HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) focuses on identifying and controlling specific hazards within the food production process to ensure safety, whereas GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) provide general guidelines for maintaining hygiene and operational standards in food manufacturing environments. Implementing HACCP offers a systematic approach to hazard prevention, while GMP establishes foundational practices that support HACCP's effectiveness. Together, these frameworks form a comprehensive food safety management system essential for minimizing contamination risks and ensuring product quality.
Table of Comparison
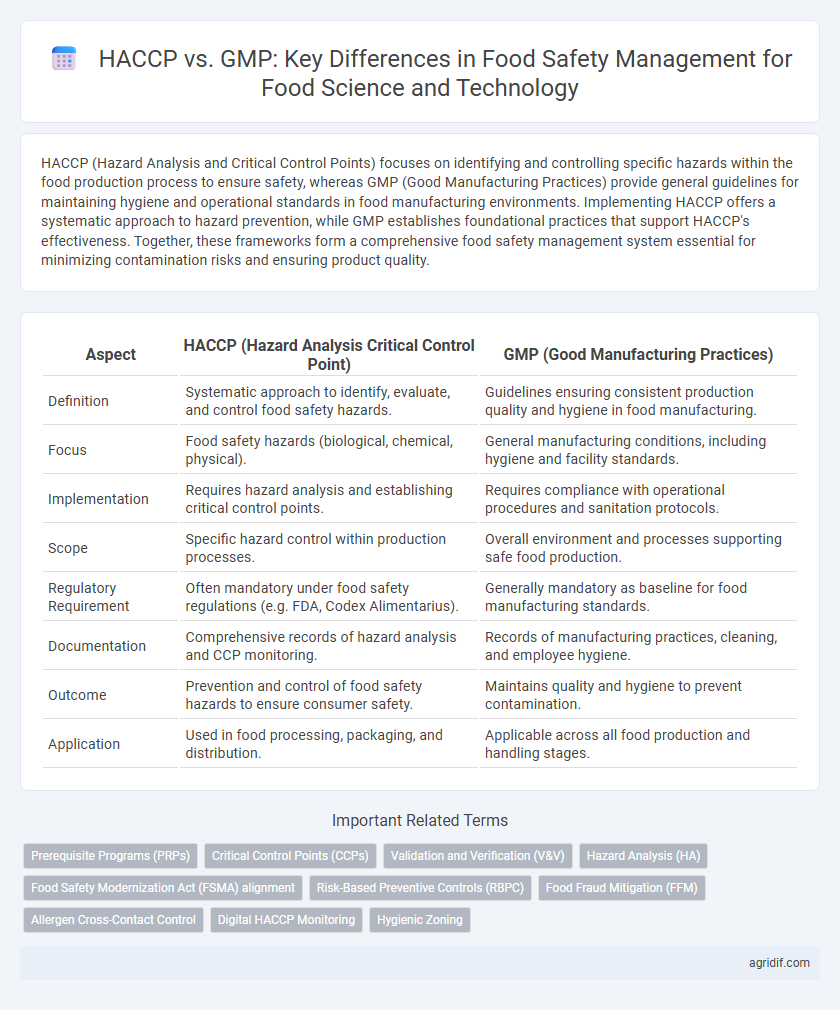
| Aspect | HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point) | GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Systematic approach to identify, evaluate, and control food safety hazards. | Guidelines ensuring consistent production quality and hygiene in food manufacturing. |
| Focus | Food safety hazards (biological, chemical, physical). | General manufacturing conditions, including hygiene and facility standards. |
| Implementation | Requires hazard analysis and establishing critical control points. | Requires compliance with operational procedures and sanitation protocols. |
| Scope | Specific hazard control within production processes. | Overall environment and processes supporting safe food production. |
| Regulatory Requirement | Often mandatory under food safety regulations (e.g. FDA, Codex Alimentarius). | Generally mandatory as baseline for food manufacturing standards. |
| Documentation | Comprehensive records of hazard analysis and CCP monitoring. | Records of manufacturing practices, cleaning, and employee hygiene. |
| Outcome | Prevention and control of food safety hazards to ensure consumer safety. | Maintains quality and hygiene to prevent contamination. |
| Application | Used in food processing, packaging, and distribution. | Applicable across all food production and handling stages. |
Introduction to Food Safety Management in Agriculture
HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) and GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) are essential frameworks in food safety management within agriculture, addressing biological, chemical, and physical hazards from farm to fork. HACCP specifically targets critical points in production processes to prevent contamination, while GMP establishes foundational sanitation, personnel hygiene, and facility standards to maintain overall food safety. Integrating HACCP with GMP enhances risk control, ensuring safer agricultural products and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Understanding HACCP: Principles and Applications
HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) is a systematic food safety management system focused on identifying, evaluating, and controlling biological, chemical, and physical hazards throughout the food production process. Its seven principles--conducting hazard analysis, determining critical control points, establishing critical limits, monitoring procedures, corrective actions, verification procedures, and record-keeping--ensure targeted prevention rather than end-product testing. Widely applied in food manufacturing, HACCP enhances food safety by systematically addressing risks and preventing contamination at critical stages of production.
What is GMP? Key Practices in Food Production
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) are essential guidelines in food production ensuring products are consistently produced and controlled according to quality standards. Key practices in GMP include maintaining clean and hygienic manufacturing areas, controlling cross-contamination, proper employee training, quality ingredient sourcing, and thorough documentation of processes. Effective implementation of GMP minimizes food safety hazards and supports compliance with regulatory requirements in the food industry.
Core Differences Between HACCP and GMP
HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) focuses on identifying and controlling specific biological, chemical, and physical hazards during food production to ensure product safety. GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) encompasses comprehensive guidelines for maintaining hygienic and operational conditions, including facility design, personnel training, and equipment sanitation. The core difference lies in HACCP's preventive approach targeting critical control points, whereas GMP establishes the foundational operational environment to minimize contamination risks.
The Role of HACCP in Controlling Food Safety Hazards
HACCP plays a critical role in controlling food safety hazards by systematically identifying, evaluating, and preventing risks throughout the entire food production process. Unlike GMP, which sets foundational operational guidelines, HACCP provides a scientific, risk-based approach specifically targeting critical control points to minimize contamination and ensure product safety. Implementing HACCP enhances hazard detection precision, supports regulatory compliance, and significantly reduces incidents of foodborne illnesses.
GMP: Laying the Foundation for Food Safety
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) establish the essential operational conditions and procedures necessary for producing safe food, serving as the foundation for effective food safety management systems. GMP covers critical areas such as employee hygiene, equipment maintenance, sanitation, and proper handling of raw materials, ensuring a consistent environment to prevent contamination. By implementing GMP, food manufacturers create the baseline controls that support Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) programs, enhancing overall food safety compliance and risk reduction.
Implementing HACCP and GMP in Agricultural Settings
Implementing HACCP and GMP in agricultural settings enhances food safety by identifying critical control points and maintaining good manufacturing practices from farm to harvest. HACCP focuses on hazard analysis to prevent contamination, while GMP ensures proper sanitation, handling, and worker hygiene throughout production. Combining these systems reduces risks of microbial contamination and chemical residues, promoting safer fresh produce and raw agricultural materials.
Integrating HACCP and GMP for Enhanced Food Safety
Integrating HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) and GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) creates a comprehensive food safety management system that addresses both hazard prevention and operational controls. HACCP focuses on identifying and controlling critical points in the production process, while GMP establishes foundational hygiene and manufacturing standards to prevent contamination. Combining these methodologies enhances risk mitigation, ensures regulatory compliance, and improves overall food safety outcomes in the industry.
Regulatory Requirements: HACCP vs GMP in Agriculture
HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) and GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) are critical regulatory frameworks in agriculture for food safety management. HACCP emphasizes systematic identification and control of hazards at specific points, mandated by agencies like the FDA and EFSA, whereas GMP focuses on maintaining overall hygiene and operational standards as defined by local agricultural authorities. Understanding the distinct regulatory requirements of HACCP for hazard control and GMP for facility and process conditions is essential for compliance and ensuring safe agricultural food production.
Future Trends in Food Safety Management Systems
Future trends in food safety management systems emphasize the integration of HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) with advanced GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) frameworks, driven by digital innovation and real-time monitoring technologies. Predictive analytics and blockchain are increasingly utilized to enhance traceability, ensuring more proactive control over contamination risks and compliance. Automation and sensor-based inspections are set to revolutionize both HACCP and GMP protocols, reducing human error and improving precision in food safety management.
Related Important Terms
Prerequisite Programs (PRPs)
Prerequisite Programs (PRPs) establish foundational hygiene and operational conditions essential for implementing both HACCP and GMP in food safety management. While GMP focuses on general manufacturing practices such as sanitation and employee hygiene, PRPs within HACCP provide specific control measures that support hazard analysis and critical control points identification.
Critical Control Points (CCPs)
HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) specifically identifies and manages Critical Control Points (CCPs) in food production to prevent, eliminate, or reduce hazards to safe levels, ensuring food safety throughout the process. GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) provide a broader framework for overall hygiene and operational conditions but do not focus explicitly on CCPs, making HACCP essential for controlling critical risks in food safety management.
Validation and Verification (V&V)
HACCP emphasizes hazard analysis and critical control points validated through scientific evidence to ensure process control, while GMP focuses on establishing standardized operational procedures verified by routine inspections to maintain hygiene and prevent contamination. Validation in HACCP involves confirming that control measures effectively prevent hazards, whereas GMP verification ensures compliance with prescribed manufacturing practices to sustain food safety standards throughout production.
Hazard Analysis (HA)
Hazard Analysis (HA) under HACCP systematically identifies and evaluates potential biological, chemical, and physical hazards at critical control points, ensuring targeted preventive controls in food safety management. GMP provides foundational hygienic practices and operational conditions that support hazard reduction but lacks the detailed, hazard-specific risk assessment integral to HACCP's approach.
Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) alignment
HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Points) and GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) are both essential frameworks for food safety management, with HACCP focusing on identifying and controlling critical points in the production process, while GMP emphasizes maintaining hygienic and operational conditions. The Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) aligns more closely with HACCP by requiring preventive controls and risk-based approaches to ensure food safety throughout the supply chain.
Risk-Based Preventive Controls (RBPC)
HACCP and GMP both serve as foundational frameworks in food safety management, with HACCP emphasizing Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points to identify and control potential hazards, while GMP focuses on establishing general operational conditions to ensure product safety and quality. Risk-Based Preventive Controls (RBPC) integrate principles from both systems by systematically identifying and mitigating specific risks throughout the food production process, thereby enhancing overall preventive strategies and regulatory compliance.
Food Fraud Mitigation (FFM)
HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) provides a systematic approach to identifying and controlling potential hazards in food production, while GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) establishes the foundational operational conditions for safe manufacturing processes. Effective Food Fraud Mitigation (FFM) integrates HACCP's risk-based control measures with GMP's compliance standards to prevent adulteration and ensure product authenticity throughout the food supply chain.
Allergen Cross-Contact Control
HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) systematically identifies and monitors critical control points to prevent allergen cross-contact, ensuring targeted risk management in food production. GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) establishes fundamental sanitation and operational protocols that minimize allergen contamination but lack the focused hazard-specific controls inherent in HACCP systems.
Digital HACCP Monitoring
Digital HACCP monitoring enhances traditional HACCP protocols by automating hazard analysis and critical control point tracking, improving accuracy and real-time responsiveness in food safety management systems. While GMP establishes foundational hygiene and operational standards, integrating digital HACCP tools ensures continuous compliance and data-driven decision-making to prevent contamination and product recalls.
Hygienic Zoning
HACCP emphasizes critical control points for preventing hazards within designated hygienic zones, ensuring targeted food safety interventions. GMP provides foundational sanitation practices that support hygienic zoning by maintaining overall facility cleanliness and preventing cross-contamination during food processing.
HACCP vs GMP for Food Safety Management Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com