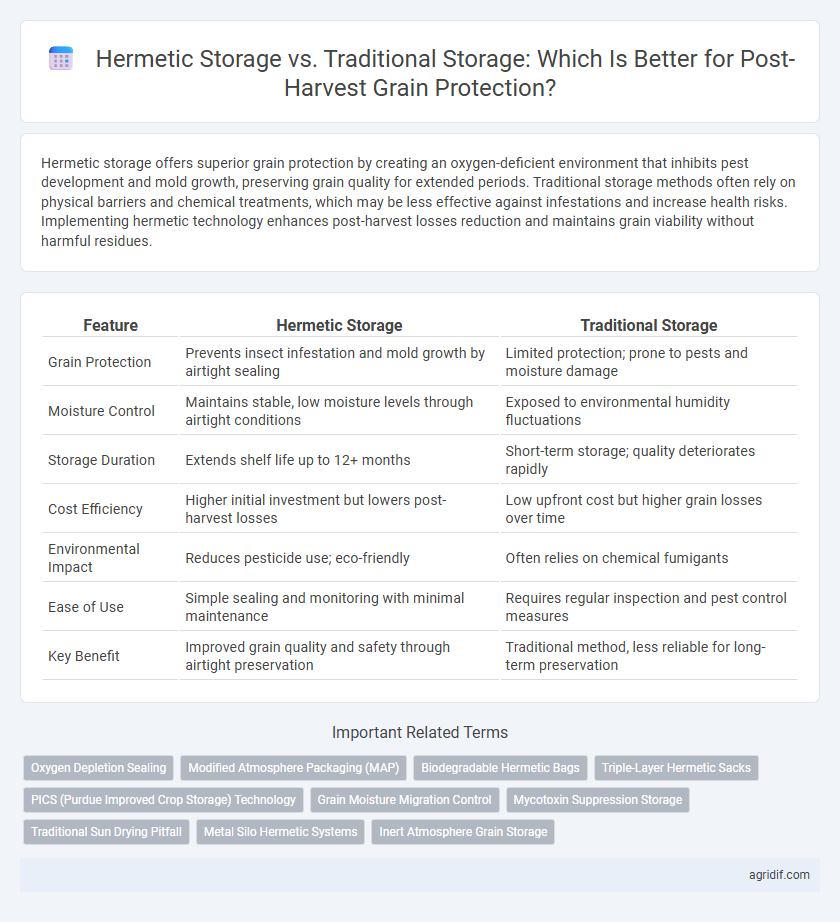
| Feature | Hermetic Storage | Traditional Storage |
|---|---|---|
| Grain Protection | Prevents insect infestation and mold growth by airtight sealing | Limited protection; prone to pests and moisture damage |
| Moisture Control | Maintains stable, low moisture levels through airtight conditions | Exposed to environmental humidity fluctuations |
| Storage Duration | Extends shelf life up to 12+ months | Short-term storage; quality deteriorates rapidly |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher initial investment but lowers post-harvest losses | Low upfront cost but higher grain losses over time |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces pesticide use; eco-friendly | Often relies on chemical fumigants |
| Ease of Use | Simple sealing and monitoring with minimal maintenance | Requires regular inspection and pest control measures |
| Key Benefit | Improved grain quality and safety through airtight preservation | Traditional method, less reliable for long-term preservation |
Introduction to Grain Storage Methods
Hermetic storage provides an airtight environment that prevents oxygen exchange, effectively reducing insect infestation and mold growth in stored grain. Traditional storage methods, such as jute sacks and open bins, often allow moisture and pests to penetrate, leading to significant post-harvest losses. Advanced hermetic technologies like Purdue Improved Crop Storage (PICS) bags have demonstrated improved grain preservation and extended shelf life compared to conventional storage solutions.
Overview of Hermetic Storage Technology
Hermetic storage technology uses airtight containers to create an oxygen-deprived environment that significantly reduces grain spoilage by inhibiting the growth of insects, fungi, and bacteria. Unlike traditional storage methods that often rely on chemical treatments and are susceptible to pest infestations and moisture, hermetic storage enhances grain preservation by maintaining optimal moisture content and preventing oxygen exchange. This technology has become essential for increasing the shelf life and quality of stored grains, especially in regions with high humidity and limited access to pest control resources.
Traditional Grain Storage Practices
Traditional grain storage practices rely heavily on natural ventilation, sun drying, and the use of materials like jute bags, mud, and wooden granaries that expose grains to pests, moisture, and fungal contamination. These methods often result in significant post-harvest losses due to inadequate protection against insects, rodents, and fluctuating environmental conditions. Despite their low cost and accessibility, traditional storage lacks airtight environments crucial for maintaining grain quality and preventing aflatoxin production during extended storage periods.
Key Differences: Hermetic vs. Traditional Storage
Hermetic storage creates an airtight environment that inhibits oxygen flow, effectively preventing insect infestation and fungal growth in stored grains, unlike traditional storage methods that rely on chemical treatments and ventilation. It maintains grain moisture content and quality over extended periods by creating a modified atmosphere that traditional jute or polypropylene bags cannot provide. Hermetic technology significantly reduces post-harvest losses while enhancing food safety and shelf life compared to traditional grain storage practices.
Pest and Insect Control in Storage Systems
Hermetic storage systems create airtight environments that effectively inhibit oxygen-dependent pest and insect development, drastically reducing infestation rates compared to traditional storage methods. Traditional storage often relies on chemical treatments and frequent monitoring, which can lead to pesticide residues and inconsistent pest control. Hermetic technology ensures prolonged grain protection by naturally suffocating pests, maintaining grain quality without chemical intervention.
Impact on Grain Quality and Shelf Life
Hermetic storage significantly enhances grain quality by creating an oxygen-limited environment that inhibits pest infestation and fungal growth, thereby maintaining moisture content and nutrient integrity. Traditional storage methods often fail to prevent insect damage and microbial contamination, leading to reduced grain quality and nutritional value over time. Hermetic bags and airtight containers extend shelf life by preserving grain freshness and reducing post-harvest losses compared to porous sacks or open storage systems.
Costs and Economic Considerations
Hermetic storage systems offer significant economic advantages over traditional storage by reducing grain losses due to pests and moisture, thereby preserving market value and enhancing profitability. Although initial investment costs for hermetic bags or silos are higher, long-term savings from decreased pesticide use and improved grain quality often result in lower overall expenses. Farmers adopting hermetic storage experience better cost-efficiency and return on investment through improved grain preservation and reduced post-harvest losses.
Environmental Implications of Storage Methods
Hermetic storage significantly reduces post-harvest grain losses by creating an oxygen-deprived environment that inhibits pest growth without chemical fumigants, thus lowering environmental contamination compared to traditional storage methods relying heavily on pesticides. Traditional grain storage often involves the use of synthetic insecticides and fumigants, contributing to soil and water pollution and posing health risks to handlers and nearby ecosystems. Hermetic technology promotes sustainable agriculture by minimizing chemical residues, reducing greenhouse gas emissions linked to pesticide production, and preserving grain quality over longer periods.
Adoption Challenges and Farmer Perspectives
Hermetic storage offers superior grain protection by preventing moisture ingress and pest infestation, yet its adoption faces challenges such as high initial costs and limited farmer awareness. Traditional storage methods, while more affordable and familiar, often expose grains to higher risks of spoilage and pest damage, diminishing overall grain quality and market value. Farmers express concerns about cost-effectiveness and ease of use, emphasizing the need for training and access to affordable hermetic solutions to increase adoption rates.
Future Trends in Grain Storage Technologies
Hermetic storage technology offers a promising future in grain protection by creating airtight conditions that inhibit pest infestation and mold growth without chemical fumigants. Advances in sensor integration and smart monitoring systems enhance the efficiency and reliability of hermetic storage, enabling real-time data on grain moisture and temperature. Emerging trends emphasize sustainability and scalability, with innovations focusing on cost-effective, energy-efficient hermetic containers suitable for smallholder farmers and large-scale storage facilities.
Related Important Terms
Oxygen Depletion Sealing
Hermetic storage creates an airtight environment that depletes oxygen levels, effectively inhibiting insect respiration and fungal growth, thereby extending grain shelf life. Traditional storage lacks oxygen sealing, allowing continuous oxygen exchange that promotes pest infestation and grain spoilage.
Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP)
Hermetic storage using Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP) significantly reduces oxygen levels, inhibiting insect infestation and fungal growth in grain compared to traditional storage methods. This controlled environment maintains grain quality by minimizing moisture fluctuations and preserving nutritional value during long-term storage.
Biodegradable Hermetic Bags
Biodegradable hermetic bags provide superior grain protection by creating an oxygen-limiting environment that effectively prevents insect infestation and fungal growth, unlike traditional storage methods which often rely on chemical fumigants and allow moisture ingress. These eco-friendly storage solutions enhance grain quality retention, reduce post-harvest losses, and promote sustainability by decomposing naturally without leaving harmful residues.
Triple-Layer Hermetic Sacks
Triple-layer hermetic sacks provide superior grain protection by creating an airtight barrier that effectively prevents moisture ingress, pest infestation, and fungal growth, significantly reducing post-harvest losses compared to traditional storage methods. Studies show these sacks maintain grain quality by preserving moisture content and inhibiting oxygen exchange, thereby enhancing shelf life and food security for smallholder farmers.
PICS (Purdue Improved Crop Storage) Technology
PICS Technology utilizes hermetic storage bags that create airtight conditions, effectively preventing oxygen exchange and inhibiting pest infestation in stored grains compared to traditional storage methods. Studies show PICS bags maintain grain quality for up to 12 months by reducing moisture content and controlling insect population without chemical treatments.
Grain Moisture Migration Control
Hermetic storage effectively controls grain moisture migration by creating an airtight environment that limits oxygen and moisture exchange, preventing fungal growth and spoilage. Traditional storage methods often allow fluctuations in humidity and temperature, increasing the risk of moisture migration and grain quality degradation.
Mycotoxin Suppression Storage
Hermetic storage significantly reduces moisture ingress and oxygen levels, effectively suppressing the growth of mycotoxin-producing fungi such as Aspergillus and Fusarium in stored grains. Traditional storage methods, lacking airtight sealing, often allow higher humidity and oxygen exposure, creating favorable conditions for mycotoxin contamination and compromising grain safety.
Traditional Sun Drying Pitfall
Traditional sun drying exposes grains to unpredictable weather, insect infestations, and microbial contamination, leading to substantial losses in quality and quantity. Hermetic storage prevents these issues by creating an airtight environment that inhibits pest proliferation and maintains grain moisture levels.
Metal Silo Hermetic Systems
Metal silo hermetic systems provide superior grain protection by creating airtight environments that prevent insect infestation and mold growth, preserving grain quality without chemical treatments. Compared to traditional storage methods, these systems significantly reduce post-harvest losses by maintaining optimal moisture levels and inhibiting pest development through oxygen depletion.
Inert Atmosphere Grain Storage
Hermetic storage creates an oxygen-deprived environment by sealing grain tightly, effectively inhibiting insect respiration and fungal growth without chemical fumigants, making it superior to traditional storage methods that rely on synthetic pesticides and are prone to pest infestations. Inert atmosphere grain storage, employing gases like nitrogen or carbon dioxide to displace oxygen, offers enhanced preservation by maintaining grain quality, reducing moisture loss, and extending shelf life compared to conventional storage that often results in spoilage and significant post-harvest losses.
Hermetic Storage vs Traditional Storage for Grain Protection Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com