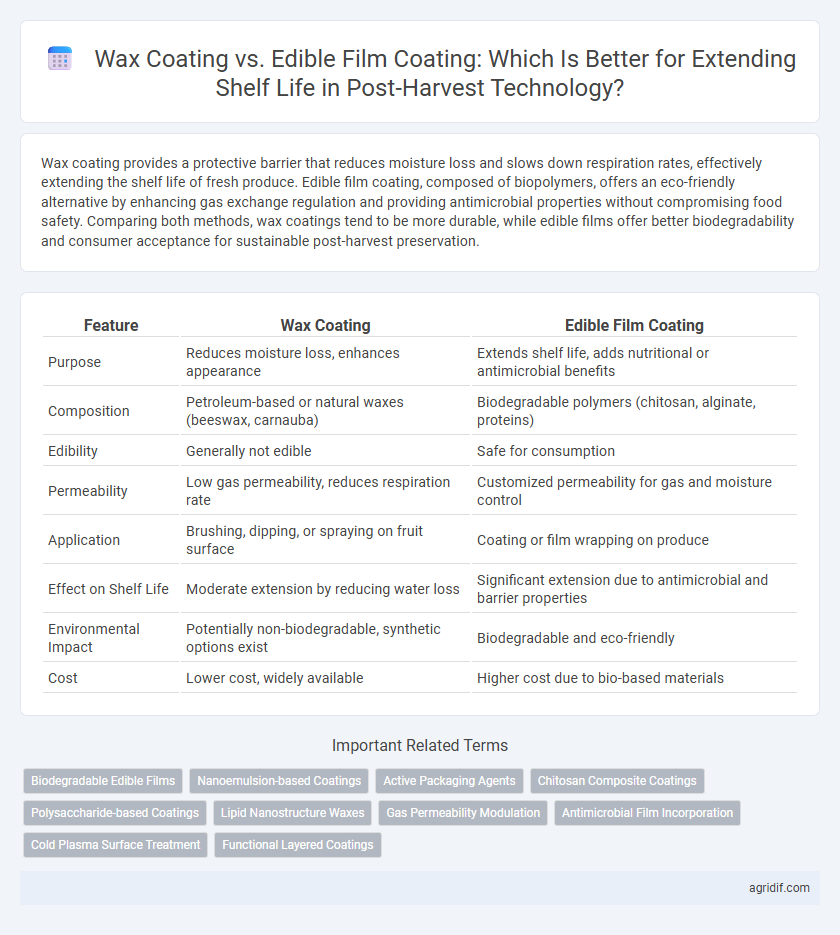
Wax coating provides a protective barrier that reduces moisture loss and slows down respiration rates, effectively extending the shelf life of fresh produce. Edible film coating, composed of biopolymers, offers an eco-friendly alternative by enhancing gas exchange regulation and providing antimicrobial properties without compromising food safety. Comparing both methods, wax coatings tend to be more durable, while edible films offer better biodegradability and consumer acceptance for sustainable post-harvest preservation.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wax Coating | Edible Film Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Reduces moisture loss, enhances appearance | Extends shelf life, adds nutritional or antimicrobial benefits |
| Composition | Petroleum-based or natural waxes (beeswax, carnauba) | Biodegradable polymers (chitosan, alginate, proteins) |
| Edibility | Generally not edible | Safe for consumption |
| Permeability | Low gas permeability, reduces respiration rate | Customized permeability for gas and moisture control |
| Application | Brushing, dipping, or spraying on fruit surface | Coating or film wrapping on produce |
| Effect on Shelf Life | Moderate extension by reducing water loss | Significant extension due to antimicrobial and barrier properties |
| Environmental Impact | Potentially non-biodegradable, synthetic options exist | Biodegradable and eco-friendly |
| Cost | Lower cost, widely available | Higher cost due to bio-based materials |
Introduction to Post-Harvest Shelf Life Challenges
Post-harvest shelf life challenges primarily arise from moisture loss, microbial decay, and physiological deterioration, which significantly reduce the freshness and marketability of fruits and vegetables. Wax coatings provide a moisture barrier and enhance appearance but may limit gas exchange, sometimes leading to anaerobic respiration. Edible film coatings, composed of polysaccharides, proteins, or lipids, offer biodegradable protection by controlling moisture, gas permeability, and microbial growth, effectively extending shelf life while maintaining quality attributes.
Understanding Wax Coating Technology
Wax coating technology involves applying a thin layer of food-grade wax on the surface of fruits to reduce moisture loss and oxygen penetration, effectively slowing down ripening and decay processes. This method enhances shelf life by creating a protective barrier that maintains firmness and freshness, especially in citrus fruits, apples, and cucumbers. Compared to edible film coatings, wax coatings are generally more durable, cost-effective, and easier to apply on a commercial scale.
Overview of Edible Film Coating Methods
Edible film coating methods for post-harvest technology involve applying thin, biodegradable layers of natural polymers such as proteins, polysaccharides, or lipids to fruits and vegetables, effectively reducing moisture loss and gas exchange. Techniques like dipping, spraying, and brushing enhance uniform coverage and improve the shelf life by creating a semi-permeable barrier that maintains quality and freshness. Compared to wax coating, edible films offer better biodegradability and consumer safety while supporting controlled respiration rates and delaying ripening processes.
Material Composition: Wax vs. Edible Films
Wax coatings for post-harvest preservation typically consist of natural or synthetic resins, oils, and emulsifiers that create a water-resistant barrier, reducing moisture loss and gas exchange in fruits and vegetables. Edible film coatings, made from polysaccharides, proteins, and lipids, provide a biodegradable, consumable layer that enhances shelf life by controlling respiration rates and microbial growth without compromising safety. The choice between wax and edible films hinges on material composition, where wax offers superior moisture retention but limited breathability, whereas edible films balance preservation with environmental sustainability and consumer health benefits.
Mechanisms of Shelf Life Extension
Wax coating extends shelf life by creating a semi-permeable barrier that reduces moisture loss and gas exchange, thereby slowing down respiration and delaying fruit senescence. Edible film coatings enhance shelf life through their biodegradable layers composed of polysaccharides, proteins, or lipids, which provide microbial protection and regulate gas permeability for controlled ripening. Both methods modify the fruit's microenvironment to minimize oxidative stress and moisture evaporation, but edible films often offer additional benefits like nutrient delivery and improved product safety.
Impact on Fruit and Vegetable Quality
Wax coating enhances fruit and vegetable shelf life by creating a moisture barrier that reduces water loss and slows respiration, thus preserving firmness and color. Edible film coatings, made from natural biopolymers like chitosan or starch, also maintain quality by providing antimicrobial properties and gas exchange regulation, which help to reduce decay and oxidative damage. Studies show that while wax coatings are more effective for moisture retention, edible films improve overall safety and may better preserve nutritional content and sensory attributes.
Safety, Allergenicity, and Consumer Perception
Wax coatings provide an effective barrier against moisture loss and microbial contamination, extending shelf life while generally posing low allergenicity risks. Edible film coatings, composed of natural polymers like chitosan or cellulose, enhance safety by being fully consumable and often incorporate antimicrobial agents that reduce spoilage. Consumer perception favors edible films due to their natural origin and transparency, though some may prefer wax coatings for traditional preservation methods despite minor concerns about chemical residues.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Wax coating and edible film coating both extend the shelf life of fruits by reducing moisture loss and delaying ripening, but edible films offer superior environmental benefits due to their biodegradability and use of natural, non-toxic materials. Wax coatings often rely on petroleum-based products and may create disposal challenges, whereas edible films made from biopolymers such as chitosan, starch, or alginate enhance sustainability by minimizing plastic waste. Selecting edible film coatings aligns with eco-friendly practices in post-harvest technology by reducing environmental impact and supporting circular economy principles.
Cost Efficiency and Scalability in Commercial Use
Wax coating offers a cost-efficient solution for extending the shelf life of fruits, providing a durable barrier against moisture loss and microbial contamination, which supports large-scale commercial application with relatively low investment. Edible film coatings, while often more expensive due to specialized biopolymers and production processes, offer enhanced consumer appeal and environmental benefits but may require advanced equipment and higher operational costs that challenge scalability. Commercial enterprises prioritize wax coatings for their straightforward application and scalability, whereas edible films are selected for niche markets valuing sustainability despite the higher cost implications.
Future Trends in Post-Harvest Coating Innovations
Emerging trends in post-harvest technology highlight the increasing adoption of bio-based edible film coatings over traditional wax coatings due to their enhanced biodegradability and ability to incorporate natural antimicrobial agents. Advances in nanotechnology enable the development of smart coatings that respond to environmental stimuli, improving preservation efficacy and shelf life of fruits and vegetables. Integration of these innovative coatings with sensor technology promises real-time monitoring of freshness parameters, driving a new era of intelligent post-harvest management.
Related Important Terms
Biodegradable Edible Films
Biodegradable edible films enhance post-harvest technology by providing a sustainable alternative to traditional wax coatings, effectively extending shelf life through moisture retention and reduced microbial growth. These films, composed of natural polymers like chitosan and starch, ensure food safety and environmental compatibility while maintaining the fruit's sensory qualities.
Nanoemulsion-based Coatings
Nanoemulsion-based wax coatings exhibit superior barrier properties and antimicrobial effects compared to traditional edible film coatings, significantly enhancing fruit shelf life by reducing moisture loss and microbial spoilage. These nanostructured coatings improve the uniformity and stability of the protective layer, enabling more efficient preservation of post-harvest quality in perishable produce.
Active Packaging Agents
Wax coatings provide a robust barrier against moisture loss and microbial contamination, enhancing shelf life by minimizing respiration rates in fruits and vegetables through hydrophobic properties. Edible film coatings with active packaging agents, such as antimicrobials and antioxidants, offer controlled release mechanisms that inhibit spoilage organisms and oxidative degradation, effectively preserving freshness and nutritional quality during post-harvest storage.
Chitosan Composite Coatings
Chitosan composite coatings in edible film technology provide superior antimicrobial properties and moisture barrier effects compared to traditional wax coatings, significantly extending the shelf life of fresh produce. Their biodegradability and ability to enhance fruit firmness and inhibit microbial growth make chitosan-based films a sustainable and effective alternative for post-harvest storage.
Polysaccharide-based Coatings
Polysaccharide-based coatings, such as chitosan and alginate, offer effective edible film solutions that enhance fruit and vegetable shelf life by providing a biodegradable, breathable barrier against moisture loss and microbial spoilage. Compared to traditional wax coatings, these natural polysaccharide films improve gas exchange, maintain produce firmness, and reduce chemical residues, aligning with sustainable post-harvest technology practices.
Lipid Nanostructure Waxes
Lipid nanostructure waxes in wax coatings create a hydrophobic barrier that effectively reduces moisture loss and gas exchange, significantly extending the shelf life of fruits and vegetables by preserving firmness and freshness. Compared to edible film coatings, these waxes offer superior water vapor resistance and enhanced durability, making them a preferred choice in post-harvest technology for maintaining produce quality during storage and transportation.
Gas Permeability Modulation
Wax coatings reduce gas permeability by creating a hydrophobic barrier that limits moisture loss and oxygen exchange, effectively slowing respiration rates in fruits and vegetables. Edible film coatings offer a more controlled modulation of gas permeability through incorporation of biopolymers and plasticizers, allowing selective gas exchange that better maintains product freshness and extends shelf life.
Antimicrobial Film Incorporation
In post-harvest technology, antimicrobial film incorporation within edible coatings demonstrates superior efficacy in extending shelf life by directly inhibiting microbial growth on the produce surface, unlike traditional wax coatings which primarily reduce moisture loss. Edible films embedded with natural antimicrobials such as chitosan or essential oils provide targeted pathogen control while maintaining fruit respiration, enhancing overall preservation and reducing spoilage rates.
Cold Plasma Surface Treatment
Cold plasma surface treatment enhances the adhesion and efficacy of both wax coating and edible film coating by improving surface wettability and microbial decontamination on post-harvest produce. This innovative method extends shelf life more effectively than traditional coatings alone by creating a uniform, antimicrobial barrier that reduces spoilage and maintains fruit quality during storage.
Functional Layered Coatings
Functional layered coatings in post-harvest technology, such as wax coatings and edible film coatings, significantly enhance shelf life by creating protective barriers against moisture loss, microbial contamination, and oxidative damage. Wax coatings offer durable, hydrophobic layers primarily for fruits like apples and citrus, while edible films composed of biopolymers provide biodegradable, breathable protection ideal for sensitive produce, optimizing gas exchange and maintaining quality during storage.
Wax Coating vs Edible Film Coating for Extending Shelf Life Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com