Modified humidity packaging regulates moisture levels to prevent condensation and microbial growth, extending vegetable freshness by maintaining optimal humidity. MAP (Modified Atmosphere Packaging) alters gas composition around vegetables, reducing oxygen and increasing carbon dioxide to slow respiration and delay spoilage. Both techniques enhance shelf life, but modified humidity packaging specifically targets moisture control, which is critical for crispness and texture preservation in fresh produce.
Table of Comparison
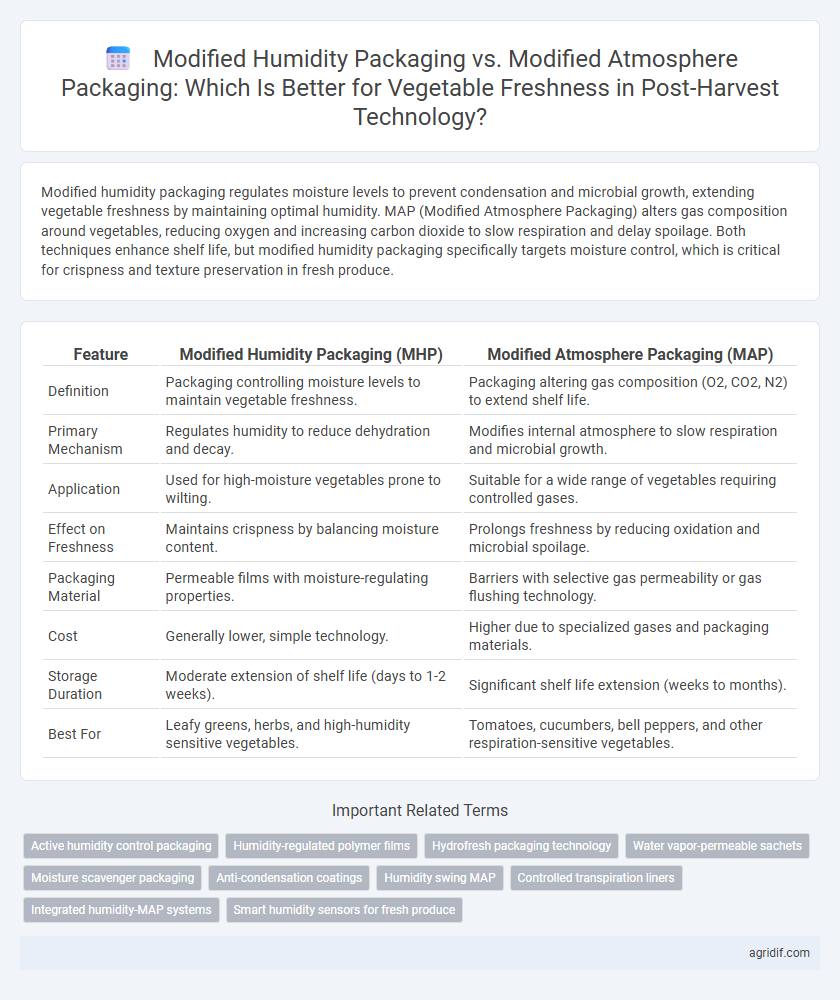
| Feature | Modified Humidity Packaging (MHP) | Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Packaging controlling moisture levels to maintain vegetable freshness. | Packaging altering gas composition (O2, CO2, N2) to extend shelf life. |
| Primary Mechanism | Regulates humidity to reduce dehydration and decay. | Modifies internal atmosphere to slow respiration and microbial growth. |
| Application | Used for high-moisture vegetables prone to wilting. | Suitable for a wide range of vegetables requiring controlled gases. |
| Effect on Freshness | Maintains crispness by balancing moisture content. | Prolongs freshness by reducing oxidation and microbial spoilage. |
| Packaging Material | Permeable films with moisture-regulating properties. | Barriers with selective gas permeability or gas flushing technology. |
| Cost | Generally lower, simple technology. | Higher due to specialized gases and packaging materials. |
| Storage Duration | Moderate extension of shelf life (days to 1-2 weeks). | Significant shelf life extension (weeks to months). |
| Best For | Leafy greens, herbs, and high-humidity sensitive vegetables. | Tomatoes, cucumbers, bell peppers, and other respiration-sensitive vegetables. |
Introduction to Post-Harvest Vegetable Preservation
Modified humidity packaging controls moisture levels within the package to reduce condensation and slow down respiration rates in vegetables, maintaining freshness and extending shelf life. Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP) alters the gas composition surrounding the produce, typically reducing oxygen and increasing carbon dioxide to inhibit microbial growth and delay ripening. Both techniques are critical post-harvest technologies aimed at minimizing spoilage and preserving the nutritional quality of fresh vegetables during storage and transport.
Understanding Modified Humidity Packaging (MHP)
Modified Humidity Packaging (MHP) enhances vegetable freshness by regulating moisture levels within the packaging environment, reducing water loss and microbial growth more effectively than traditional Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP). By maintaining optimal humidity, MHP slows down respiration rates and preserves cell turgidity, extending shelf life and retaining nutritional quality. This packaging technology is particularly beneficial for leafy greens and other high-moisture vegetables, ensuring freshness during distribution and storage.
Principles of Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP)
Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP) maintains vegetable freshness by regulating gas composition, typically reducing oxygen and increasing carbon dioxide levels to slow respiration and microbial growth. Modified humidity packaging focuses on controlling moisture levels, preventing dehydration and condensation, which can cause spoilage and texture loss. Effective MAP combines gas modification with humidity control to optimize shelf life and maintain quality in post-harvest vegetable storage.
Comparative Mechanisms: MHP vs MAP
Modified Humidity Packaging (MHP) controls moisture levels by using absorbent or breathable materials to maintain an optimal humidity microenvironment, reducing moisture loss and microbial growth on vegetables. Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP) alters the gaseous composition within the package, typically lowering oxygen and increasing carbon dioxide concentrations to slow respiration rates and delay senescence in vegetables. Unlike MAP's gas exchange focus, MHP emphasizes humidity regulation, making it more effective in preserving texture and preventing dehydration during post-harvest storage.
Impact on Vegetable Shelf Life
Modified humidity packaging controls moisture levels to reduce condensation and decay in vegetables, significantly extending shelf life by maintaining optimal humidity. Modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) alters gas composition, primarily reducing oxygen and increasing carbon dioxide, which slows respiration and microbial growth, enhancing freshness duration. Both techniques effectively prolong vegetable shelf life, but their impact varies with vegetable type and storage conditions, with MAP typically offering longer preservation in high-respiration produce.
Effects on Nutritional and Sensory Quality
Modified humidity packaging effectively maintains vegetable freshness by controlling moisture levels, which helps preserve nutritional compounds such as vitamin C and antioxidants. In comparison, Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP) alters gas composition, reducing respiration rates and delaying sensory degradation like texture softening and color loss. Studies show modified humidity packaging better retains sensory qualities like crunchiness and natural flavor while maintaining key nutrients longer than MAP in certain leafy vegetables.
Cost Analysis: MHP versus MAP Implementation
Modified Humidity Packaging (MHP) offers a cost-effective solution for extending vegetable freshness by regulating moisture levels with simpler materials and lower energy consumption compared to Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP). While MAP requires advanced gas mixtures, specialized equipment, and continuous monitoring, driving higher initial investment and operational costs, MHP relies on breathable films or humidity control agents, reducing packaging expenses and maintenance. This cost differential makes MHP preferable for small to medium-scale producers seeking economical post-harvest preservation without compromising product quality.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
Modified humidity packaging enhances vegetable freshness by adjusting moisture levels to reduce spoilage, using biodegradable materials that lower environmental impact. MAP (Modified Atmosphere Packaging) extends shelf life through gas composition control, but often relies on plastic films with limited recyclability, raising sustainability concerns. Choosing packaging that balances effective preservation with eco-friendly materials supports sustainable post-harvest management and reduces plastic waste.
Industrial Applications and Case Studies
Modified humidity packaging controls moisture levels to extend vegetable freshness by creating an optimal microenvironment, reducing spoilage and weight loss in industrial applications. Case studies show that this method outperforms traditional Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP) in maintaining crispness and nutrient retention during extended storage and transportation. Industries adopting modified humidity systems report improved shelf life, reduced waste, and enhanced marketability for leafy greens and root vegetables.
Future Trends in Packaging for Vegetable Freshness
Modified humidity packaging enhances vegetable freshness by controlling moisture levels within the package, reducing spoilage and maintaining crispness through optimal humidity regulation. Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP) extends shelf life by altering gas composition, primarily lowering oxygen and increasing carbon dioxide, which slows respiration and microbial growth in vegetables. Future trends in packaging for vegetable freshness emphasize integrating smart sensors with MAP and humidity control systems to provide real-time monitoring of produce quality and dynamically adjust internal conditions to maximize shelf life.
Related Important Terms
Active humidity control packaging
Active humidity control packaging regulates moisture levels within the package to maintain optimal freshness and extend shelf life of vegetables by preventing condensation and microbial growth. Unlike traditional Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP), which modifies gas composition, active humidity control directly manages internal humidity, resulting in improved texture retention and reduced spoilage.
Humidity-regulated polymer films
Humidity-regulated polymer films in modified humidity packaging maintain optimal moisture levels, reducing condensation and microbial growth to preserve vegetable freshness more effectively than conventional Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP). These films selectively absorb and release water vapor, extending shelf life by stabilizing the microenvironment and minimizing quality degradation.
Hydrofresh packaging technology
Hydrofresh packaging technology enhances vegetable freshness by precisely regulating humidity levels within sealed environments, preventing moisture loss and microbial growth more effectively than traditional Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP). This advanced approach maintains optimal moisture balance and gas composition, extending shelf life and preserving nutrient quality in fresh produce.
Water vapor-permeable sachets
Water vapor-permeable sachets in modified humidity packaging regulate moisture levels to maintain optimal freshness and reduce condensation in vegetables, enhancing shelf life without compromising texture. Unlike traditional Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP) that primarily alters gas composition, these sachets actively control humidity, minimizing microbial growth and moisture-related spoilage.
Moisture scavenger packaging
Moisture scavenger packaging significantly enhances vegetable freshness by actively absorbing excess moisture, preventing microbial growth and spoilage more effectively than traditional Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP). This technology maintains optimal humidity levels inside the package, extending shelf life and preserving texture and nutritional quality.
Anti-condensation coatings
Modified humidity packaging preserves vegetable freshness by controlling moisture levels to minimize decay, while MAP (Modified Atmosphere Packaging) adjusts gas composition to extend shelf life. Anti-condensation coatings in modified humidity packaging prevent water droplets on the inner surface, reducing microbial growth and maintaining optimal respiration rates for vegetables.
Humidity swing MAP
Humidity swing MAP (Modified Atmosphere Packaging) optimizes vegetable freshness by dynamically adjusting internal moisture levels to prevent condensation and microbial growth, enhancing shelf life compared to traditional modified humidity packaging that often results in static humidity conditions. This adaptive humidity regulation reduces transpiration and spoilage, maintaining texture and nutritional quality more effectively in perishable vegetables.
Controlled transpiration liners
Controlled transpiration liners in modified humidity packaging regulate moisture exchange, reducing condensation and preserving vegetable freshness more effectively than traditional MAP methods. These liners optimize microenvironment humidity levels, minimizing water loss and decay while maintaining crispness during storage and transport.
Integrated humidity-MAP systems
Integrated humidity-modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) systems enhance vegetable freshness by precisely controlling both humidity levels and atmospheric gas composition, thereby reducing respiration rates and moisture loss. This dual optimization extends shelf life more effectively than conventional MAP alone, minimizing spoilage and maintaining quality during post-harvest storage and transportation.
Smart humidity sensors for fresh produce
Modified humidity packaging regulates moisture levels to extend vegetable freshness by preventing condensation, while Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP) alters gas composition for preservation; smart humidity sensors integrated into these systems provide real-time monitoring and precise control, enhancing shelf life and reducing spoilage. These sensors detect fluctuations in humidity within packaging, enabling dynamic adjustments that optimize the microenvironment for fresh produce.
Modified humidity packaging vs MAP for vegetable freshness Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com