Omega-3 eggs contain significantly higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids, such as EPA and DHA, compared to conventional eggs, which enhances their nutritional profile. Nutritional labeling for omega-3 eggs highlights these essential fatty acids, appealing to health-conscious consumers seeking cardiovascular and cognitive benefits. Accurate labeling differentiates omega-3 eggs by showcasing their enriched nutrient content, supporting informed dietary choices in the market.
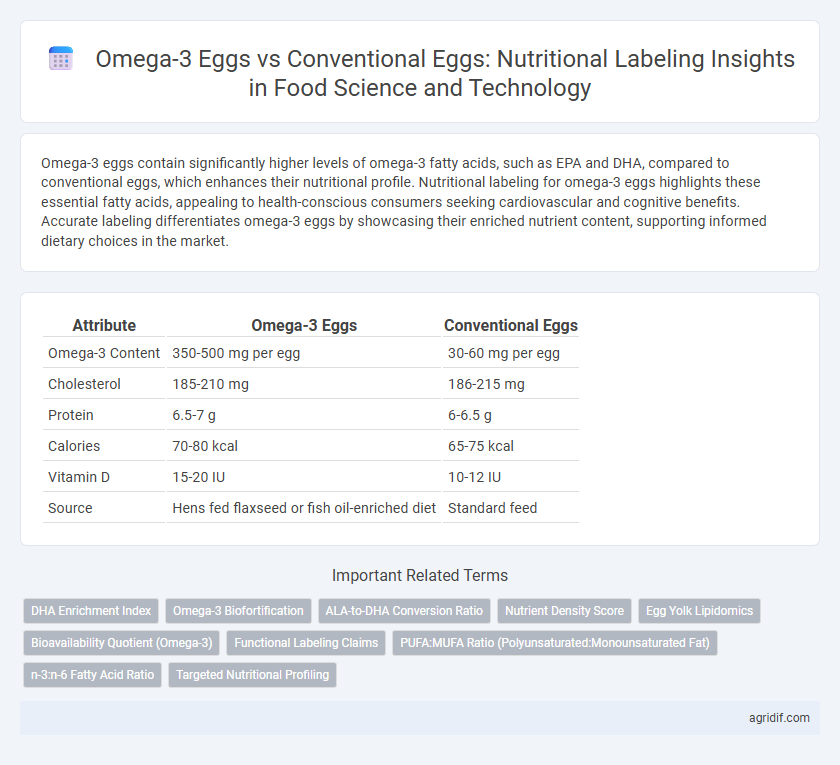
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Omega-3 Eggs | Conventional Eggs |
|---|---|---|
| Omega-3 Content | 350-500 mg per egg | 30-60 mg per egg |
| Cholesterol | 185-210 mg | 186-215 mg |
| Protein | 6.5-7 g | 6-6.5 g |
| Calories | 70-80 kcal | 65-75 kcal |
| Vitamin D | 15-20 IU | 10-12 IU |
| Source | Hens fed flaxseed or fish oil-enriched diet | Standard feed |
Comparative Nutrient Profiles of Omega-3 and Conventional Eggs
Omega-3 eggs contain significantly higher levels of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) compared to conventional eggs, enhancing their nutritional value for cardiovascular health. Conventional eggs typically have higher saturated fat content and lower polyunsaturated fatty acids, impacting overall lipid profiles in the diet. Nutritional labeling should highlight omega-3 egg advantages in essential fatty acids to inform consumers seeking heart-healthy dietary options.
Omega-3 Fortification: Methods and Implications for Eggs
Omega-3 fortification in eggs involves enhancing the hens' diet with sources rich in alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), such as flaxseed, fish oil, and algae. These modifications elevate the omega-3 fatty acid content in eggs, which must be accurately reflected on nutritional labels to inform consumer choices and comply with food labeling regulations. Fortified eggs offer a significant nutritional advantage by providing higher levels of essential fatty acids linked to cardiovascular and cognitive health benefits compared to conventional eggs.
Labeling Regulations for Omega-3 Enriched Eggs
Labeling regulations for Omega-3 enriched eggs require precise nutrient content disclosure, including EPA and DHA levels, to accurately inform consumers about the enhanced health benefits compared to conventional eggs. Regulatory agencies like the FDA and EFSA mandate that claims about Omega-3 content must be substantiated by standardized analytical testing and comply with defined criteria for nutrient claims. Compliance with these regulations ensures transparent nutritional labeling, enabling consumers to differentiate between Omega-3 enriched eggs and conventional eggs based on scientifically validated health attributes.
Health Benefits Highlighted on Omega-3 Egg Labels
Omega-3 eggs typically contain 100-200 mg of omega-3 fatty acids per egg, significantly higher than conventional eggs, which usually have less than 50 mg. Nutritional labeling on omega-3 eggs emphasizes heart health benefits, including reduced risk of cardiovascular disease and improved cholesterol profiles. These labels often highlight the presence of DHA and EPA, essential fatty acids linked to brain function and anti-inflammatory effects.
Consumer Perceptions of Nutritional Claims on Egg Packaging
Consumers often perceive Omega-3 eggs as healthier compared to conventional eggs due to nutritional claims highlighting higher levels of essential fatty acids. Nutritional labeling emphasizing Omega-3 content influences purchase decisions by signaling cardiovascular and cognitive benefits supported by clinical research. Marketing strategies leveraging clear, scientifically-backed labeling increase consumer trust and willingness to pay premium prices for Omega-3 enriched eggs.
Bioavailability of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Enriched Eggs
Omega-3 eggs contain higher levels of EPA and DHA, enhancing the bioavailability of these essential fatty acids compared to conventional eggs that primarily offer ALA. The lipid matrix in enriched eggs facilitates better absorption and conversion of omega-3 fatty acids in the human body. Accurate nutritional labeling must reflect the superior bioavailability of long-chain omega-3s to guide consumer choices effectively.
Nutritional Label Accuracy: Omega-3 vs. Conventional Eggs
Nutritional label accuracy of Omega-3 eggs versus conventional eggs is critical for consumer transparency, as Omega-3 eggs contain higher levels of alpha-linolenic acid, EPA, and DHA, which must be precisely quantified to meet regulatory standards. Variability in feed composition and hen metabolism can impact Omega-3 content, necessitating rigorous laboratory analysis and updated labeling protocols to reflect actual nutrient concentrations. Accurate nutritional labeling ensures consumers receive reliable information to make informed dietary decisions, especially regarding essential fatty acid intake.
Technological Advances in Omega-3 Egg Production
Technological advances in omega-3 egg production include the use of enriched hen feed containing flaxseed, fish oil, or algae, significantly increasing the omega-3 fatty acid content compared to conventional eggs. Precision feeding strategies and genetic selection enhance the stability and concentration of EPA and DHA in eggs, resulting in improved nutritional labeling accuracy. These innovations enable producers to market omega-3 eggs with verified health benefits, meeting regulatory standards for functional food claims.
Market Trends in Omega-3 Egg Labeling
Market trends in Omega-3 egg labeling show increasing consumer demand for transparent nutritional information emphasizing enhanced health benefits, such as higher levels of EPA and DHA. Regulatory bodies are imposing stricter guidelines to ensure accurate claims on fortified eggs compared to conventional ones, prompting clearer differentiation in retail packaging. Growth in functional food markets drives innovation in marketing strategies that highlight Omega-3 content to attract health-conscious buyers.
Challenges in Standardizing Nutritional Labels for Eggs
Standardizing nutritional labels for Omega-3 enriched eggs versus conventional eggs presents challenges due to variations in fatty acid content influenced by hen diet and breed. Regulatory bodies require precise quantification methods for EPA and DHA levels, which often differ seasonally and geographically, complicating consistent label information. Moreover, ensuring consumer understanding of Omega-3 benefits while complying with regional labeling standards demands harmonized guidelines and rigorous quality control across the egg production industry.
Related Important Terms
DHA Enrichment Index
Omega-3 eggs demonstrate a significantly higher DHA Enrichment Index compared to conventional eggs, reflecting enhanced docosahexaenoic acid content crucial for cardiovascular and cognitive health benefits. Nutritional labeling of omega-3 eggs must accurately represent this elevated DHA concentration to inform consumers about their superior omega-3 fatty acid intake.
Omega-3 Biofortification
Omega-3 biofortification in eggs significantly enhances their nutritional profile by increasing levels of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), essential omega-3 fatty acids linked to cardiovascular and cognitive health benefits. Nutritional labeling for omega-3 enriched eggs must accurately reflect elevated omega-3 content per serving, complying with regulatory standards to inform consumers about the enhanced health value compared to conventional eggs.
ALA-to-DHA Conversion Ratio
Omega-3 eggs contain higher levels of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), but the human body's limited ALA-to-DHA conversion ratio often results in lower docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) availability compared to direct DHA enrichment found in some conventional omega-3-fortified eggs. Nutritional labeling should emphasize the actual DHA content rather than ALA amounts to provide accurate health benefits for consumers choosing omega-3 eggs.
Nutrient Density Score
Omega-3 eggs have a significantly higher Nutrient Density Score compared to conventional eggs due to their enriched levels of EPA and DHA, contributing to enhanced cardiovascular and cognitive benefits. This improved nutrient profile makes Omega-3 eggs a superior choice for nutritional labeling, emphasizing their functional health advantages over standard eggs.
Egg Yolk Lipidomics
Omega-3 eggs contain significantly higher levels of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in the egg yolk compared to conventional eggs, altering the lipidomic profile with enhanced phospholipid and triglyceride concentrations rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids. Nutritional labeling of omega-3 eggs should reflect these lipidomic differences by quantifying specific omega-3 fatty acids and lipid species, providing consumers with accurate information on improved cardiovascular and cognitive health benefits.
Bioavailability Quotient (Omega-3)
Omega-3 eggs exhibit a significantly higher Bioavailability Quotient (Omega-3) compared to conventional eggs, reflecting enhanced absorption and utilization of essential fatty acids in human metabolism. This superior bioavailability supports more accurate and meaningful nutritional labeling, emphasizing the health benefits associated with omega-3 enriched eggs.
Functional Labeling Claims
Omega-3 eggs contain significantly higher levels of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) compared to conventional eggs, enabling functional labeling claims related to cardiovascular health and brain development. These enriched eggs must meet regulatory thresholds for omega-3 content, allowing manufacturers to highlight heart-healthy benefits and support consumer demand for nutrient-rich functional foods.
PUFA:MUFA Ratio (Polyunsaturated:Monounsaturated Fat)
Omega-3 eggs typically exhibit a higher PUFA:MUFA ratio compared to conventional eggs, reflecting increased levels of polyunsaturated fatty acids beneficial for cardiovascular health. This enhanced ratio is a critical nutritional labeling attribute, highlighting the superior content of omega-3 fatty acids such as EPA and DHA in omega-3 enriched eggs.
n-3:n-6 Fatty Acid Ratio
Omega-3 eggs exhibit a significantly higher n-3:n-6 fatty acid ratio compared to conventional eggs, enhancing their nutritional profile by promoting anti-inflammatory benefits and cardiovascular health. This improved ratio is a key factor for nutritional labeling, highlighting the superior functional lipid quality in omega-3 enriched eggs versus standard eggs.
Targeted Nutritional Profiling
Omega-3 eggs contain significantly higher levels of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), making their nutritional labels rich in essential fatty acids compared to conventional eggs. Targeted nutritional profiling highlights enhanced omega-3 content and improved omega-6 to omega-3 ratios, supporting clearer consumer guidance on heart-healthy dietary choices.
Omega-3 eggs vs conventional eggs for nutritional labeling Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com